Fix the CPU Throttling on a Laptop: 3 Quick Solutions
Adjusting the power plan may fix the issue temporarily
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- CPU throttling on your laptop occurs if your device exceeds the normal working temperature.
- One way to fix this issue is to change your power settings and disable throttling completely.
- Alternatively, be sure to check your PC temperature, and clean it from dust if needed.
To achieve maximum performance on your laptop, it must have proper cooling. This is especially important if you’re performing resource-intensive tasks.
If, for some reason, you can’t achieve this, the performance of your laptop will be affected to prevent overheating and damage to your PC.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to fix CPU throttling on your laptop and make it snappy again.
What causes CPU throttling?
High temperature is the leading cause of CPU throttling. When you’re performing intensive tasks, your hardware generates more heat.
To prevent overheating and damage, your computer reduces the performance of your processor. Doing so will make your PC slower, but it won’t overheat and will remain stable.
How can I fix the high CPU temperature?
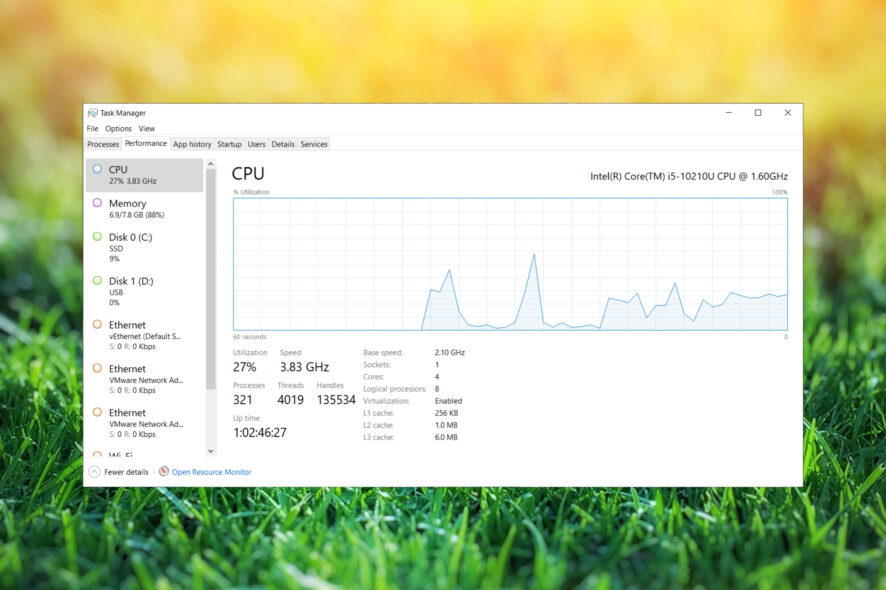
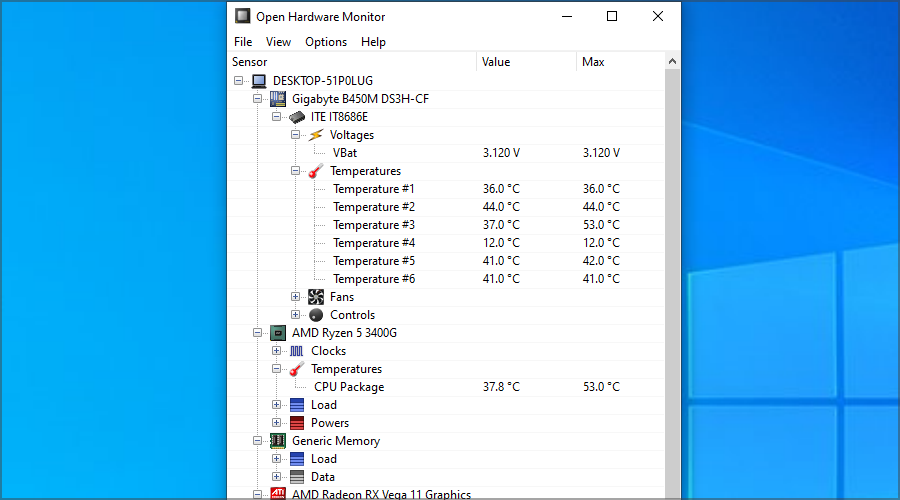
Usually, the processor is causing the most heat, so we recommend using CPU monitoring software to check PC temperature.
