What is Event ID 800 & How to Quickly Fix It
Check out the proven solutions to fix the event ID 800
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Event ID 800 occurs when the DNS clients cannot resolve the primary server address for the zone.
- Reconfiguring the SOA (Start of Authority) helps fix the Event ID 800 error on Windows DNS Server.
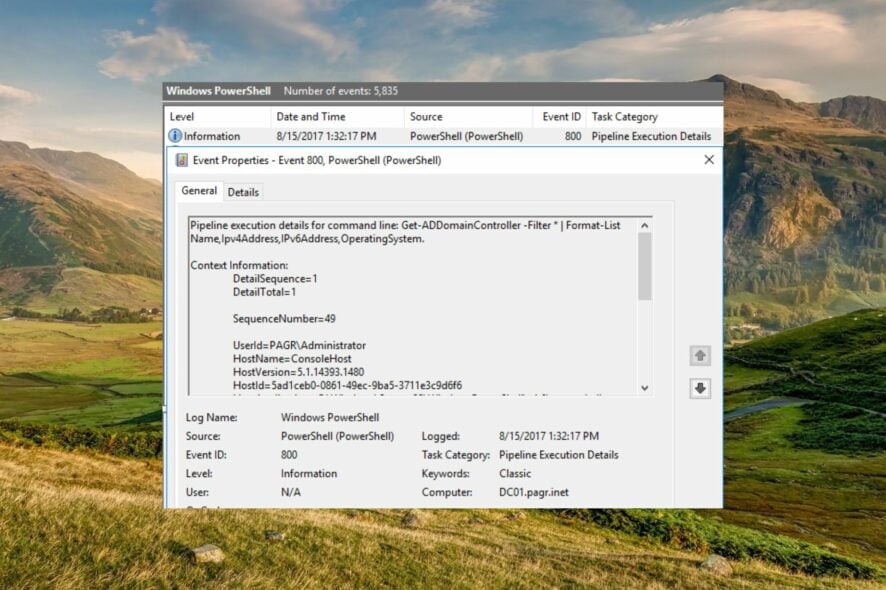
The Event ID 800, typically represented by the symbolic name DNS_EVENT_ZONE_BAD_PRIMARY_SERVER typically addresses the issue with the Windows DNS Server Service.
This comprehensive troubleshooting guide presents the different methods to troubleshoot the error with the DNS server, which ultimately resolves the Event ID 800.
What does Event ID 800 mean?
The event ID 800 describes the issue when the zone is configured to accept updates, but the A record for the primary server in the zone’s SOA record is not available on this DNS server.
When the DNS clients are unable to resolve the address of the primary server for the zone, they will not be able to locate a server to accept updates for this zone. This will leave the DNS clients to be unable to perform DNS updates.
Summing up, you can say that the event ID 800 signifies the configuration problem with the DNS server.
Now that you know about event ID 800, let’s check out the proven solutions to fix it.
What can I do to fix the Event ID 800 on Windows?
1. Fix the zone SOA configuration problem
 NOTE
NOTE
- Press the Windows key to launch the Start menu on the DNS server, type server manager, and select the relevant search result to launch Server Manager.
- Expand Roles followed by DNS Server and DNS in the console tree of the left navigation pane.
- Right-click the DNS server, and then select Properties from the context menu.
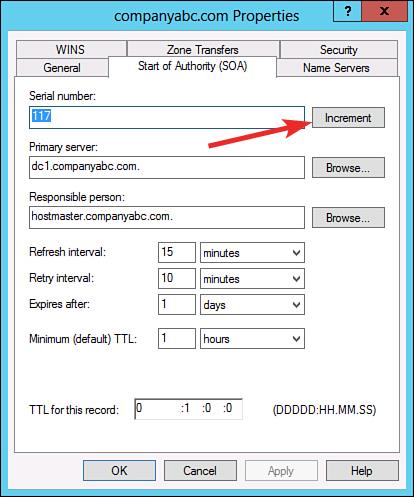
- Switch to the Start of Authority (SOA) tab and then verify that the correct server is enlisted as the Primary server.
