Gpedit.msc vs. Secpol.msc: What is the Difference?
Gpedit.msc is for configuration of group policies & secpol.msc is for a single device
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more

Gpedit.msc and Secpol.msc configure system policies and security settings, respectively. However, they serve distinct purposes and are used for different aspects of Windows management. Let’s learn more about the distinctions between gpedit.msc vs. secpol.msc.
Gpedit.msc vs. Secpol.msc: What is the difference?
What is gpedit.msc?

Gpedit.msc, or Group Policy Editor, is a Windows tool for managing group policies within a Windows environment. Group policies are set of rules that administrators apply to users and computers in a network to change security settings, system behavior, and more.
Main functions of gpedit.msc:
- Allows IT admins to define and enforce group policies across multiple devices in a domain.
- Provides better control over Windows settings, including software installation policies and system maintenance schedules.
- Centralized console for configuring policies, which can be then distributed to client machines within the network.
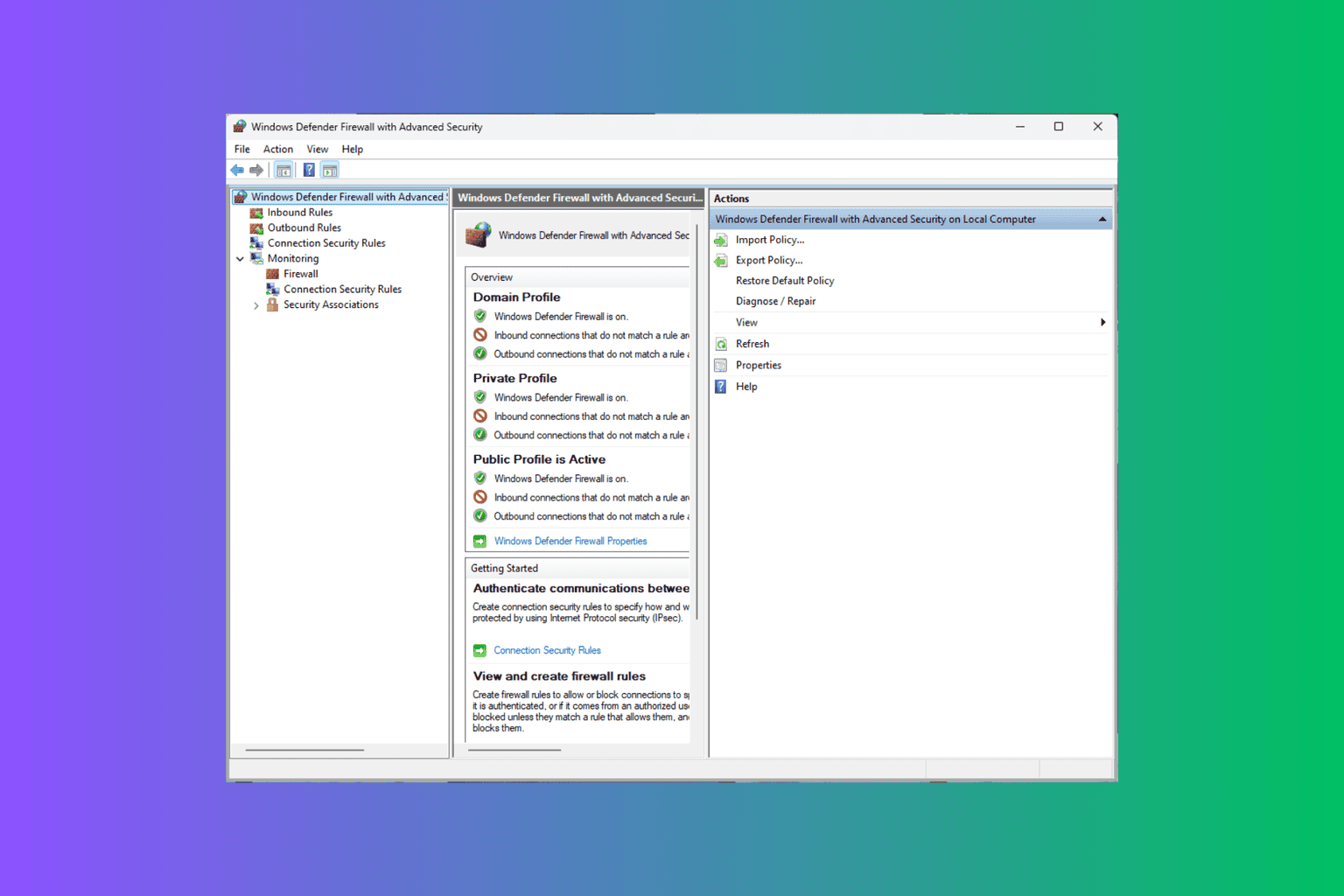
What is secpol.msc?