If you notice unusual values, try cleaning the laptop air vents with pressurized air. If your device isn’t under warranty, open it and clear the dust and the heatsink.
You can also replace the thermal paste on the CPU while you’re at it. This is a highly technical procedure, and you can damage your laptop if you’re not careful, so use extra caution or contact an expert.
How can I fix CPU throttling on a laptop?
1. Change the power plan
1.1 Change the power plan mode
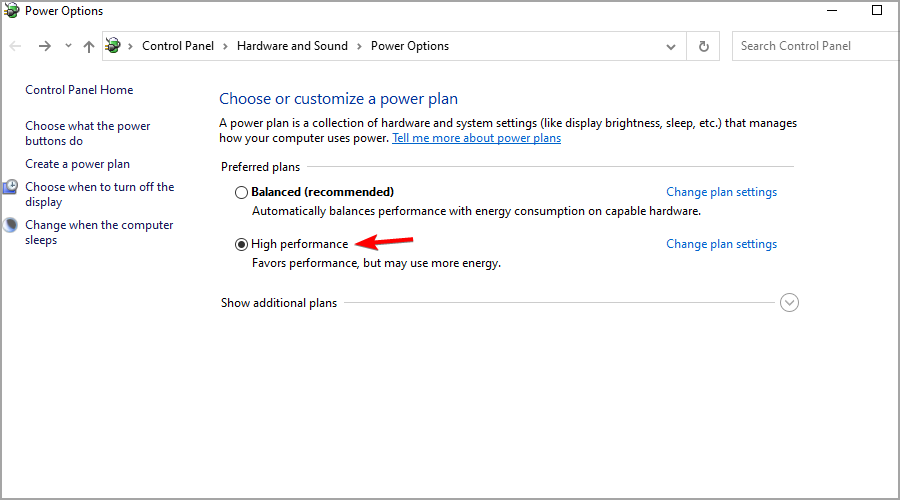
- Press Windows Key + S and enter power plan. Select Choose a power plan from the list of results.
- The Power Options window will now appear.
- Select High performance from the list of power plans.
Keep in mind that changing the power plan to High performance will drain your battery faster.
1.2 Adjust the power plan settings
- Use Windows Key + S shortcut to open the search.
- Now enter power plan and select Choose a power plan.
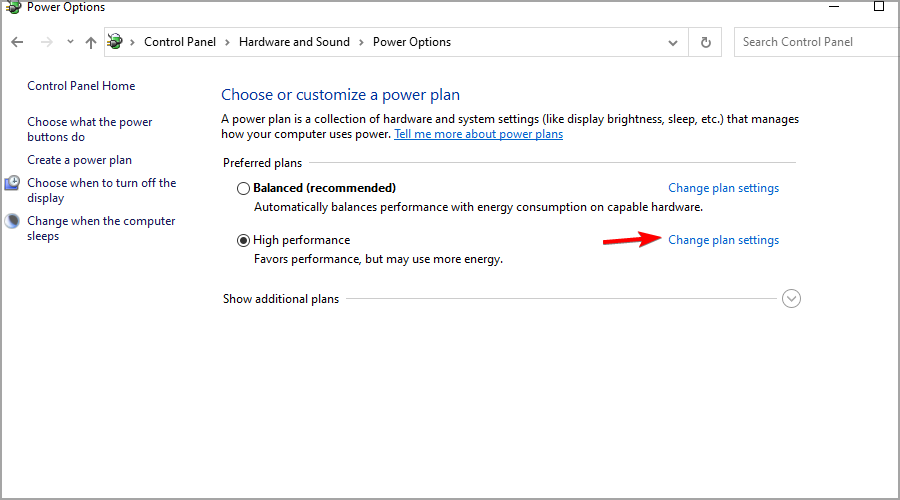
- Locate your currently selected plan and click on Change plan settings.
