VPN Application Blocked by Security Settings [Solved]
7 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Having your VPN blocked by security settings means your privacy will be compromised.
- More so, you won’t be able to circumvent any restrictions, including geoblocking.
- Fortunately, there are a few ways you can restore your VPN’s functionality.
- Check out our guide and learn how you can restore your VPN in no time.
VPN connections can be blocked for several reasons, such as geo-restrictions, network administrator settings, or even your security settings, such as firewalls, antivirus, and/or anti-spyware programs.
Usually, VPN clients require specific ports and protocols in order to function as they should, and these should be allowed for this to happen successfully. Otherwise, you may encounter VPN blocked connection errors.
You may contact your VPN vendor for a complete list of ports necessary for your VPN client, or you could create relevant exceptions in your security settings.
At the same time, different users reported such issues with the VPN that caused this error message:
This failure is likely the result of a firewall, extension, or VPN setting blocking the request. please check your settings for more help with the resolution.
If none of this helps, try some of the solutions below and see what works.
What is blocking my VPN connection?
There are various elements that can block your VPN connection, including your firewall blocking the VPN or antivirus program. However, other factors that generate VPN blocking are:
- License and copyright rules for restricted content
- Official government block
- Employers or school VPN restrictions
- VPN blocked by the administrator
- Fraud and crimes VPN traffic limitations
So before going to our descriptive solutions, be sure you fully understand the reasons for blocking VPN usage.
What to do if security or firewall settings blocked VPN connection
1. Disable your security software
- Configure your firewall settings to allow your VPN.
- Change the security level depending on the program, and you can choose from High to Medium and grant an exception to your VPN. (Set it to Trust your VPN. Check with the instructions for your own security software).
- If you can reinstall the program blocking your VPN, install it after your VPN is already installed as this will let it allow your VPN to connect.
This is how to allow VPN through Firewall on Windows 10. Try and disable your firewall, antivirus, or anti-spyware program and see if your VPN connection unblocks.
Do this by uninstalling your VPN and the security software that is blocking your VPN. Then install the VPN and the security program again.
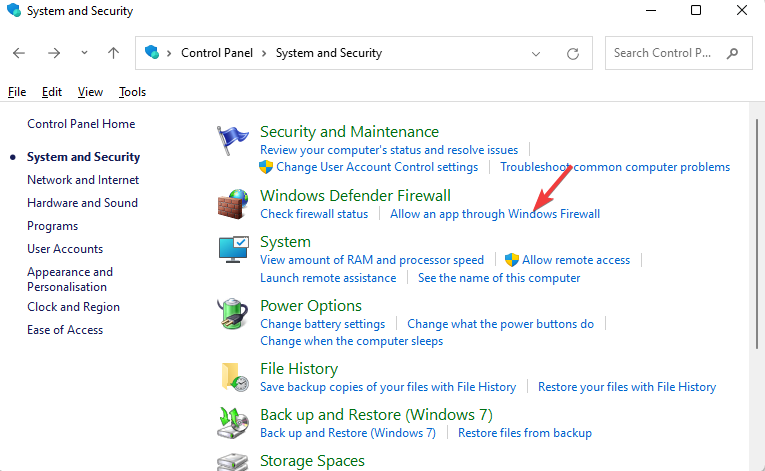
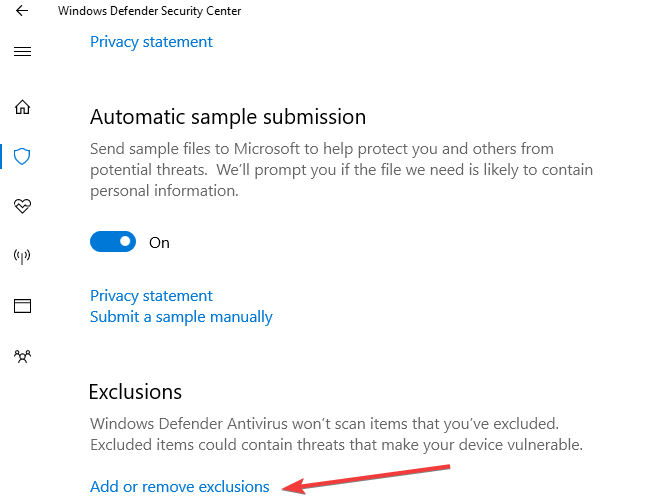
2. Add an exclusion
- Go to Windows System and Security.
