Intel Speed Shift Technology: Everything you Need to Know
This technology optimizes the CPU performance on your PC
4 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
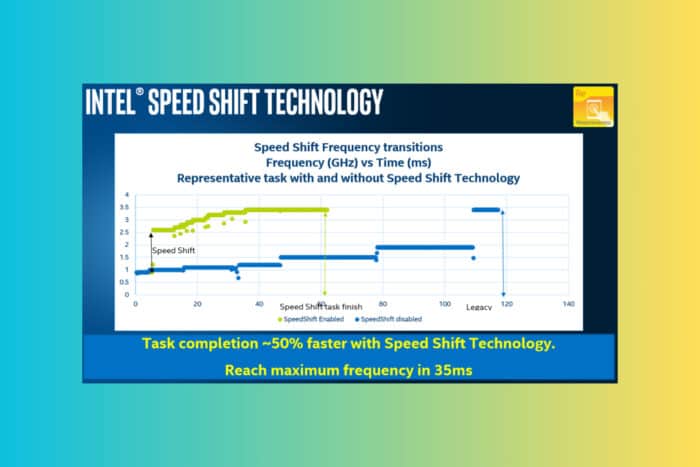
Ever wondered how to squeeze more performance out of your Intel processor? Intel Speed Shift Technology might be the key. This guide will walk you through understanding, enabling, and optimizing this feature to boost your PC’s performance.
What is Intel Speed Shift and what does it do?
1. Understanding Intel Speed Shift Technology
Intel Speed Shift technology, also known as Hardware P-states (HWP), is built into many modern Intel processors. It basically allows the processor to more quickly select its optimal operating frequency and voltage, leading to quicker responsiveness with short-duration performance shifts. This essentially means your system can respond faster to performance demands.
This feature allows the CPU to handle power state transitions autonomously, reducing the latency associated with these changes compared to when the operating system handles them. This results in improved performance and power efficiency.
Intel Speed Shift is typically enabled or disabled in the motherboard’s BIOS settings. By default, it should be enabled, but it’s worth checking. You may also disable it, but it’s a pretty useful feature.
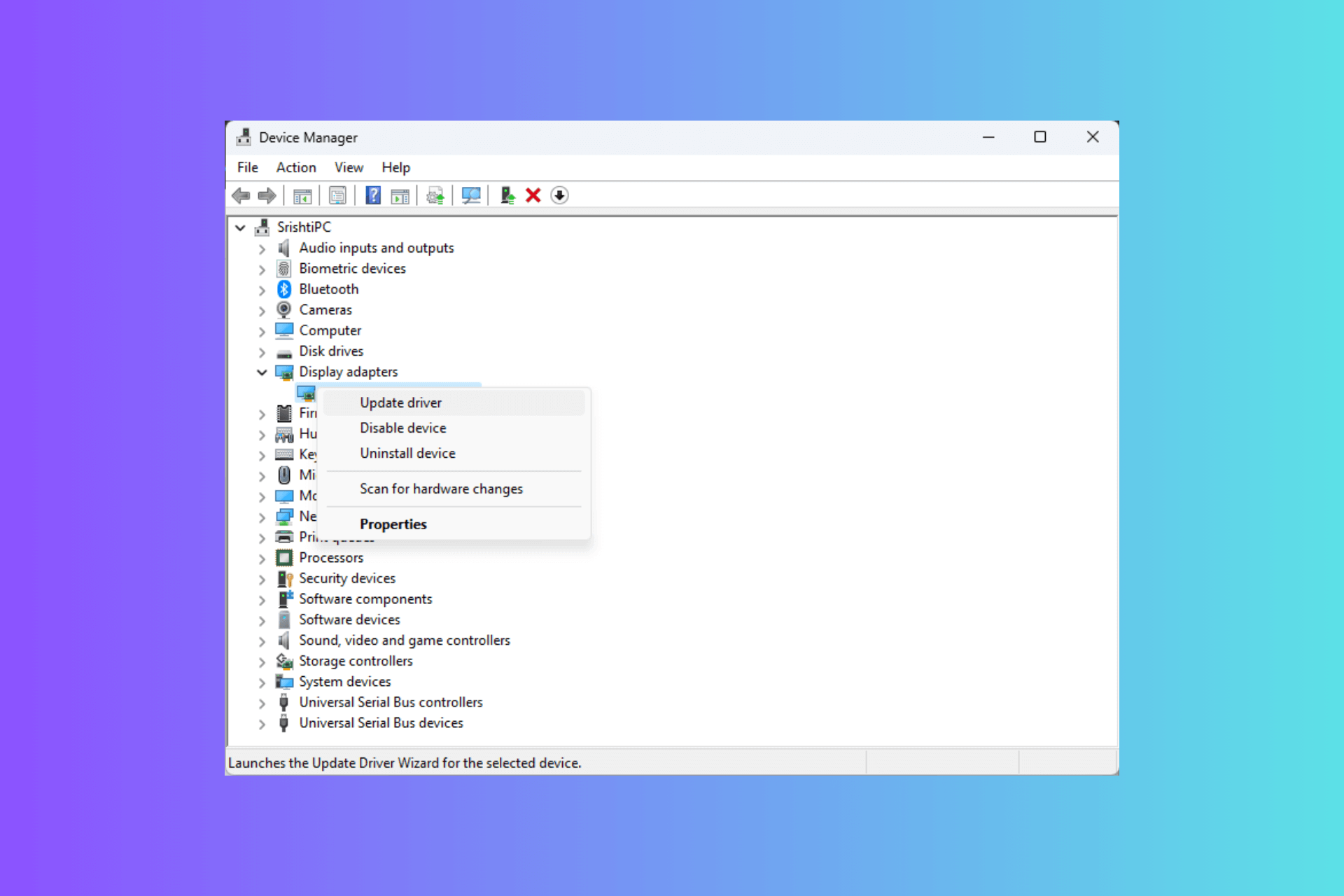
2. Enabling Intel Speed Shift in BIOS
- Restart your computer and press the key (usually F2, F12, Del, or Esc) to enter the BIOS setup during the initial boot process.
- In the BIOS menu, find the section related to CPU configurations or advanced system settings (the exact location will vary depending on your motherboard manufacturer).
- Look for the Intel Speed Shift Technology or HWP setting and change it to Enabled. If you do not see this setting, make sure your BIOS is updated to the latest version, as older versions might not support this feature.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS setup (this is usually done by pressing F10).
By enabling Intel Speed Shift in your BIOS, you allow your processor to manage its performance states more efficiently, leading to quicker responses and potentially better performance in application workloads.