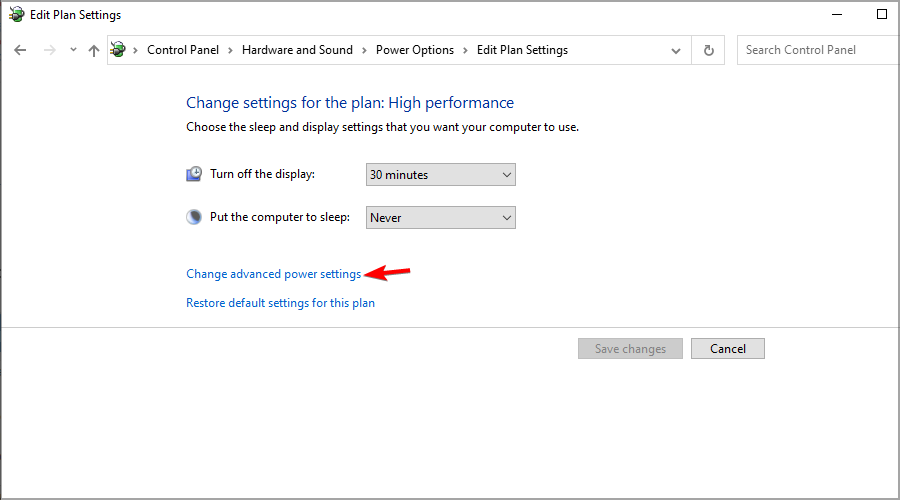
- Navigate to Change advanced power settings.
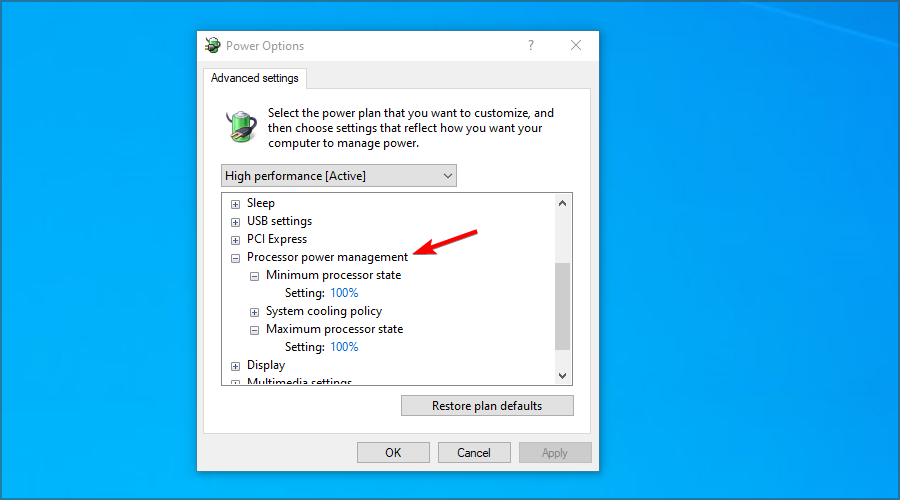
- Now expand the Processor power management section.
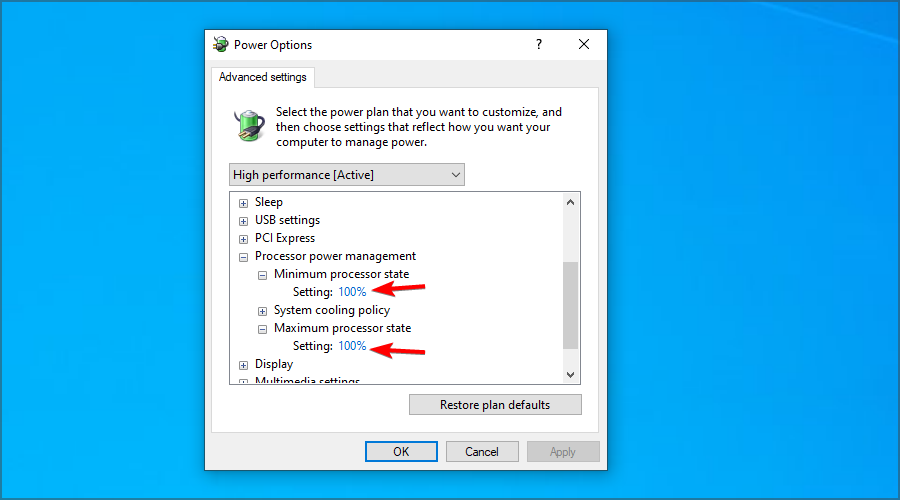
- Set Minimum processor state and Maximum processor state to 100% for both On battery and Plugged in.
