Fix: Gpedit Startup Script is Not Running or Working
Add script folder to startup in Gpedit for an easy solution
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Different people have encountered issues with GPO not running startup scripts.
- Incorrect script location, syntax errors, disabled startup script, and conflicting policies can affect GPO startup.
- Adding a startup folder, restarting, resetting, and enabling GPO will help troubleshoot the issue.
Gpedit (Group Policy Editor) is a powerful management tool utilized by system administrators to configure policies and settings on Windows computers. However, many reported that Gpedit startup script is not running.
Thus, we provide practical solutions to fix it, allowing you to leverage Gpedit in managing your Windows environment. Also, we have a detailed guide on fixing the Gpedit shutdown script not running on Windows.
Why is the gpedit startup script not running?
- Incorrect script location or path specified in the Group Policy settings.
- Insufficient permissions for the user or group running the startup script.
- An incorrect Syntax or typos errors in the GPO script itself.
- The startup script is not enabled or configured correctly in the Group Policy settings.
- Conflicting or overriding policies interfering with the startup script.
- Dependency on external resources (e.g., network drives, services) unavailable during system startup.
- System or software restrictions that block the execution of specific scripts.
- Errors or warnings in system logs or error messages indicate issues with the startup script.
The above causes vary in different circumstances. However, we discuss step-by-step details to troubleshoot the error.
How do I run a startup script in group policy?
- Confirm if you have Implemented a user policy instead of a computer policy in the given context.
- Temporarily block inheritance to isolate the problem to a specific OU to reduce the complexity of identifying conflicting policies.
- Log in to the computer with administrative privileges to access and modify Group Policy settings.
- Manually execute the script to ensure it runs successfully without any errors before configuring it in Group Policy.
What can I do if Gpedit startup script is not running?
1. Add folder to startup
- Right-click the Windows icon and select Run from the pop-up menu to open the Run dialog box.
- Type gpedit.msc into the dialog box and press Enter.
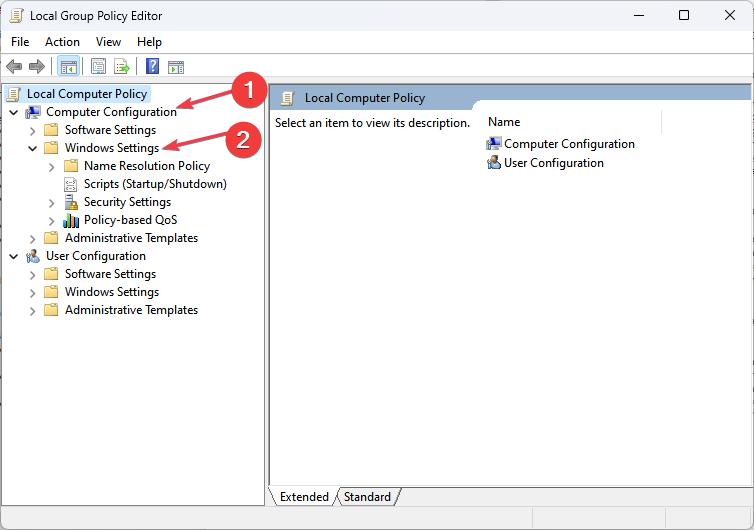
- Then, click the Computer Configuration drop-down arrow, expand Windows Settings, and select Scripts.
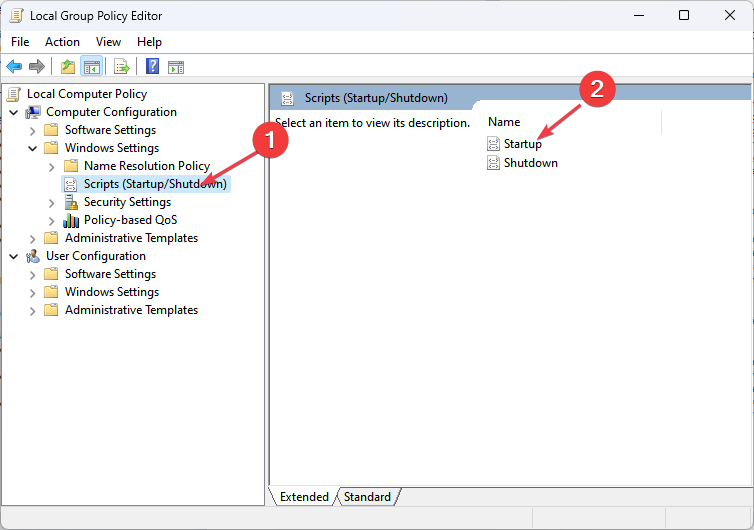
- Double-click on Startup.