- Under Virus & Threat protection settings, select Exclusions.
- Click Add or remove exclusions.
- Click Add an exclusion.
- Add your VPN client.
Note: Usually, ports 500 and 4500 UDP are used by VPNs, while port 1723 is used for TCP. If you find these not working, add a new rule or exception to allow them in Windows Firewall Advanced Settings.
3. Change your VPN software
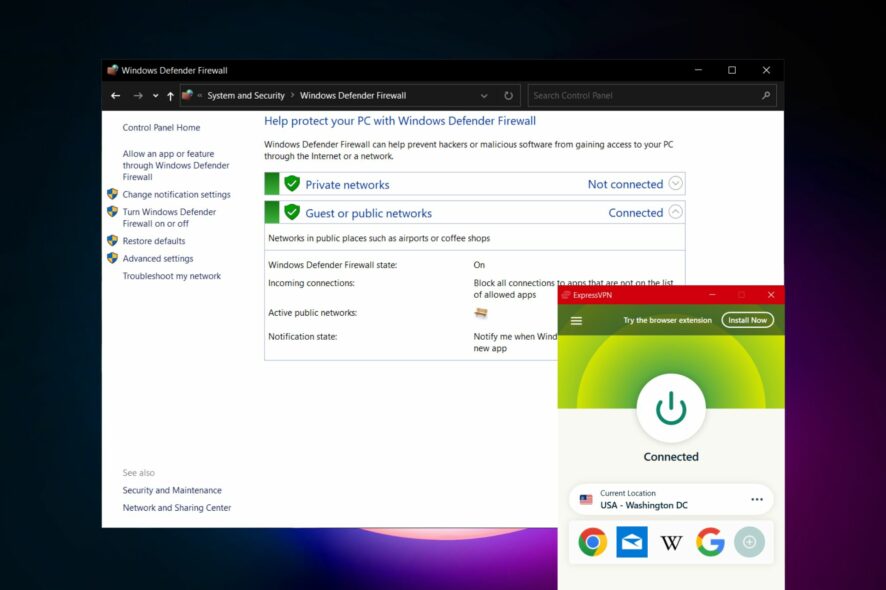
If you find that your Security or Firewall settings might be blocking your VPN connection, the first thing that you should try is an effective VPN called ExpressVPN.
Unlike other VPNs, the auto-configuration feature makes it easier than ever to avoid conflict between software, thus eliminating the possibility of encountering this same issue.
This VPN was created by Kape Technologies with speed and efficiency in mind, and the result speaks for itself.
What makes ExpressVPN stand out, even more, is the fact that the company doesn’t keep any logs of your app usage, and offers private DNS for each server from 94 different regions.

ExpressVPN
Use this compatible VPN to navigate privately without any security settings blocking.4. Open ports
To allow your VPN to pass through your security settings, open the following ports: IP Protocol=TCP, TCP Port number=1723, and IP Protocol=GRE (value 47).
Ensure that these ports are allowed on Windows Firewall with the corresponding network profile.
Note: if you are running on the same server RRAS-based NAT router functionality, Do Not configure RRAS static filters, because they are stateless and NAT translation requires a stateful edge firewall like ISA firewall.