- Click Apply and OK to save changes.
Some of our readers reported that setting the processor state to 99% instead of 100% fixed the problem for them, so try that as well.
2. Use the Group Policy Editor
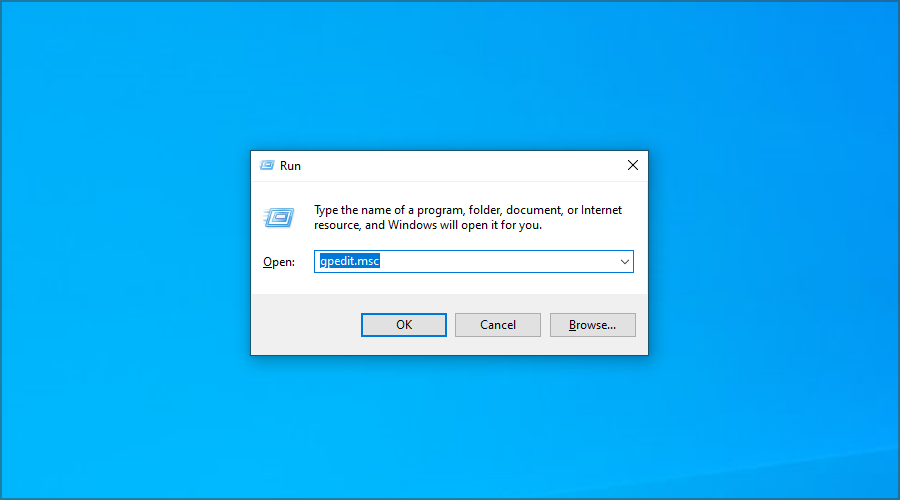
- Press Windows Key + R and enter gpedit.msc. Press Enter.
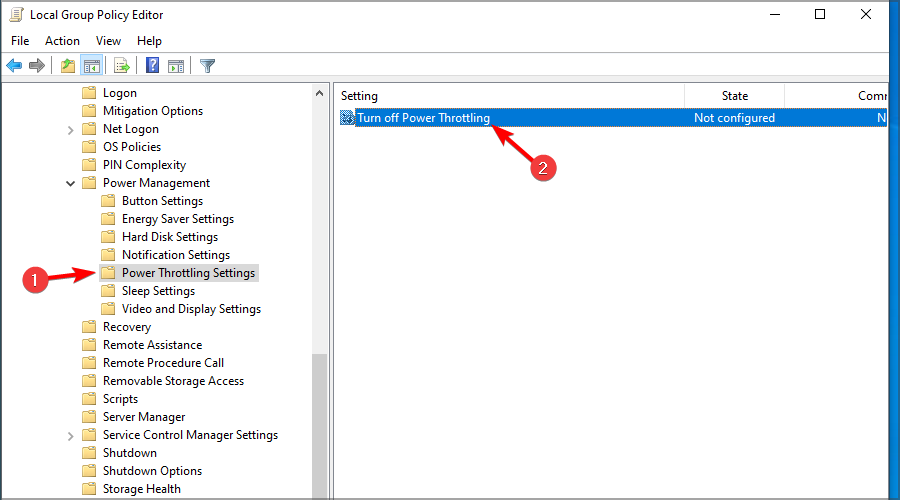
- In the left pane, expand Administrative Templates in the Computer Configuration. Now choose System. Head over to the Power Management and select Power Throttling Settings. In the left pane, double-click Turn off Power Throttling.