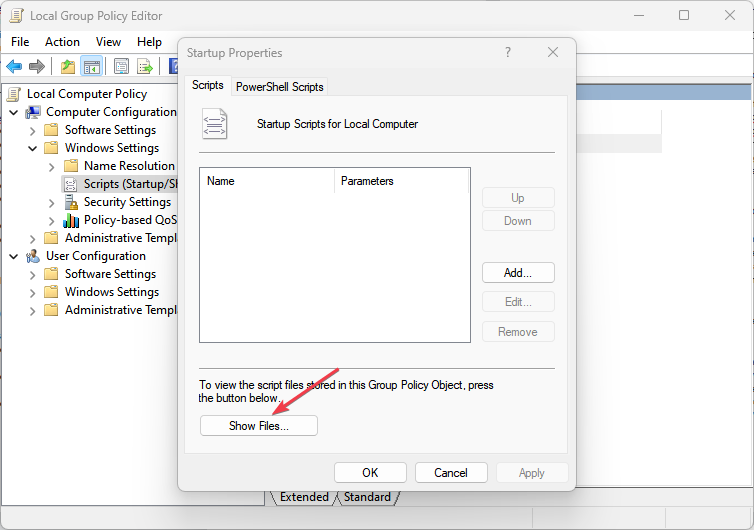
- Then, select Show Files.
- Copy and paste your file into the folder and select the Add button on the startup property.
- Select the Browse button, double-click on your script to choose it, and click OK to enable settings.
Adding folder to startup troubleshoot GPO startup script not working on Windows.
2. Reset Group Policy
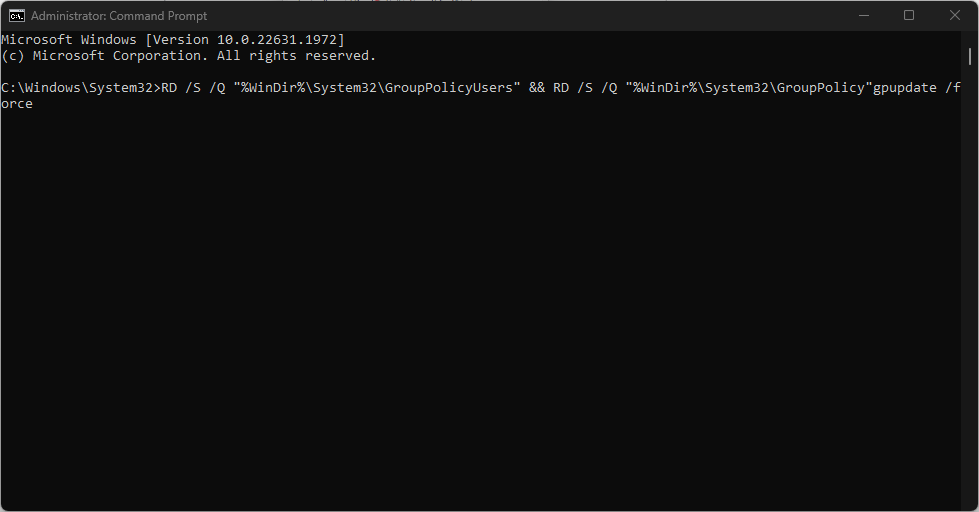
- Left-click the Windows icon, type CMD, and select Run as Administrator.
- Then, type the following command into the Command Prompt and click Enter:
RD /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicyUsers" && RD /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicy"gpupdate /force - Close the interface and reset your PC.
Resetting the GPO aids in troubleshooting issues related to Group Policy, resolving conflicts, or rectifying unintended consequences caused by misconfiguration.
3. Force restart the GPO
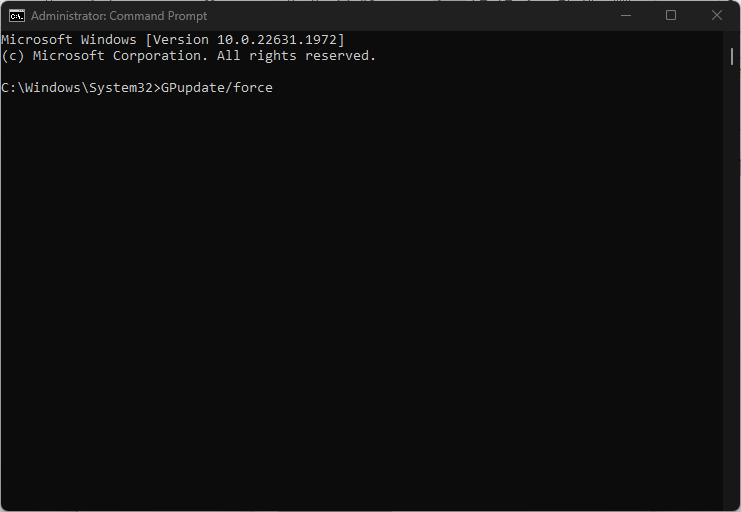
- Left-click the Windows icon, type Command Prompt, and select Run as Administrator to open it.
- Copy and paste the following command and press Enter:
GPupdate/force - Then, close the Command Prompt and restart your computer.
Restarting the GPO allows the seamless and timely deployment of new policies and updates, reducing and enhancing overall system management.
