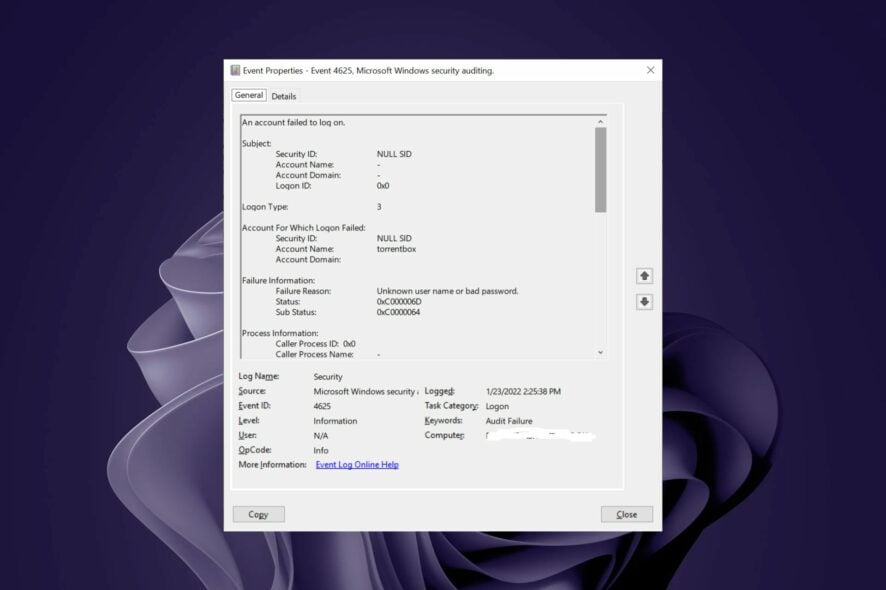
Event ID 4625: How to Fix the Failed Logon Error
Delete saved passwords from old cache to login again
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Event ID 4625 is a security event that indicates that the user account failed to log on.
- The most common cause is that your account's password has expired, and you have not changed it yet.
- To avoid such errors, ensure your password is up-to-date and your user account has the administrative privileges to logon.
Accessing the Windows Server can sometimes be a hassle, even for verified users. Sometimes, it’s the Windows Server Manager that’s not opening, while other times, you get a logon error dubbed Event ID 4625.
In such cases, it’s usually your password that is probably expired, so an update should do the trick. However, if that does not work, read on to find out how to bypass this logon failure.
What is Event ID 4625 failure reason?
The Event ID 4625 is a logon error that occurs when you try to access the Windows server. If accompanied by Event ID 4625 status 0xc00006d, you’ll know it’s a bad password.
Typically, this occurs because the system uses a cached password rather than an updated one you entered. This is because of how Windows stores password in a database.
When you log into a domain, it looks at this database to determine what your account’s password is. If it finds a match, then it just uses the stored version instead of prompting you for one.
Other reasons for this error include:
- Insufficient permissions – The user may not have sufficient permissions to perform the action, or the Active Directory has been corrupted. Always check for Event ID 4625 null SID, as it will let you know whether it was a valid account.
- Workstation restriction – A workstation restriction is an action that restricts the ability of a user to log on locally.
- Change of accounts – This can happen if you use a domain account to log on to a computer and then log in with a local account. It can also occur if you change from a local account to a domain account or vice versa.
- Logon Process from an untrusted logon processes list – User accounts are usually added to the Trusted Logons Group. If you get a logon error, the logon process has not been validated by the security system.
- Account expiry – If the user account hasn’t been used for a long time, you may get the username does not exist error. It’s possible that the account has been marked as inactive by AD and needs reactivation.
How can I fix Event ID 4625 logon error?
Before you attempt any of the recommended solutions below, ensure you check the following:
- Check that you have not misspelled your password.
- Clear any cache that may contain any expired saved passwords.
- Verify that the account you’re using to log on has enough privileges.
- Check whether there’s a mismatch between the logon type and the account you’re using to logon.
- Ensure you’re not using an account restricted to an internal IP address.
- Confirm from your Administrator that your account is still active.
1. Rejoin the domain
- Hit the Windows + R keys to open the Run command.
- Type regedit in the dialog box and hit Enter.
