OpenGL Driver for Windows: How to Download & Update
Downloading from the manufacturer's website is the best alternative
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- An OpenGL graphics card is a graphics card that supports the OpenGL graphics API.
- Some of the most popular brands include NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel and they vary in price depending on performance and features.
We recognize the need to install the most recent OpenGL drivers to guarantee optimum performance and compatibility.
So that you may use the full capabilities of your graphics hardware, we will guide you step-by-step through installing and upgrading OpenGL drivers on your Windows PC in this article.
What is an OpenGL driver?
The rendering of 2D and 3D computer graphics is made easier by the widely used cross-platform OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) API (Application Programming Interface). It acts as a link between the software programs and the computer’s graphics hardware.
An OpenGL driver is a software component that creates communication between the operating system and your graphics hardware. Sometimes, they are referred to as graphics card drivers or display drivers.
These drivers serve as middlemen. Hence, they allow the software to fully use your graphics card’s capabilities, produce aesthetically spectacular images, and perform quickly.
How do I download an OpenGL driver?
1. Identify your graphics card
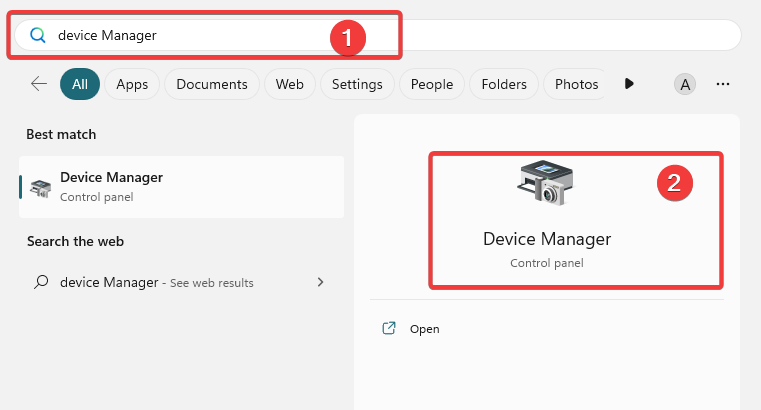
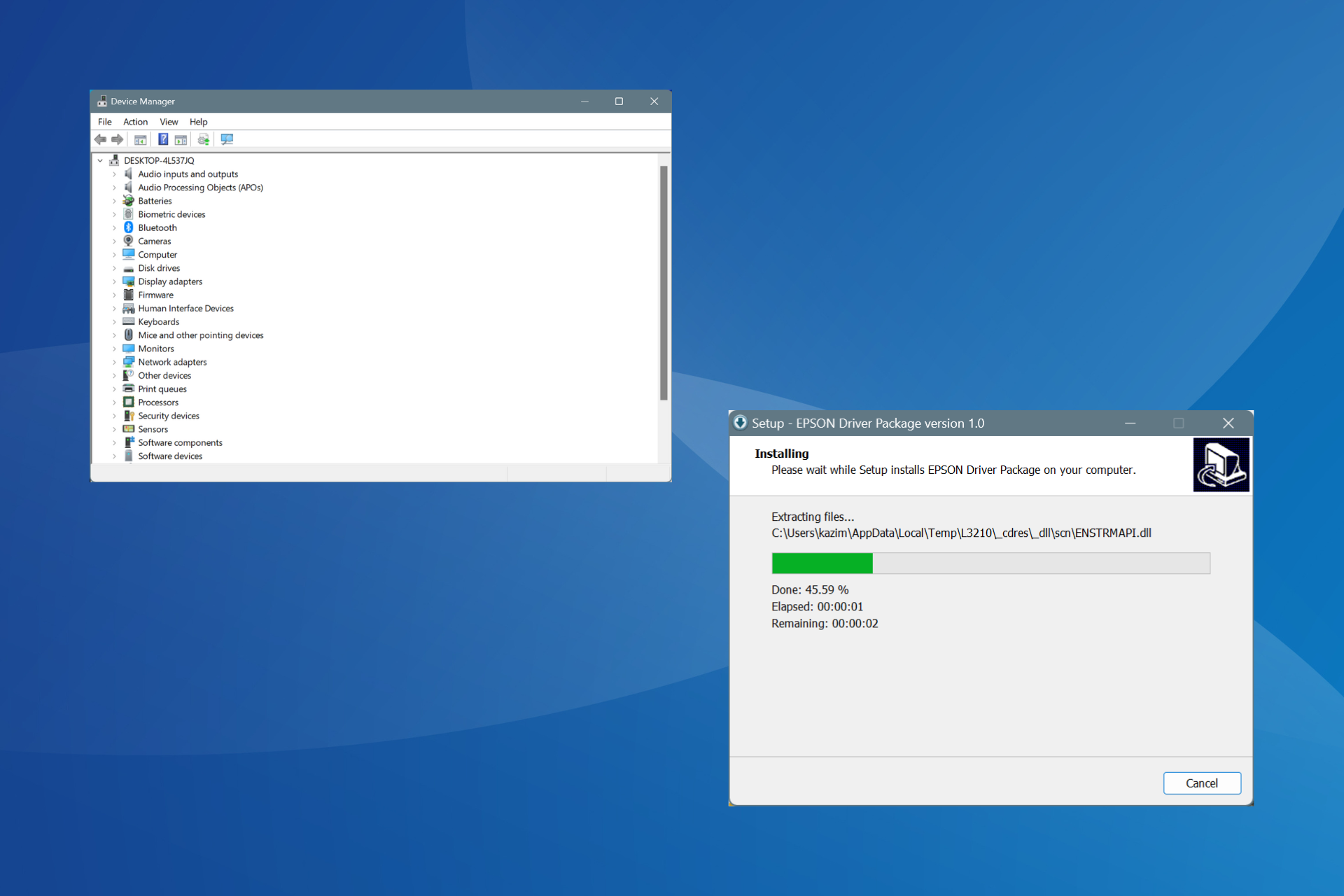
- Press the Windows key to open the Start menu.
- Type Device Manager and select it from the search results.
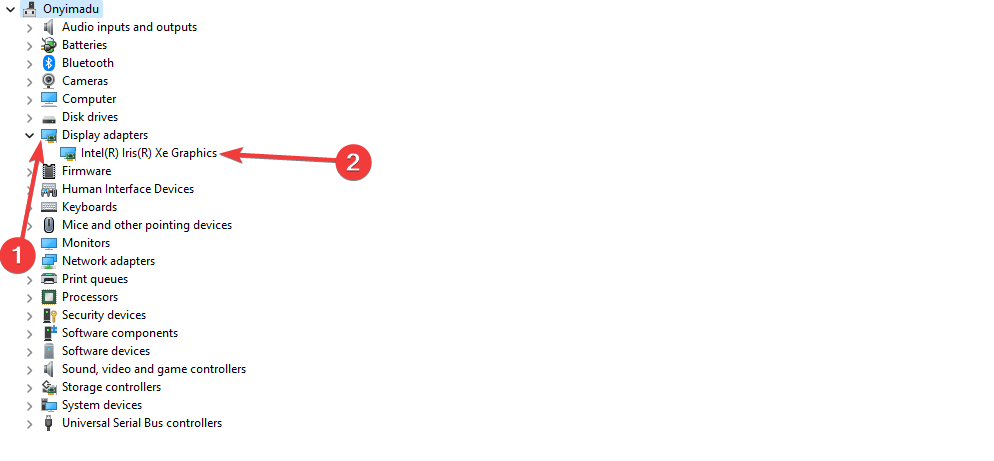
- In the Device Manager window, expand the Display adapters category and double-click on your graphics driver.
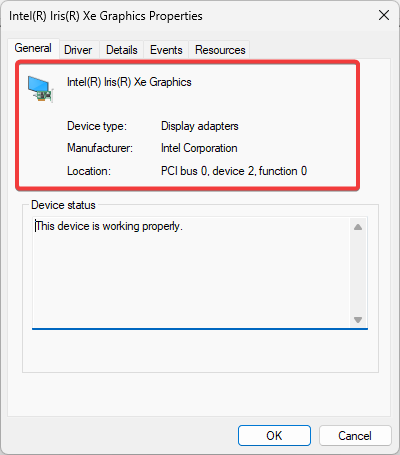
- You will find the name of your graphics card listed here. Lastly, note down the manufacturer and model information.