3. Monitoring and adjusting Speed Shift performance
Tools like HWInfo or Intel’s own Performance Maximizer can be used to monitor the performance states of your CPU. This helps you see how Speed Shift is influencing power and performance.
In some advanced CPU management software (like Quick CPU), you can adjust the Speed Shift settings, such as minimum and maximum allowed performance states, and energy performance preferences.
You can create different performance profiles that cater to various scenarios, such as high performance for gaming or power saving for everyday tasks. This can further optimize how Speed Shift manages CPU states.
Should I disable Intel Speed Shift?
Some users recommend keeping Intel SpeedStep enabled and disabling Intel Speed Shift. However, we listed a few benefits of this technology and how to troubleshoot eventual issues with it. Basically, monitoring your PC and assessing its performance changes will tell you whether you disable Intel Speed Shift.
- Benefits:
- Improved responsiveness, especially in tasks requiring short bursts of high performance, like web browsing or light gaming.
- Better power efficiency leading to potentially longer battery life in laptops.
- Enhanced overall system performance in multitasking environments.
- Troubleshooting:
- If you encounter issues with stability or performance, try updating your BIOS and CPU drivers.
- Ensure that other power management settings, like Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology, are appropriately configured to work alongside Speed Shift.
- If problems persist, consider disabling Speed Shift or reverting to default BIOS settings and observe any changes.
If you want to monitor the PC performance, check our list of the best system information tools. You might also be interested in how to limit the CPU usage of a process on your computer.
To keep your system running smoothly, regularly update your BIOS and CPU drivers. Also, periodically check your BIOS settings to ensure optimal configurations.
For any other questions or suggestions, drop us a line in the comments section below.


User forum
0 messages