Password Spray vs Credential Stuffing: Differences & Prevention
All the information you need on these brute-force attacks
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Credential stuffing is when a bad actor tries to use a user's leaked login credentials for one online account for another account.
- To prevent these brute-force attacks, you need to use unique passwords for all your accounts.
- Using 2FA (2 - Factor Authentication) & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is another way to prevent attacks online.
The major difference between password spray and credential stuffing is the requirement needed to carry out the attack. They are both brute-force attacks used by bad actors to illegally gain access to user accounts.
While this might sound scary at first, they still depend on mistakes from your end. In this password spray vs credential stuffing guide, we will show how to prevent these attacks and the differences between them.
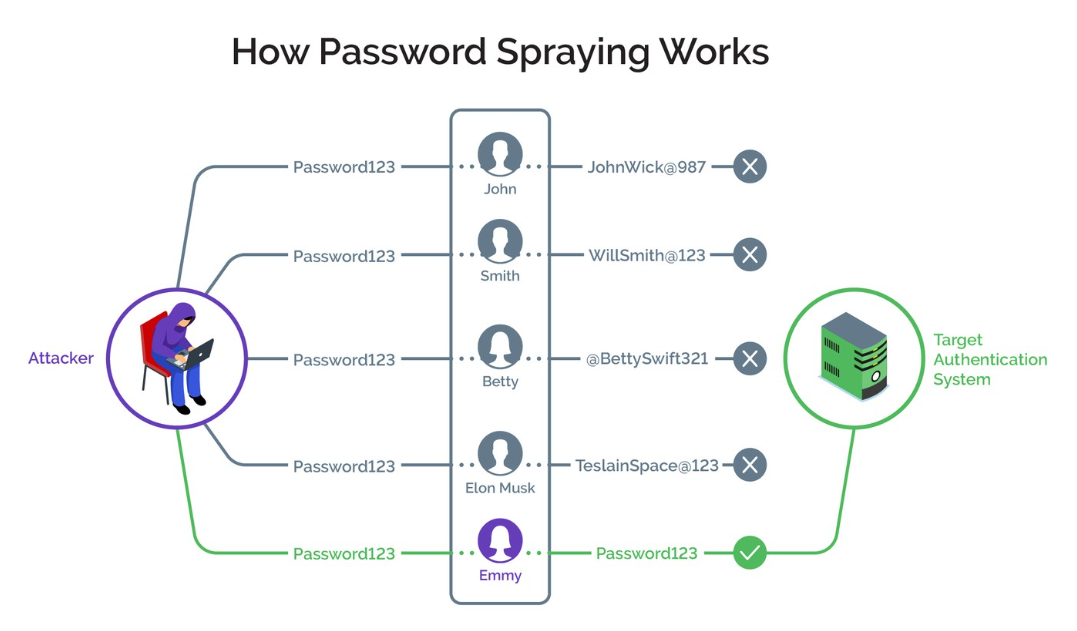
What is password spray?
A password spray is a form of brute-force attack where the wrongdoer tries some random commonly used password on different valid usernames. That means that the attacker does not have any legitimate information.
Instead, they spray some of the common and easy-to-remember passwords an average user uses on many valid usernames. Some of these weak passwords include password, 123456, 123abc, and 111111 etc.
They repeat this procedure with different common passwords till they eventually breach one of the accounts.
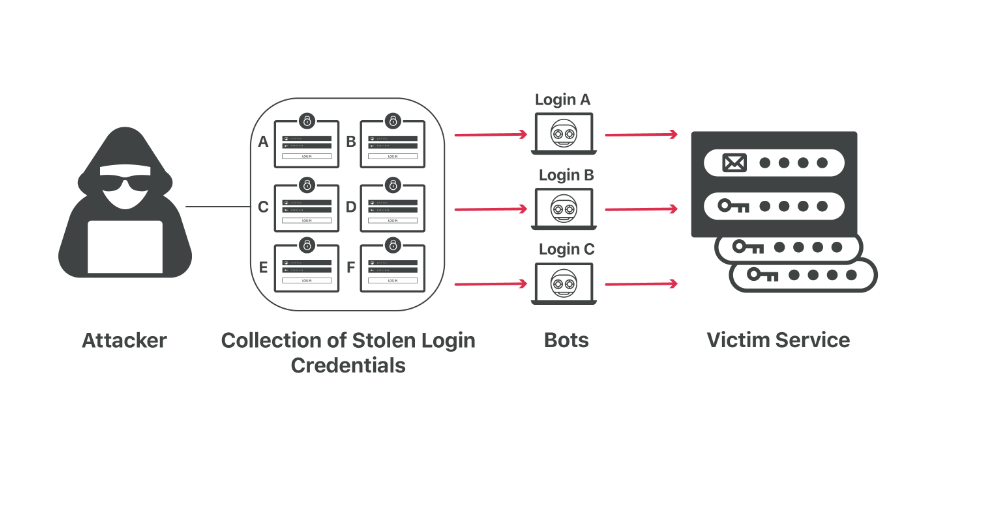
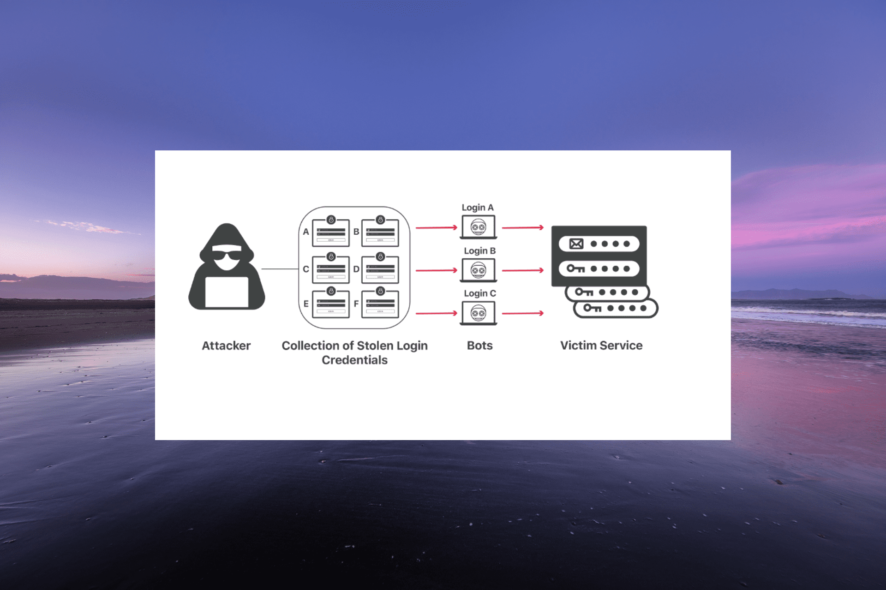
What is credential stuffing?
Unlike password spray, in credential stuffing, the attacker gets access to the login credentials for a user’s account. This usually happens via online leaks; maybe the website’s database where you have an account got compromised.
With the password from the single account, the bad actor tries to get access to other online accounts held by the same user. If the password does not, the hacker tries different variations of the same password.
For example, a hacker might get access to a user’s Facebook username, email, and password. He then will try the password to get into the person’s Twitter or Gmail account. If this does not work, they use a variation of the password instead.
What is the difference between password spraying and credential stuffing?
1. Objective of attack
The major objective of these two types of attacks is to illegally get access to users’ accounts. However, for credential stuffing, the objective is to use a leaked user credential for one account to get access to multiple accounts held by the same user.
Password spraying, on the other hand, requires the bad actor to have a list of common passwords that will be sprayed on different valid usernames.
2. Requirement
The requirement for a credential stuffing attack is a leaked online credential base to work with. They usually get this through online leaks or by hacking an organization’s database.