2. Downloading the driver from the manufacturer site
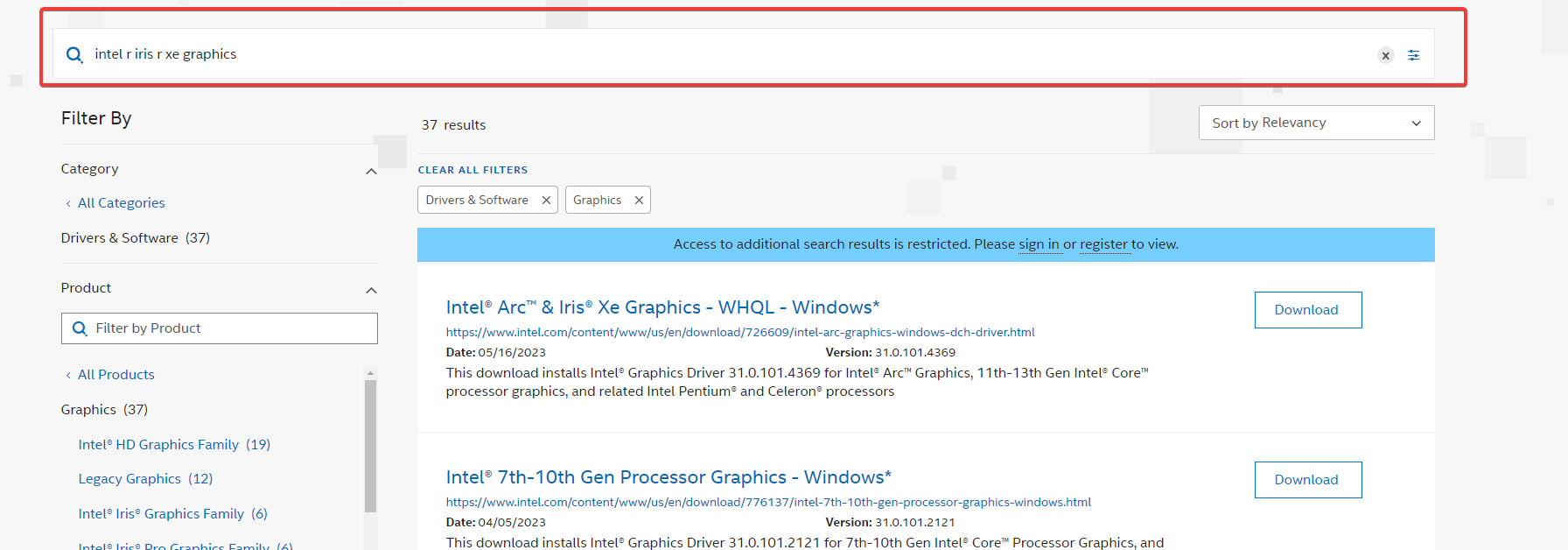
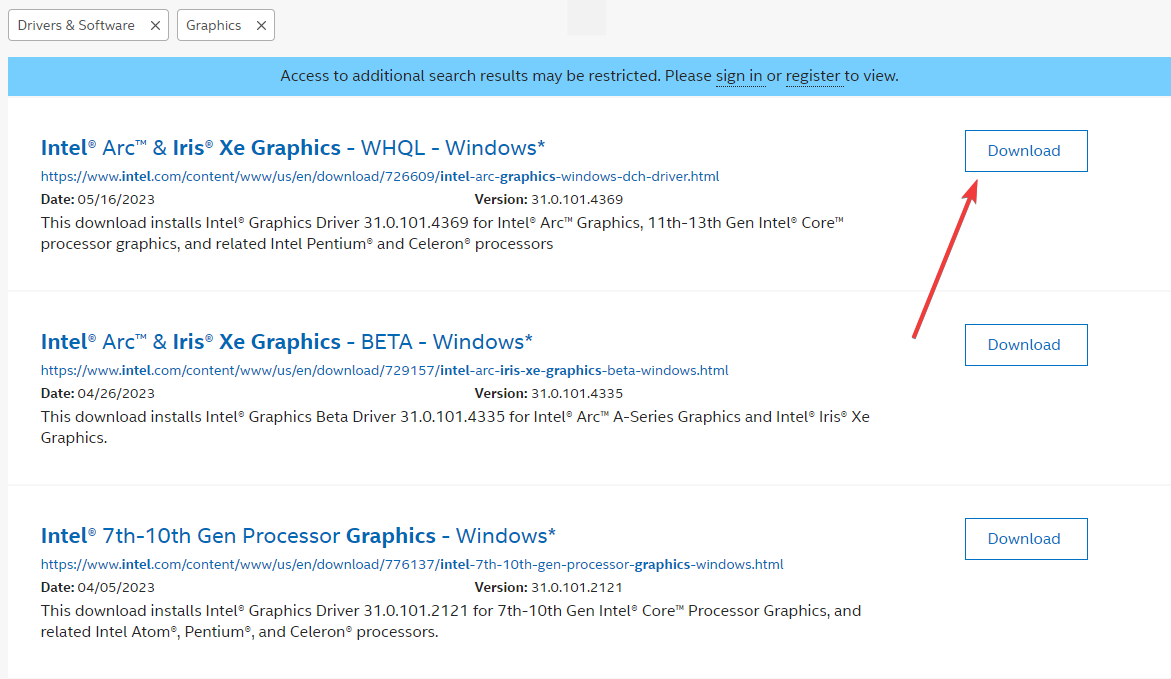
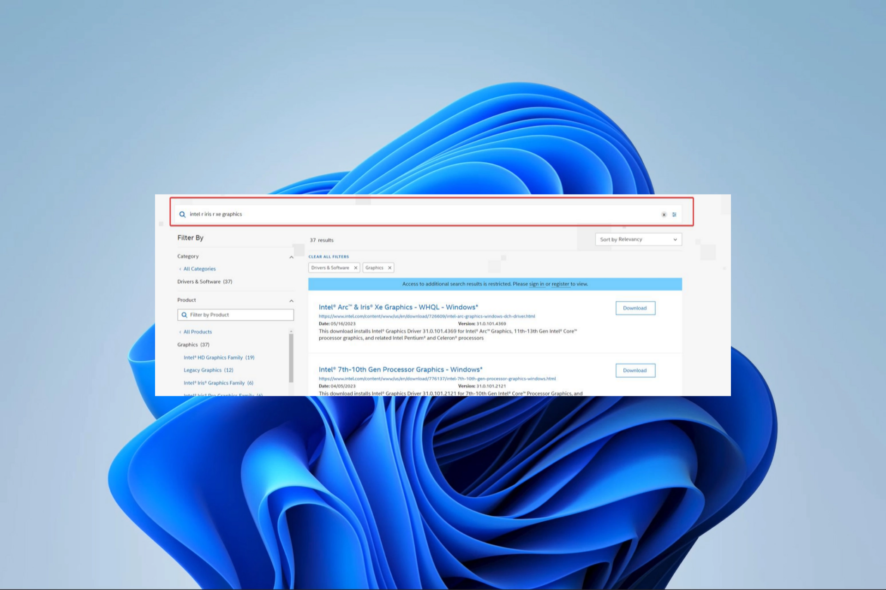
- Navigate to the manufacturer’s website. In this case, we use the Intel website; the process may be slightly different for other manufacturers, like for downloading NVIDIA OpenGL drivers for Windows 11, for example.
- Input your graphics card name from Step 1 in the Search bar and hit Enter.
- Click on the Download button next to your graphics.
- To start the installation, double-click on the driver file. If asked, provide the required authorizations to continue.
- Follow the driver installer’s on-screen instructions. Normally, you’ll have to accept the terms and conditions and decide which installation alternatives to use. Then finally, restart the computer.
How do I update an OpenGL driver?
1. Download the driver from the manufacturer site
To update the driver, you will have to download the most recent version of the driver and install it using the same process mentioned above.
NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, and ATI may all use an OpenGL driver. So, once you know all the information about your graphics card, the process should be straightforward.
Also, the main graphics card manufacturers also have dedicated software for updating the drivers that you can use seamlessly.
However, this process is manual, and you may rather employ a more seamless automatic update process discussed below.
2. Update your Windows 11 drivers automatically
Managing all your drivers can be made simple with dedicated driver update software. You can easily select outdated drivers individually or all at once. Additionally, you can automatically repair broken drivers or find missing ones quickly.
Outbyte Driver Updater is a great option because it is secure and will enhance your PC performance.
If you have read thus far, you should have successfully downloaded or updated your OpenGL drivers. So, this is as much as we cover in this article.
We love to hear from you in the comments section below. Please let us know if this process was as easy for your driver manufacturer.