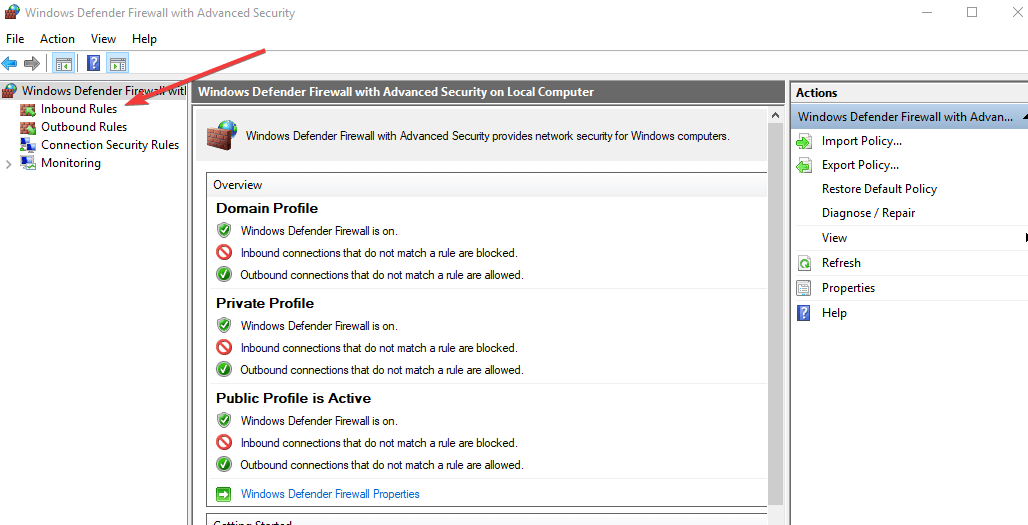
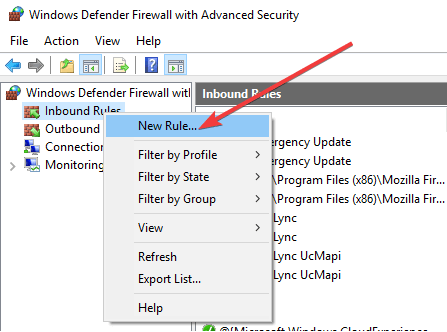
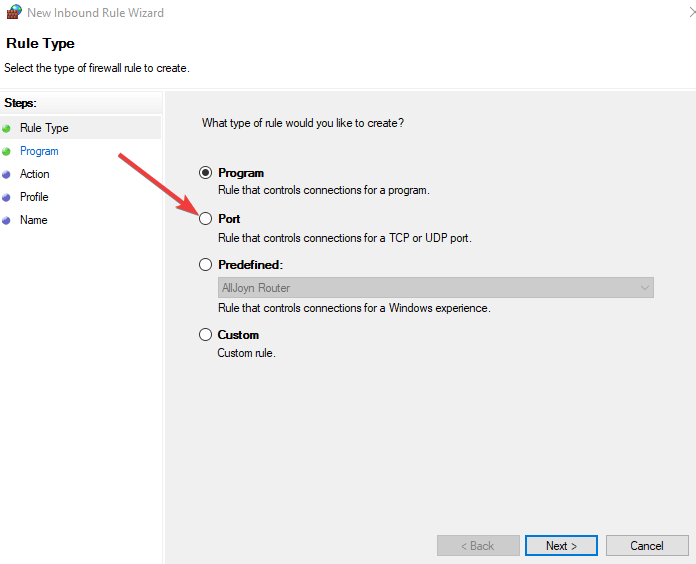
5. Create a new inbound rule
- Open Windows firewall and click inbound rules.
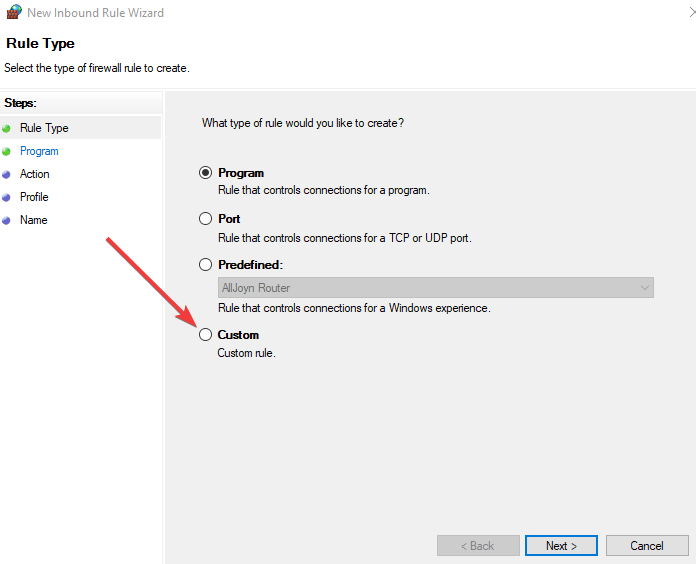
- Right-click and select New rule.