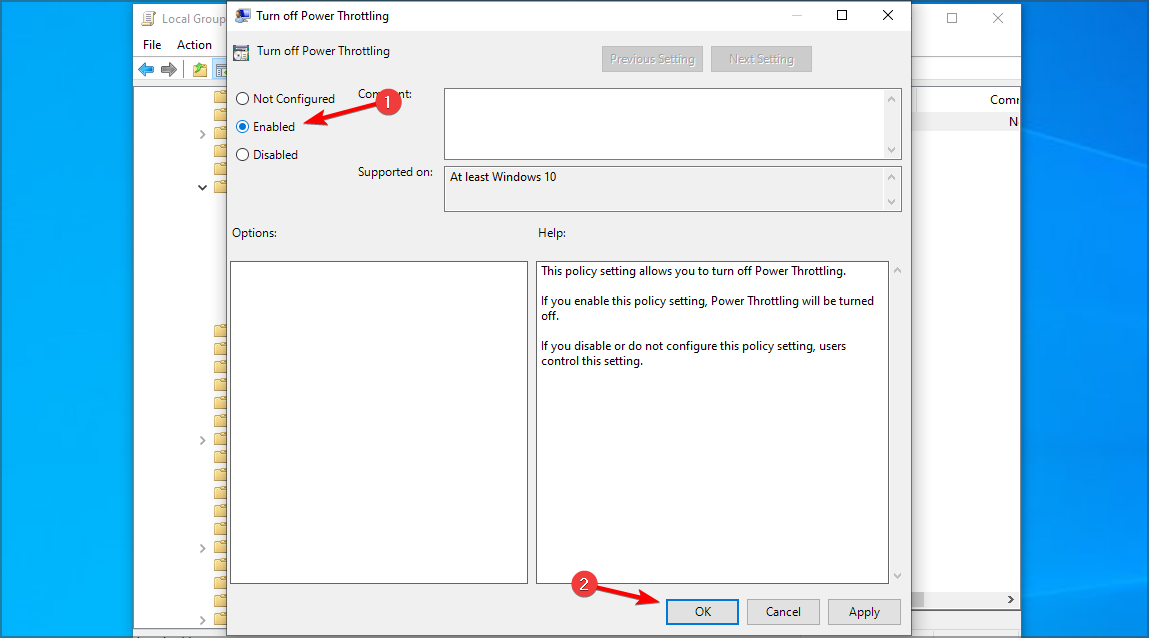
- Set it to Enabled and click on Apply and OK to save changes.
3. Use the Registry Editor
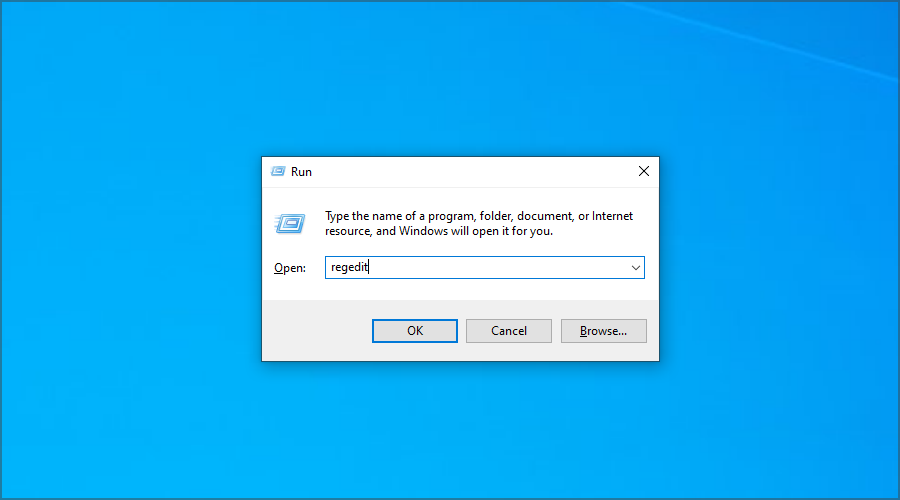
- Press Windows Key + R and enter regedit. Press Enter.