- Click Increment to apply the changes to other authoritative servers in case you change the primary server.
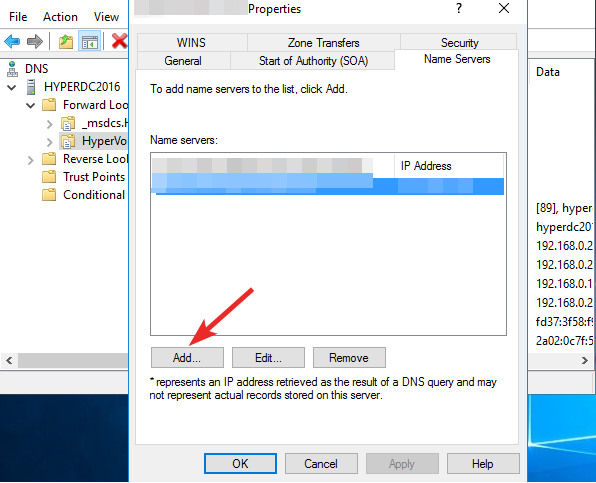
- Switch to the Name Servers tab and verify that each server enlisted matches its IP address.
- Press the Add button to change and specify the correct IP address for the server.
- Click OK to save the changes.
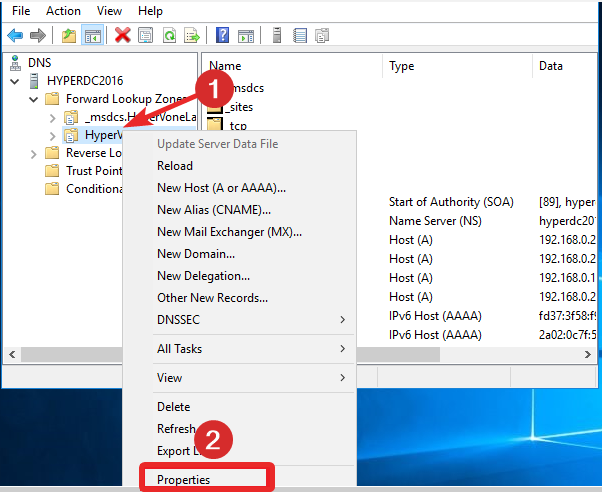
- In the right navigation pane, you need to verify that the zone includes a host (A or AAAA) resource record for the primary server.
- In case the host resource record for the primary server is absent, right-click the Zone, click New Host (A or AAAA), type the name of the primary server in the Name field, the IP address of the primary server in the IP address field, and then click Add Host button.
The DNS Server service is incompetent in discovering the server specified as the zone’s start of authority (SOA). You need to reconfigure the SOA configuration for the zone to fix this issue.
2. Verify Domain Name System configuration
2.1 Check DNS configuration settings
- Press the Windows icon on the taskbar to bring up the Start menu, type Server Manager, and select the relevant Server Manager from the search result.
- Expand the console tree on the left by double-clicking Roles followed by DNS Server, and DNS.
- Now right-click the DNS server and then choose Properties from the context menu.
- Switch to each tab in the properties window, examine the different options, and ensure that they have been assigned the correct values.
- Now exit the Properties window and expand the DNS server as well.
- Next, expand the zone folder, right-click a zone from the list, and choose Properties from the context menu.
- Ensure that the values assigned to all the options on each tab of the properties window are correct.
- Review the related settings for each zone for the DNS server.
2.2 Ensure DNS client computers can resolve names
- Press the Windows key on the keyboard to launch the Start menu, type cmd in the search bar and choose Run as administrator from the search results.
