PC Keeps Booting to BIOS: 3 Easy Ways to Fix it
In most cases, your hardware is the culprit of this issue
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- FastBoot feature can sometimes cause this problem on your PC.
- In some cases, you might need to repair Windows to fix this problem.
Many users reported that their PC keeps booting to BIOS thus preventing them from accessing Windows.
This can be a serious issue, but there are a couple of solutions that can help you fix it.
Why does my computer keep booting to UEFI?
Improperly connected hardware can sometimes cause this problem. Settings such as Fast Boot or your CMOS battery can also cause problems.
How do I fix BIOS boot loop?
1. Check the hardware connection
- Make sure your hardware is properly connected.
- Remove any recently added hardware.
- Try removing the CMOS battery temporarily or replacing it.
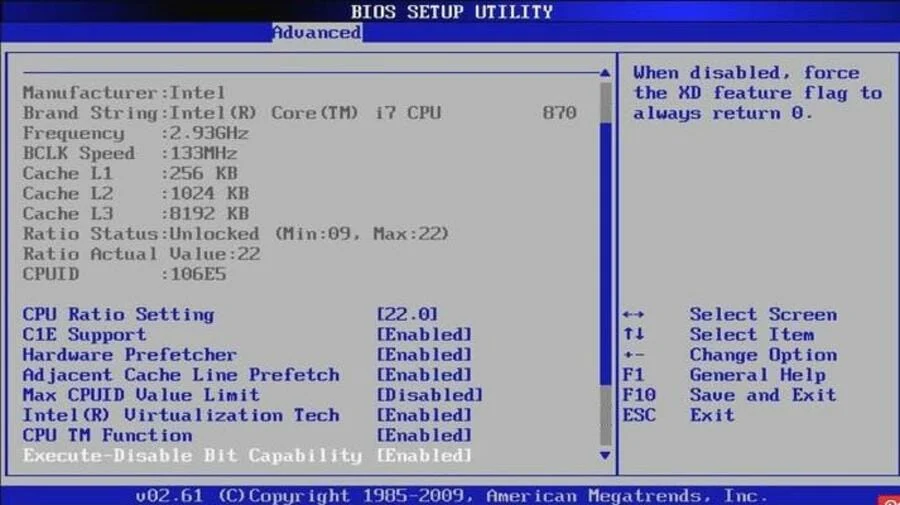
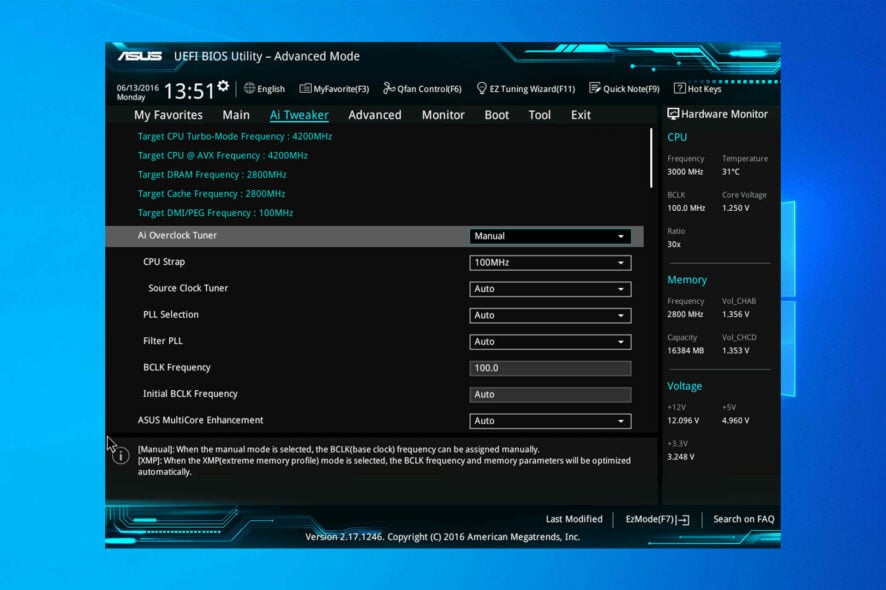
2. Disable Fast Boot and set your system drive as the primary option
- Access the BIOS utility.
- Go to Advanced settings, and choose Boot settings.
- Disable Fast Boot, save changes and restart your PC.
- Set your HDD as the primary booting device and confirm changes. The PC automatically goes to BIOS issue should be resolved.
3. Run the Windows Repair tool
- To utilize the Windows Repair tool, you’ll need a bootable Windows USB stick/DVD.
- Connect the flash drive/DVD to your PC, and set it as the Primary Boot Drive.
- Restart your PC and wait for the bootable device to load. After it finishes loading, choose the Repair your computer option and follow through with the process.
- This should fix the existing errors and make the system boot properly.
What’s the difference between UEFI and BIOS?
The Basic Input/Output System, or BIOS, is the firmware discussed in the preceding section on the boot mechanism.
It has a wide variety of utility operations that enable it to read the boot sectors of any associated storage and output information to the screen.
The abbreviation UEFI refers to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. It performs the same functions as a BIOS. Still, there is one fundamental difference between the two: all of the information regarding initialization and starting is stored in a .efi file rather than on the firmware.
This .efi file is kept on the hard drive within a specialized partition called the EFI System Partition (ESP).
To learn more about BIOS, we have a great guide on how to update BIOS that you might be interested in.
Regarding BIOS, many reported that Windows skips BIOS, but we covered that issue in a separate guide.
We hope that our recommendations from this article were helpful for you to solve your PC’s unusual behavior. For more suggestions, please access the comments section below.