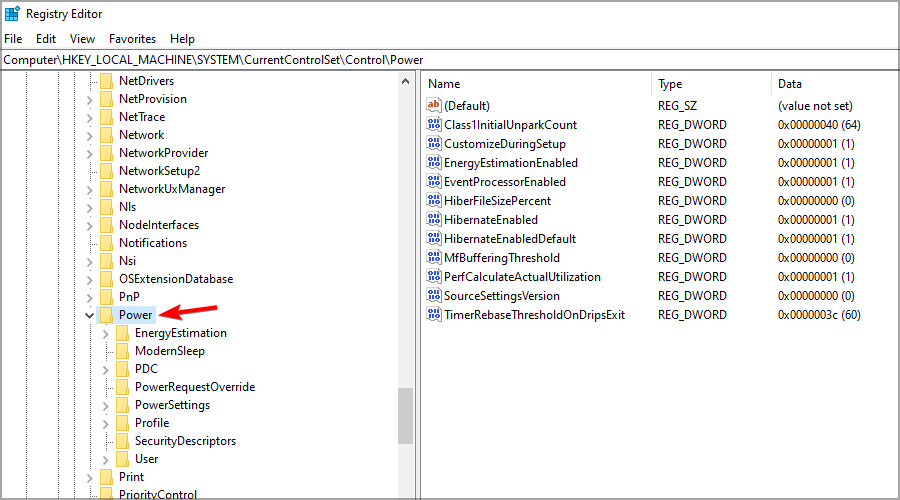
- Navigate to the following path in the left pane:
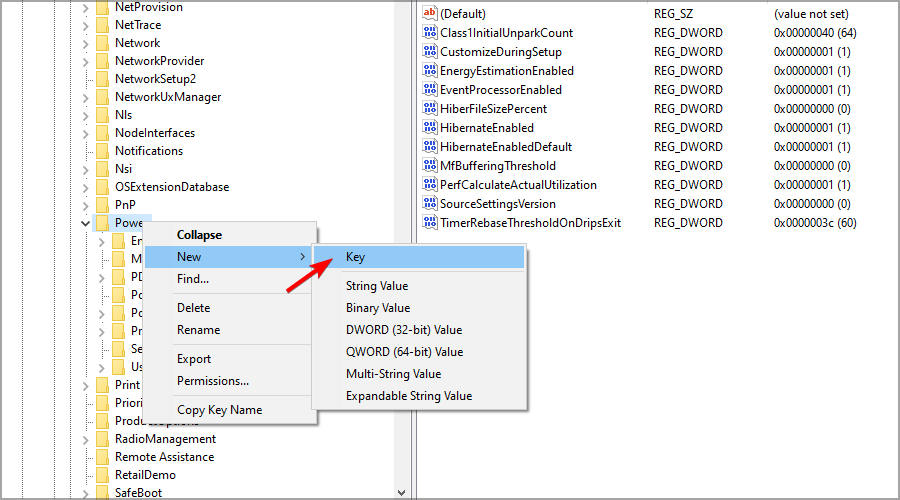
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power - Right-click the Power key. Expand the New section and select Key. Enter PowerThrottling as the name of the new key.