Secpol.msc or Local Security Policy only focuses on the security settings of the local machine and is usually for standalone PCs or non-domain-joined systems.
Main functions of Secpol.msc:
- Enables IT professionals to configure security settings, such as audit policies, account policies, user rights, and other security options specific to a local machine.
- Allows you to import and apply the security templates to streamline the configuration of security settings across multiple machines.
- Comes with tools for auditing security events and monitoring compliance with security policies at the local level.
Gpedit.msc vs. Secpol.msc: Quick comparison
| Feature / Tool | gpedit.msc | secpol.msc |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manages group policies across network domains. | Manages security settings on a standalone/local machine. |
| Scope | Network-wide policy management | Local machine security configuration |
| Administrative Access | You need admin rights and domain controller access. | You need local admin rights on the computer. |
| Configuration | Configures group policies that can be applied to multiple users/computers. | Configures security settings for a local machine. |
| Security Settings | It mainly relies on predefined policies and has a limited focus on security settings. | It comes with significant control over security settings at the local level. |
| Usage Scenario | It is suitable for managing uniform policies across large networks or domains | Allows you to customize security settings on standalone or non-domain-joined computers. |
1. Objective
Group Policy Editor lets you manage group policies within a network domain. It is a centralized tool for admins to define and enforce policies across multiple users.
Security Policy Editor lets you configure the security settings of a local machine and is usually employed on standalone computers.
2. Scope
Group Policy Editor or gpedit.msc focuses on network-wide policy management, which ensures consistency in settings, including system behavior and security options across all devices in the domain.
The Security Policy Editor, or Secpol.msc, allows you to customize security settings for a local machine, ensuring the security configurations meet a PC’s specific requirements.
3. Administrative Access
IT admins need administrative rights and access to domain controllers to use the Group Policy Editor and change policies that affect users and computers within the network.
To access Security Policy Editor, you need local administrative rights on the computer on which you have to configure and manage the security settings.
4. Configuration
Group Policy Editor or gpedit.msc lets admins manage and configure various policies, including software installation restrictions, user permissions, and system maintenance schedules.
Whereas Security Policy Editor or Secpol.msc allows IT admins to set local security policies, including password requirements, logging settings, and user permissions on a device.
5. Usage scenarios
Group Policy Editor is useful for IT admins to manage policies across large networks or domains, ensuring consistency and uniformity with organization policies.
On the other hand, secpol.msc works for admins to manage security configurations on one machine or small networks, where there is no need for a centralized policy.
To conclude, both the Security Policy Editor and the Group Policy Editor have important roles in security and Windows management, but their focus and usage differ.
If you have Windows 10 or 11 Home Edition and want to install Group Policy Editor, we have a separate guide.
However, if you have the Professional Edition of Windows and still can’t find Gpedit.msc, then you need to follow the steps mentioned in this guide.
On the other hand, if you can’t find secpol.msc on your Windows 11, you can follow these simple methods to add it to your OS.
If you want to learn more, we have a great guide on how to use gpedit.msc on Server Core, so don’t miss it.
Do you have any confusion about gpedit.msc vs. secpol.msc? Mention them in the comments section below, and we will try to answer them.


User forum
0 messages