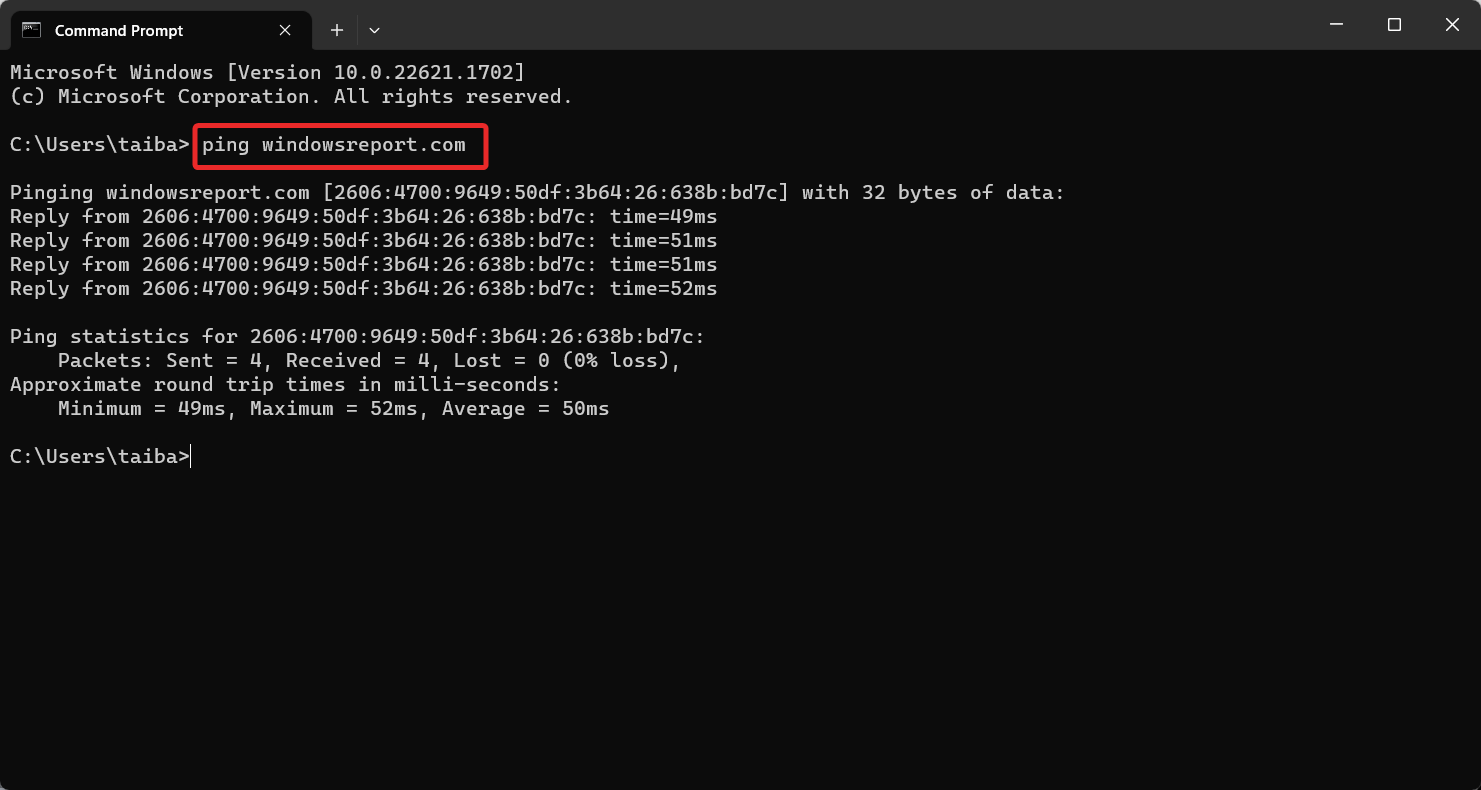
- Type or paste the following command in the command prompt window and press Enter. Replace hostname with the DNS name of a computer with a known IP address:
Ping hostname - If the DNS client can successfully resolve the name, the following message will be displayed on the command prompt window. Pinging hostname [ip_address]
- If the name resolution is not successful, the following error message is displayed.
Ping request could not find host hostname
The DNS client could successfully resolve the name even if the ping command reports that the destination is unreachable.
That’s all! Perform the methods listed in this guide to easily fix the event id 800 triggered by the Microsoft Windows DNS Server Service.
To know more about Event Viewer and identify issues with its help, go through our detailed guide.
For any comments, feedback, and queries, feel free to contact us in the comments section.

User forum
0 messages