Microsoft develops advanced camera calibration for improved user experiences
A camera calibration of this degree would take Teams meetings, or even Windows Camera app to the next level.
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Intelliframe offers a similar camera calibration but not at this level.
- The technology can be used in Windows, Teams, Skype, and other industries as well, such as gaming, and robotics.
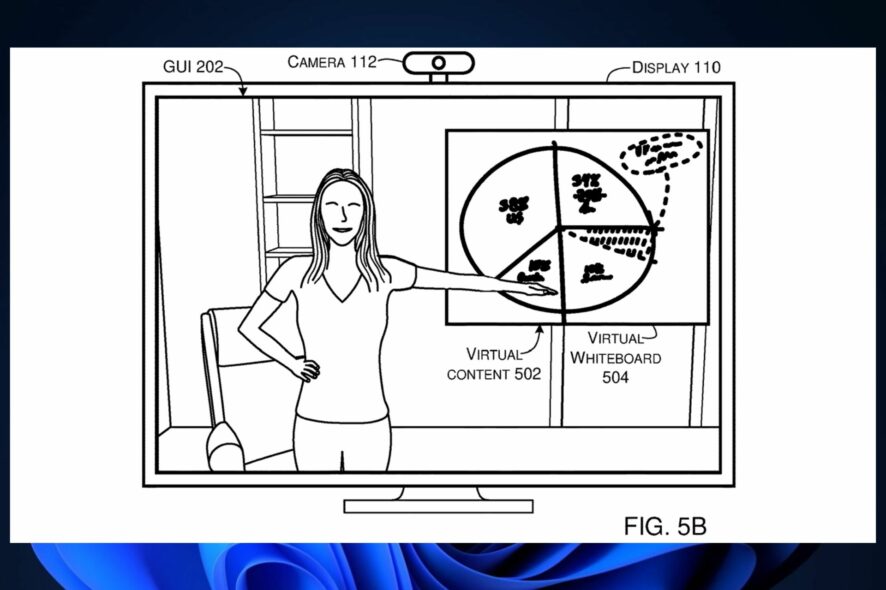
According to a patent filed by Microsoft and published recently, the Redmond-based tech giant is developing advanced camera calibration features that would greatly improve user experiences during a video conference, or virtual meeting.
It’s no secret that camera settings are important during a meeting and Microsoft also made important progress to deliver the best experience when participating in a virtual meeting. For example, the Redmond-based tech giant has been experimenting with Inteliframe on Microsoft Teams: this feature automatically detects human faces and then displays information about them, in real-time.
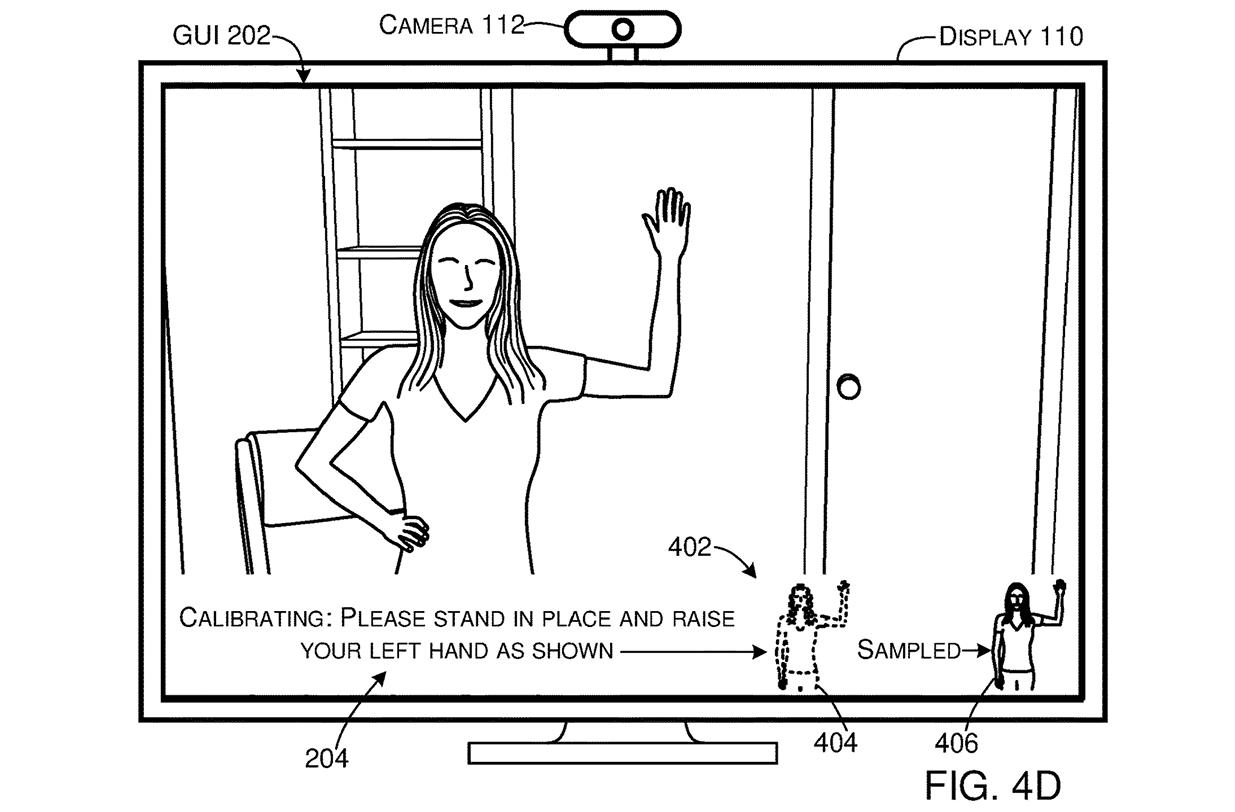