- Navigate to the following location:
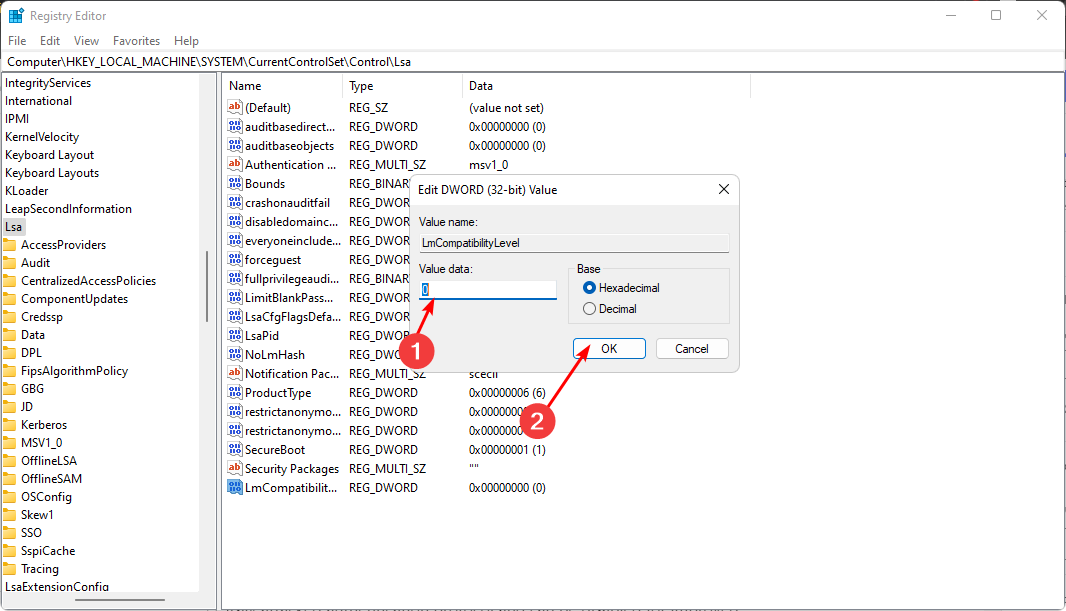
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa - Right-click on an empty space on the right and rename it as a NEW DWORD (32-bit) as LmCompatibilityLevel.
- Double-click on it and set the Value data as 1.
- Restart your PC and try logging in again.
2. Remove hidden credentials
- Hit the Windows key, type cmd in the search bar, and click Open.
- Type the following commands and hit Enter after each one:
psexec -i -s -d cmd.exerundll32 keyngr.dll KRShowKeyMgr - A list of stored usernames and passwords will appear. Delete them from your server and restart your PC.
The logon types should provide more detail to help you narrow the type of failure. If you get the Event ID 4625 logon type 3, Event ID 4625 logon type 4, or Event ID 4625 logon type 8, you should be able to get more information on where the user tried to log in from.
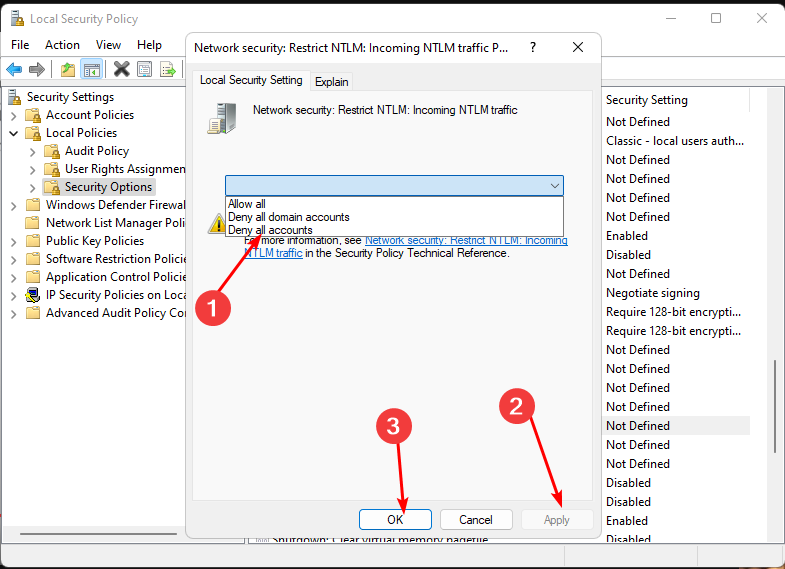
3. Disable NTLM logins
- Hit the Windows + R keys to open the Run command.
- Type secpol.msc in the dialog box and hit Enter.
- Navigate to the following location:
Local policies/Security options/Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic - Double-click on Network security: Restrict NTLM: Incoming NTLM traffic, and in the drop-down menu, select deny all accounts, then press Apply, then OK to save changes.
NTLM is an authentication protocol used by Windows systems to provide additional security when users access resources on a network. It can authenticate users against an Active Directory domain controller without supplying a password.
However, it’s also the most easily attacked authentication protocol and can be disabled for improved security.
The most common reason administrators disable NTLM authentication on their servers is that users have trouble logging into their systems when they are away from their offices or behind a proxy server.
For maximum security on your Windows Server, we recommend that you enable the TLS protocol and avoid outdated versions with known vulnerabilities.
Elsewhere, you may also encounter the Event ID 4768 error, so be sure to check out our detailed guide for various fixes.
Please let us know if you have any additional solutions in the comment section below.