- Click Custom rule.
- Specify the programs then specify ports (you can leave them as all programs or all ports).
- Click These IP addresses under the remote IP.
- Click This IP address range.
- Type From 10.8.0.1 to 10.8.0.254.
- Close and click Next, then leave as Allow the connection.
- Apply to all profiles, then give your profile a name and click Finish.
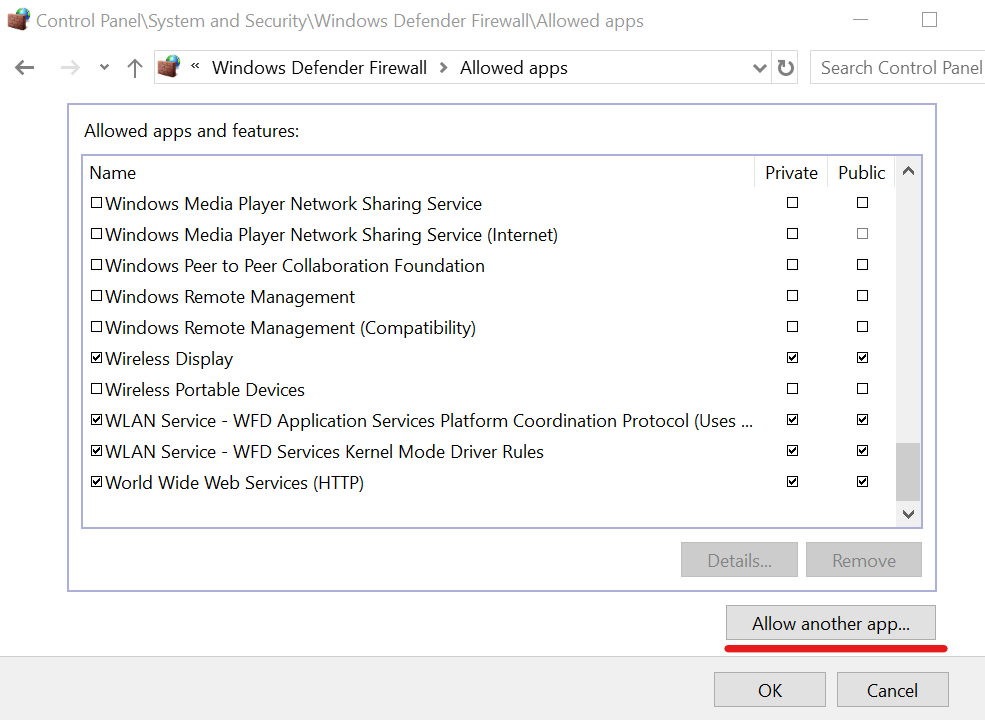
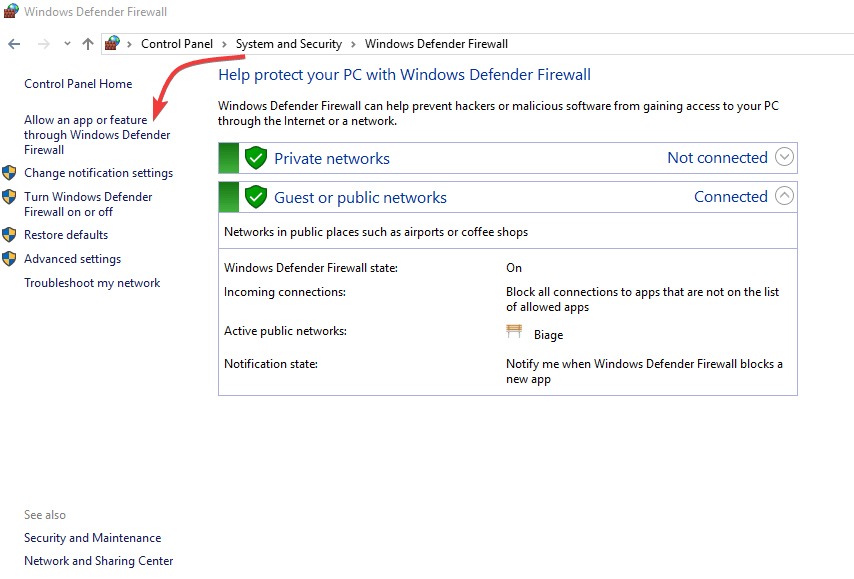
6. Change Allow app settings
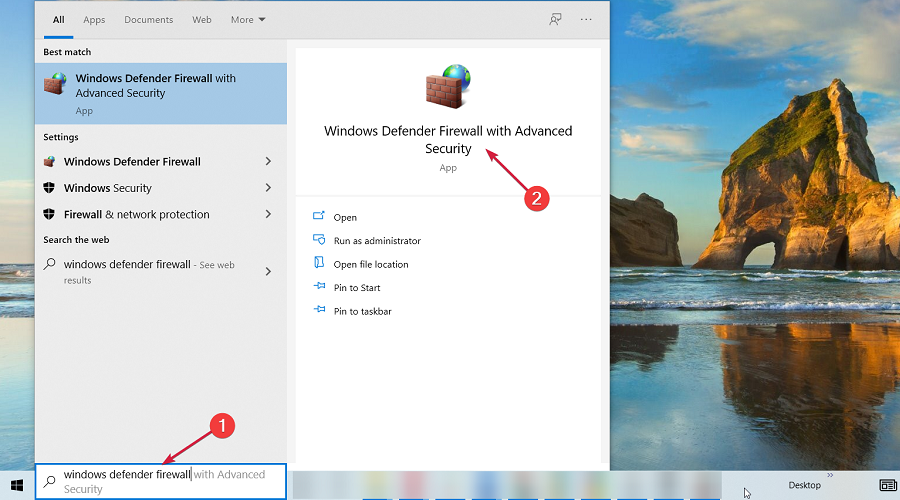
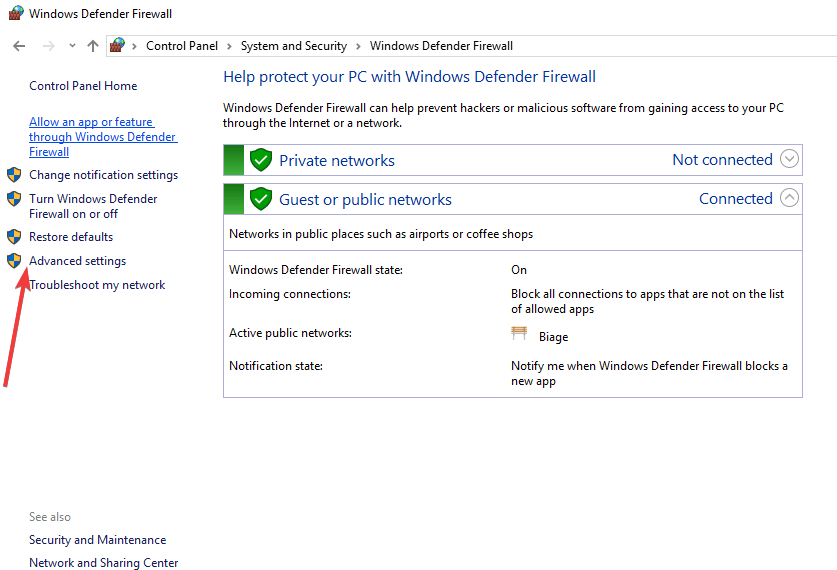
- In the search bar, type Windows Defender Firewall, and select it from the search results.
- Click Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall.