Inteliframe uses a sort of camera calibration, as well. However, the technology described in the patent is far superior, as it automatically calibrates the camera without needing a full body image of the user. The technology will correctly adjust the camera settings with partial images of the user at different locations.
Calibration of the camera can enhance various user experiences with the camera, such as integrating camera data with other data, such as virtual data.
Microsoft
The advanced camera calibration described in the patent can be easily integrated into Windows, Microsoft Teams, or any other application that uses the camera.
How would this advanced camera calibration work in Windows, or Microsoft Teams?
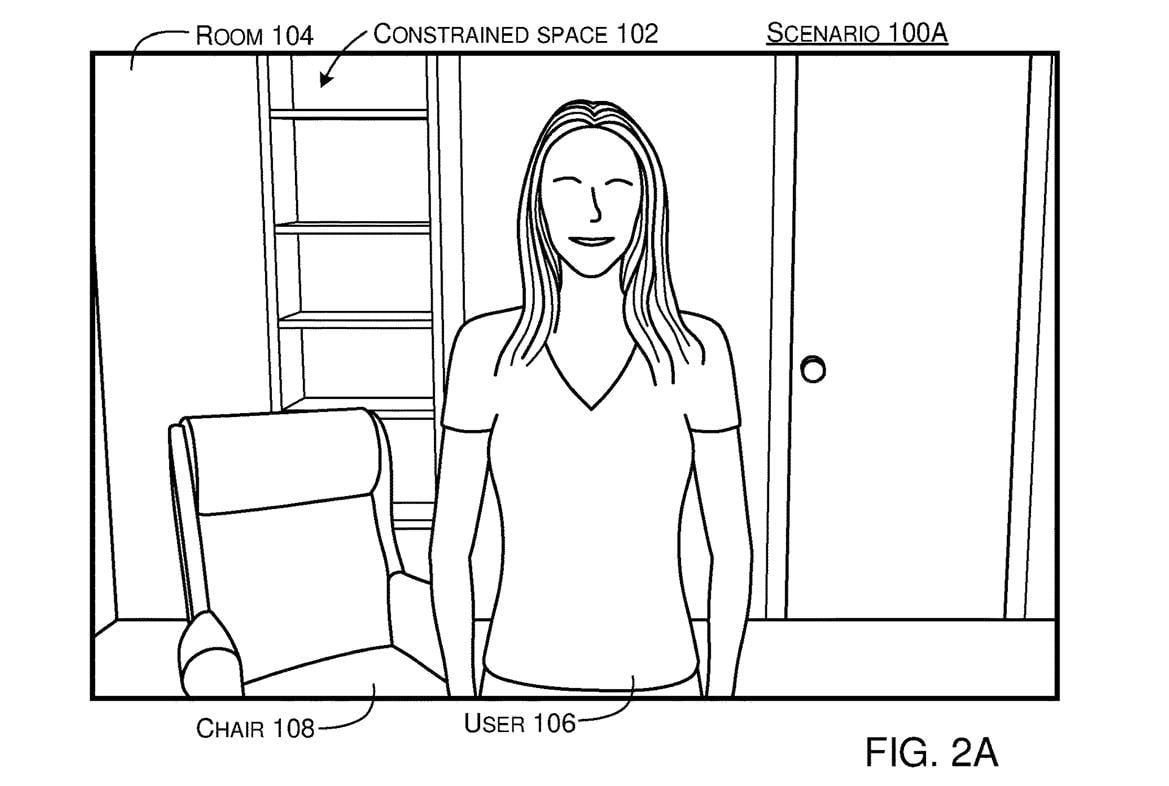
- The camera captures the first image of a user at a certain location. This image includes only the user’s upper body.
- The camera then captures a second image of the user at a different location. This image also includes the user’s upper body, but not their entire body.
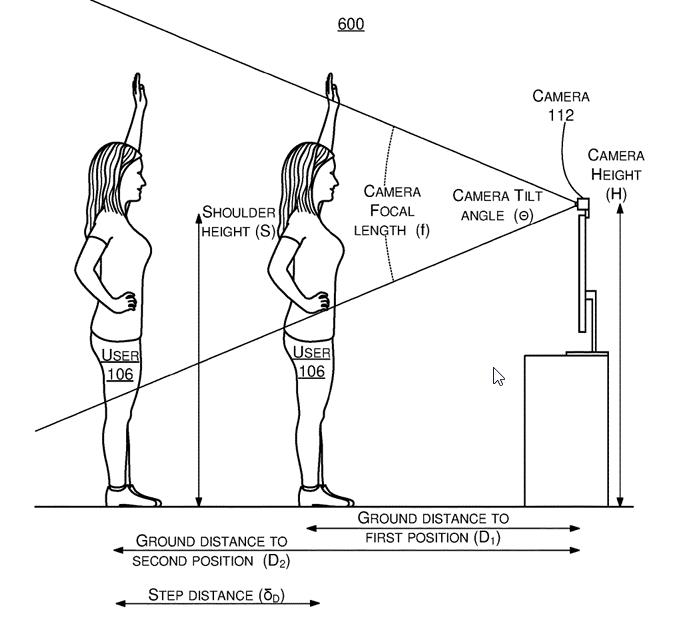
- The system estimates the distance between the first and second locations relative to the camera.
- Using the first image, the second image, and the estimated distance, the system calibrates the height and tilt angle of the camera.
As we mentioned earlier, a suitable application for this technology would be Windows or Microsoft Teams. Other Microsoft apps, such as Skype, can also implement it. However, video conferencing would be just one of the many applications for this technology, as a whole.
Security systems, interactive video games, robots, autonomous vehicles, or even smart home devices can use the technology to assert themselves according to a person’s movement, and offer the best experience.
For gaming, for example, the advanced camera calibration described in this patent would offer a more immersive gaming experience to players, by adjusting the perspective based on the player’s body position.
Speaking of gaming and camera settings, we have a great guide on the best Rocket League camera settings for beginners that might interest you.
While it’s too soon to say if Microsoft will release this technology or not, it could take Teams meetings to the next level. And the fact that it also has so many potential applications makes it even more valuable.
But we’ll see if this happens in the following months.