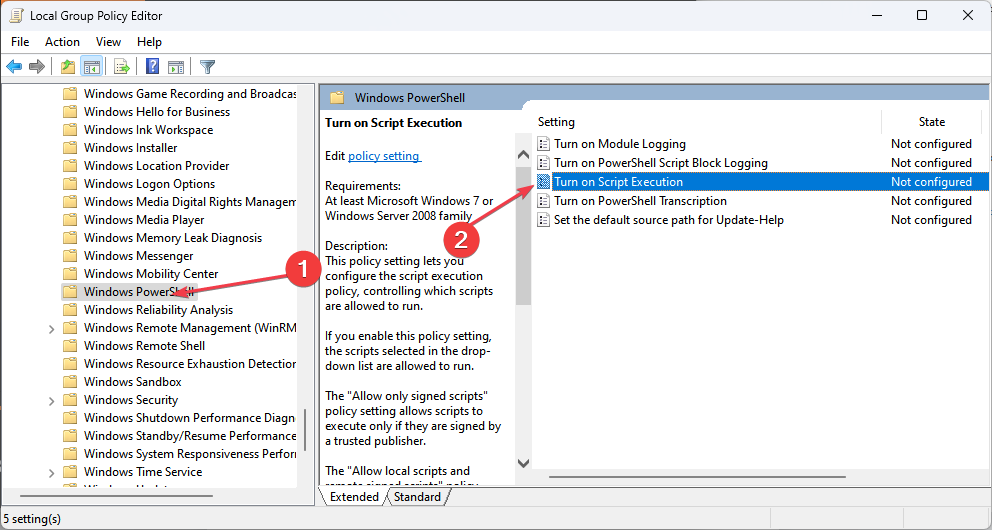
4. Activate the PowerShell script
- Press the Windows + R key to open the Run dialog box and type gpedit.msc into the dialog box and press Enter.
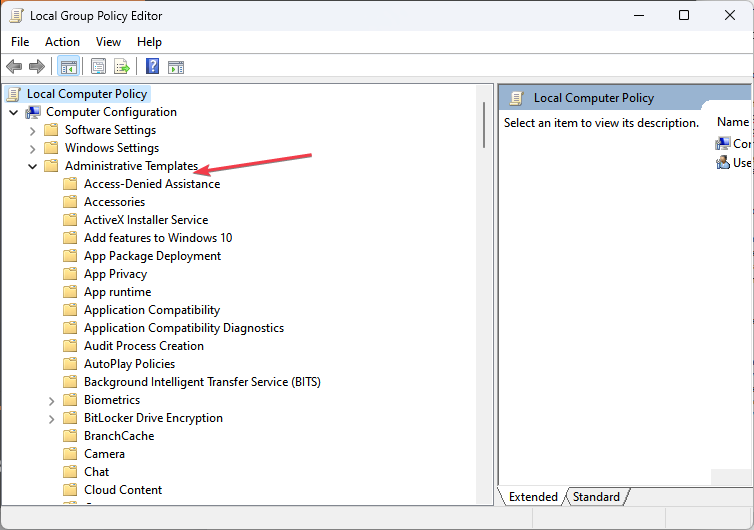
- Click the Computer Configuration drop-down arrow from the navigation pane and expand the Administrative Templates folder.
- Select Windows components, navigate to Windows PowerShell, and click on it.
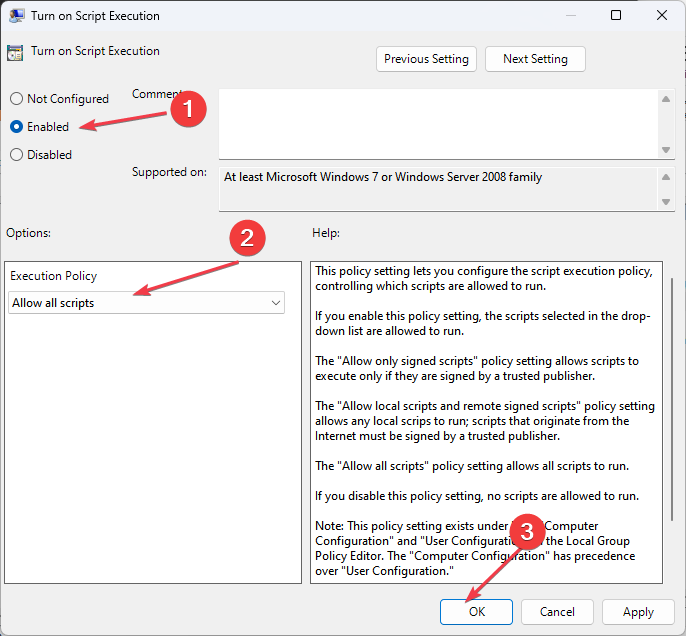
- Double-click on Turn on Script Execution and click on the Enabled radio button.
- Then, click the Execution drop-down arrow and select Allow all scripts.
- Select the OK button, close the Windows, and restart your PC.
Activating the PowerShell startup script will troubleshoot issues with the GPO startup script not running PowerShell.
Check our guide about fixing PowerShell if it’s not working or opening on Windows.
In conclusion, please read our detailed guide about disabling fast startup on Windows 11. Also, we have a complete guide on fixing Group Policy errors on your Windows computer.
Should you have further questions or suggestions, kindly drop them in the comments section.




User forum
0 messages