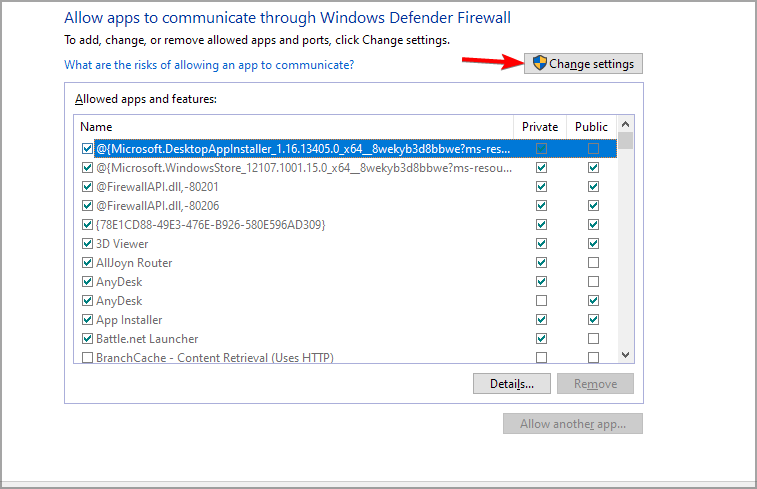
- Click Change Settings.
- Find your VPN from the list of programs/apps.
- Check Public or Private to select the network type to run your VPN on.
- Click Allow another app if your VPN isn’t on the list.
- Select your VPN.
- Click Add and then click OK.
7. Turn off SSL monitoring
The instructions to do this depend on which VPN you are using. However, here are the steps you can take if you’re using NOD32 or Kaspersky:
NOD32:
- Click on Setup.
- Select Advanced Setup.
- Click Antivirus and antispyware.
- Choose Web access protection.
- Click HTTP, HTTPS > HTTP scanner setup, and set HTTPS filtering mode to Do not use HTTPS protocol checking.
Note: If HTTPS filtering mode is greyed out, set Antivirus and antispyware > Protocol filtering > SSL to Always scan SSL protocol. Restore the previous setting after changing the HTTPS filtering mode.
Kaspersky
- Click Settings.
- Click the Traffic Monitoring panel.
- Go to Port Settings or settings.
- Choose Network.
- Click on the Port Settings and uncheck the box for port 443/SSL
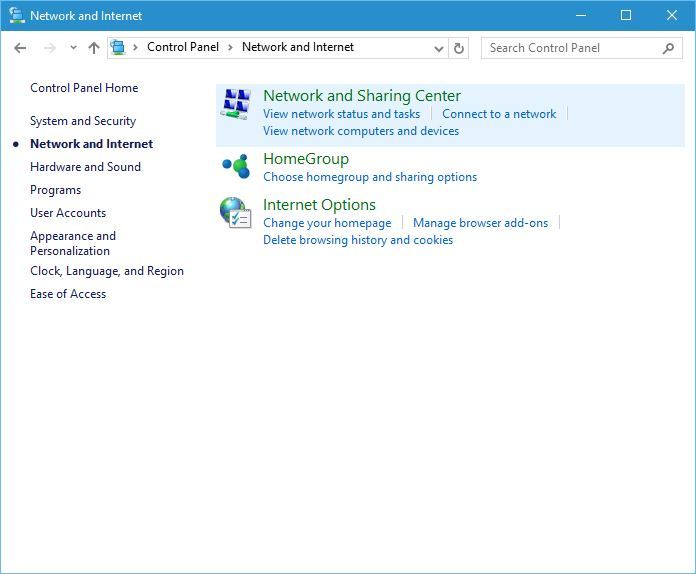
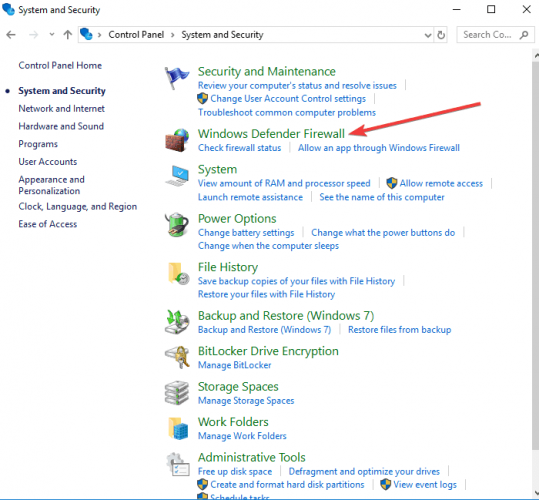
8. Change Adapter Settings
- Go to Start and select Control Panel.