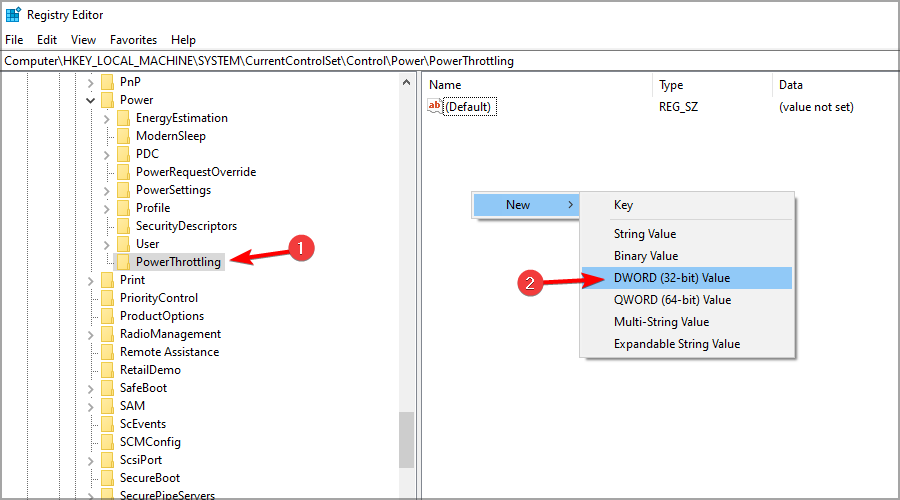
- Go to the PowerThrottling key. Right-click the right pane, expand the New section, and click on DWORD (32-bit) Value.
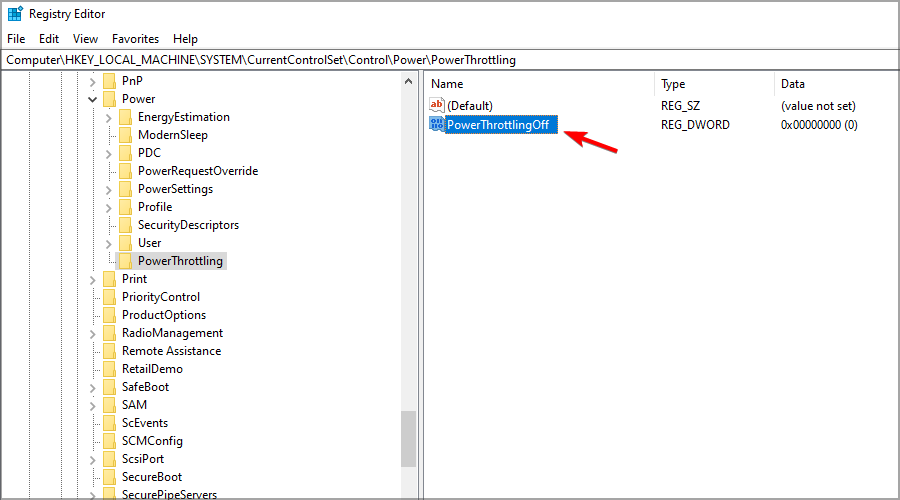
- Set the name of the new DWORD to PowerThrottlingOff. Now double-click the DWORD to see its settings.
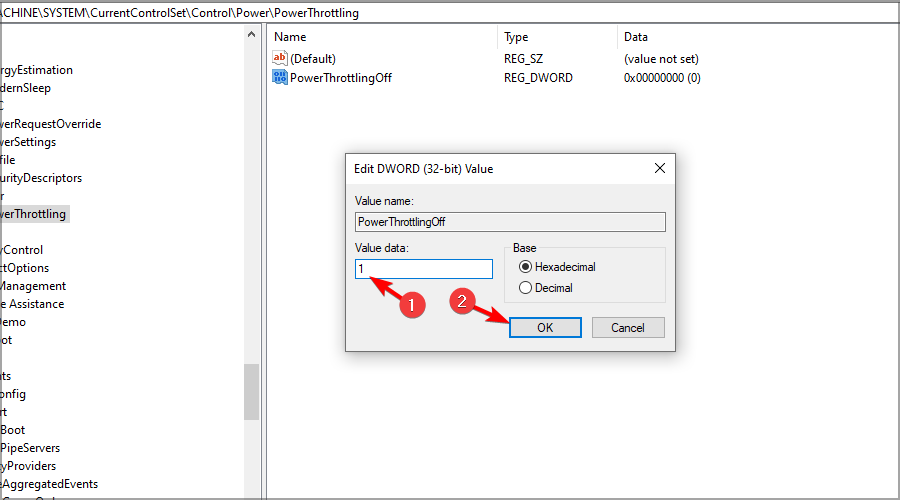
- Set the Value data to 1 and click on OK.