While password spraying requires no leaked data. Just a random list of valid usernames, which is usually an email address and commonly used and simple passwords.
3. Mode of operation
While credential stuffing can be done manually, hackers use botnets. They feed the available data to the bots that start making different variations to get access to other accounts.
This form of attack works because most internet users do not keep unique passwords for different accounts. Instead, they use the same password over and over or a variation of it.
Attackers also use botnets for password spraying. The bots work with valid usernames and match them to commonly used passwords till they get a valid credential for an account.
This form of attack is sometimes successful because an average internet user has tens of accounts that require passwords. So, most people prefer to use these weak and so-called easy-to-remember passwords. This makes it easy for hackers to get access to their accounts.
How can I prevent credential stuffing and password spraying?
Below are some of the things an organization and individual can do to prevent these brute-force attacks:
- Use unique passwords – While it is tempting to just go for the commonly used passwords, this usually ends badly. Always use a strong and unique password for different accounts. If you are worried about having to remember them all, you can use a trusted password manager instead.
- Reject commonly-used passwords – As an organization with online portals, you need to have password creation policies that reject weak and commonly-used passwords. With this, you can quickly notice a password spray attack before it comes to fruition.
- Use Multifactor Authentication (MFA) – To make the security of your portal and accounts stronger, you need to reduce the importance of passwords. One effective way to do this is to implement a two-factor (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication. With this, users will need to provide additional information, have access to their devices, or use biometric verification in addition to their passwords.
- Frequently check for database breaches – At times, some organizations check their database, especially the shared ones with a database of known leaked credentials. With this, you can know and quickly take action against breached accounts.
- Limit login attempts – Another effective way to prevent credential stuffing and password spraying is to limit the number of login attempts at a time. Also, you can introduce CAPTCHA and other liveliness detection tools into the login process to limit bots.
We have reached the end of this credential stuffing vs password spray guide. With the information therein, you now have everything you need to know about these forms of attack and how to prevent them.
If you need a list of offline password managers to help you protect your credentials, check our detailed guide for the top picks available.
Feel free to share your experience with these brute-force attacks with us in the comments below.