- Click Network & Internet.
- Click Network and Sharing center.
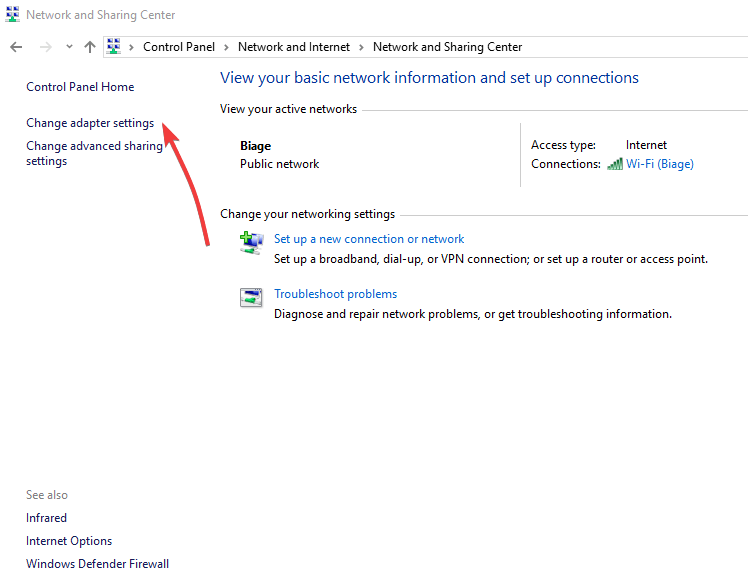
- Click Change adapter settings.
- Click on File.
- Select New incoming connection and click on the users you want to access your VPN.
- Check the Through the Internet box and click Next.
- Mark the Internet Protocols you want your VPN to connect to.
- Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
- Open Control Panel again.
- Select Windows Firewall.
- Click Advanced Settings.
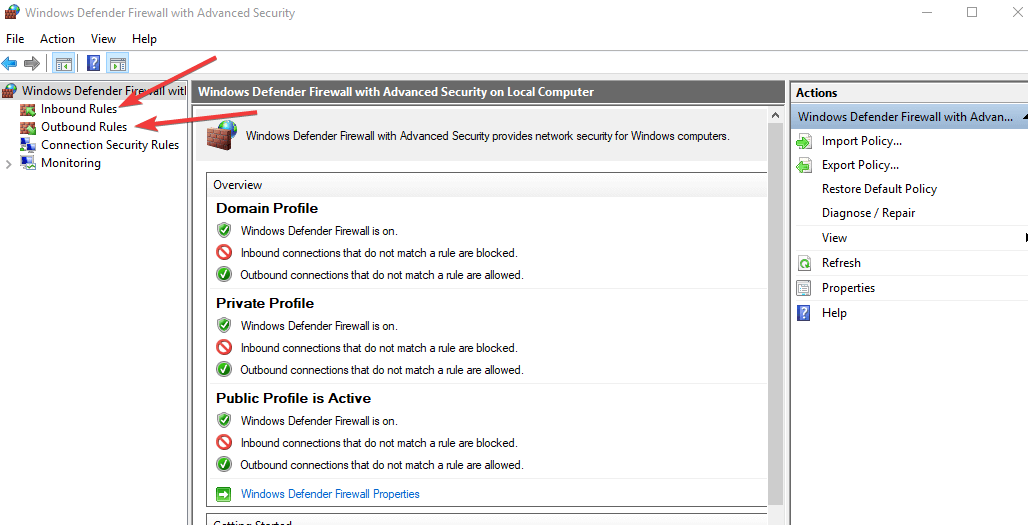
- Right-click Inbound Rules and click New Rule.
- Choose Port and click Next. Click Next again after selecting the ports.
- Select Allow the connection and click Next.
- When asked ‘When does this rule apply?’ select all options (Domain, Private, Public) and apply the rule to all.
- Choose a name and description to fill in the Name Description and click Finish.
