Chrome's Memory Saver Mode gets smarter at discarding tabs
Memory Saver estimates the probability of users revisiting tabs to discard.
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Google introduces a new mode called “Probabilistic Memory Saver Mode” to improve Chrome’s Memory Saver feature. This mode makes intelligent decisions on which tabs to discard and which to keep, thereby reducing the time it takes to reload discarded tabs.
Memory Saver is a feature in Chrome that optimizes memory usage by freeing up memory from background tabs and allocating it to active tabs. Google’s data indicates that users revisit Memory Saver tabs within 24 hours about 60% of the time. Google aims to improve this statistic by making better decisions on which tabs to discard with the Probabilistic mode.
Chrome’s new Probabilistic Memory Saver Mode
The Probabilistic mode uses probability distributions to estimate the likelihood of a tab being revisited based on observations about the tab’s state. It discards tabs that are less likely to be revisited and retains those that are more likely to be revisited.
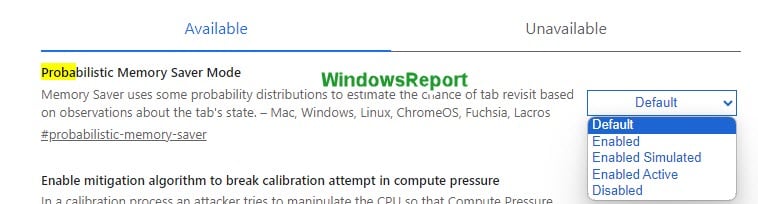
Google is testing this new feature in Chrome 121. Users can enable the feature from the chrome://flags page. The feature flag has three states:
Enabled: The feature is enabled and works normally.
Enabled Simulative: The feature is enabled but does not discard any tabs. It only simulates the discarding process and logs the results.
Enabled Active: The feature is enabled and discards tabs aggressively. It only keeps the most likely tabs to be revisited.
Development of new components: For Probabilistic mode, there are several other ongoing development efforts to improve Chrome’s Memory Saver feature. These include the development of new components such as TabPageDecorator, TabRevisitTracker, and ProbabilisticMemorySaverPolicy. These components indicate a focus on smarter tab management, especially in terms of deciding which tabs to discard and when.
Enahnced tracking and estimation: There’s also an enhanced tracking and estimation system in place, with the implementation of components like TabRevisitTracker and ProactiveDiscardEvaluator. These components suggest an approach to more accurately track user tab usage patterns and predict tab revisits.
Testing and refinement: Various commits indicate ongoing testing and refinement, such as adjustments to the time histograms and additions like TabConnectednessDecorator. The introduction of flag indicates progress towards user-end testing and potential future integration into mainstream Chrome versions.
In summary, Chrome is focusing on using probability-based methods to manage tabs, which is a complex but effective way to optimize memory. The updates show major progress in how Chrome can save memory by smartly deciding which tabs to discard, based on user habits and probability calculations.
Do you use the Memory Saver?Have you found it useful? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.