How do I check which processes are being throttled?
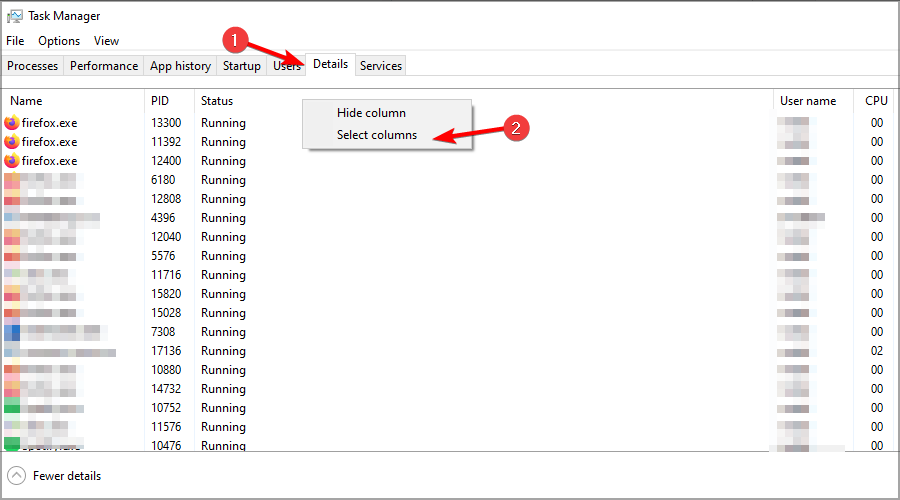
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to start Task Manager.
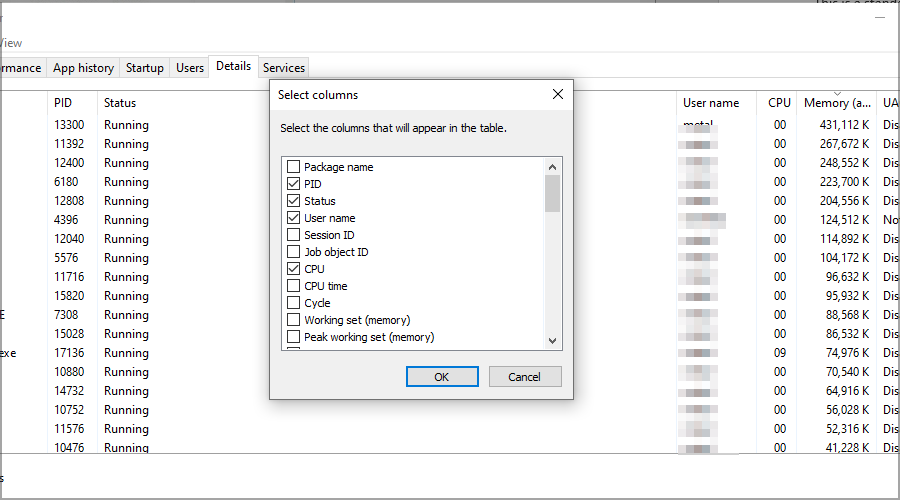
- Navigate to the Details tab. Now right-click any of the columns and choose Select columns.
- Select Power Throttling and click on OK.
- Now you should have a new Power throttling column showing all the applications being affected.
What is the normal temperature for a laptop?
Laptops are designed to handle high temperatures, and any CPU temperature below 60 C or 140 F is perfectly normal for a laptop.
If you’re performing intensive tasks, expect values up to 70 C or 160 F. Regarding the GPU, the optimal is 45 C or 110 F if you’re using it normally.
However, your graphics card can reach 80 C or 175 F if you use your device under a full load. If you’re having any issues with overheating, using a laptop cooling pad might help.
CPU throttling can be a problem and negatively impact your performance, but we hope this guide helps you fix this issue on your laptop.
Many users reported that their laptop shuts down when overheating, and if you’re having such problems, check your device temperature.
Are you having any issues with your laptop performance? Share your experiences and solutions in the comments section below.




User forum
0 messages