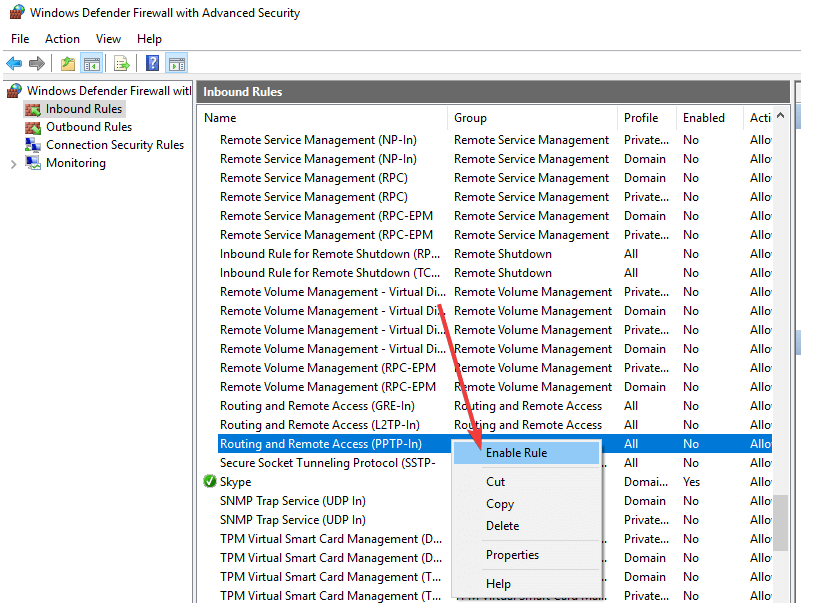
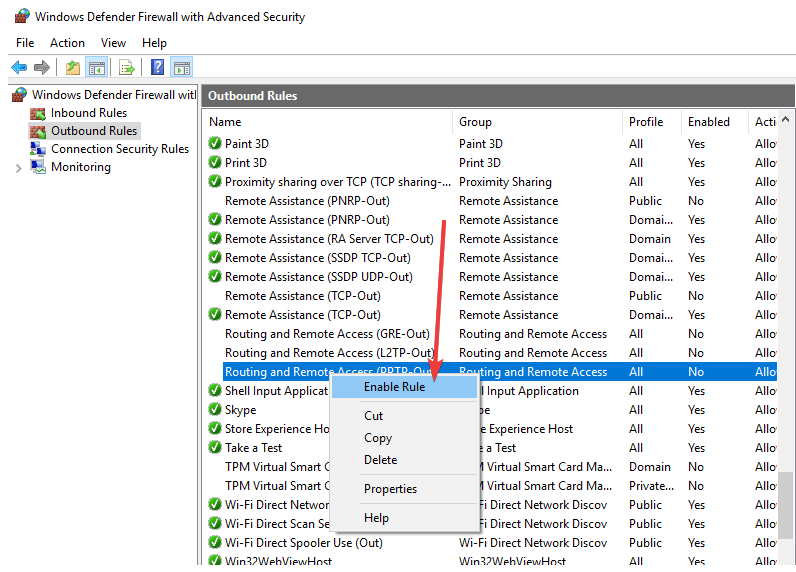
9. Enable rule for PPTP
If your VPN requires PPTP, you can perform this process:
- Click Start and select Control Panel.
- Select Windows Firewall.
- Click Advanced Settings.
- Find ‘Routing and Remote Access‘under Inbound Rules and Outbound Rules.
- For Inbound Rules, Right-click ‘Routing and Remote Access (PPTP-In)’, select Enable Rule.
- For Outbound Rules, Right-click ‘Routing and Remote Access (PPTP-Out)’, and select Enable Rule.
10. Reset your firewall or reinstall your VPN
If security settings block the VPN application, you may need to reset your firewall, and if that doesn’t help, reinstall your VPN.
If you’re using Norton firewall, reset it by clicking Settings > Firewall > General tab > Reset beside Firewall Reset, then restart your computer, and the firewall rules will be created again as you use your VPN or programs that access your network/internet.
Even more, what happens when your VPN is blocked at school, hotel, college, or university? Rest assured that our guide can help.
Were you able to resolve the problem? Let us know in the comments section below.








User forum
0 messages