How to Fix DNS Client Event 1014 & What Does it Mean
Disabling an important workflow feature can solve this problem
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
The DNS Client event 1014 is an error message that appears when a configured DNS server (Domain Name System) fails to respond to your Windows computer. More specifically, the network connection timed out. When this occurs, the computer creates an event log detailing everything, but you’ll need a log viewer to read it.
Before going into the more complex solutions, try changing the power plan to a performance one, and perform a clean boot. Of course, also check your router and cables for any issues.
How do I fix the 1014 error on my Windows computer?
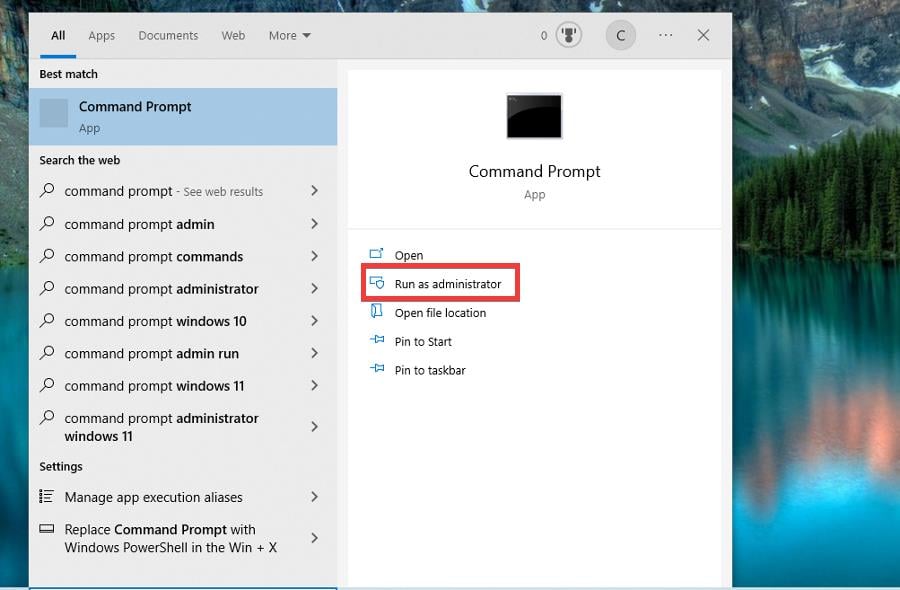
1. Disable TCP Offload
- On your Windows computer, search for the Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- In the window that appears, select Yes.
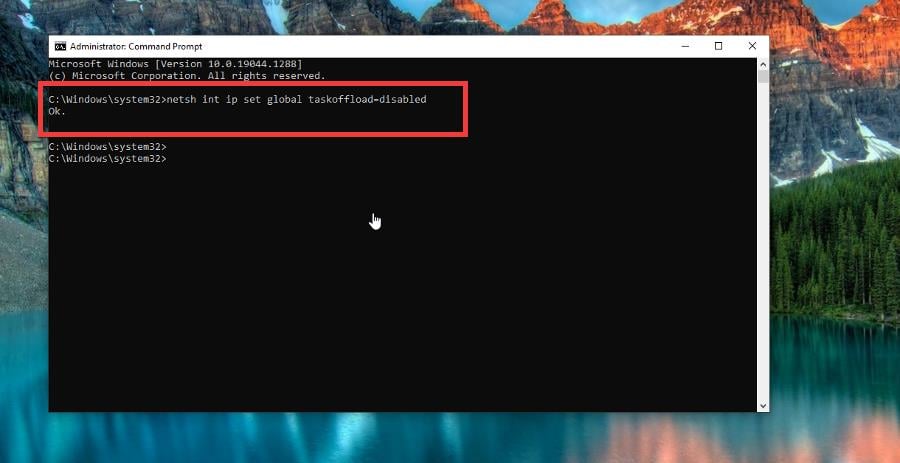
- Type the following command:
netsh int ip set global taskoffload=disabled. And hit the Enter key when you’re finished. - Command Prompt will simply say Ok to indicate Offload has been disabled.
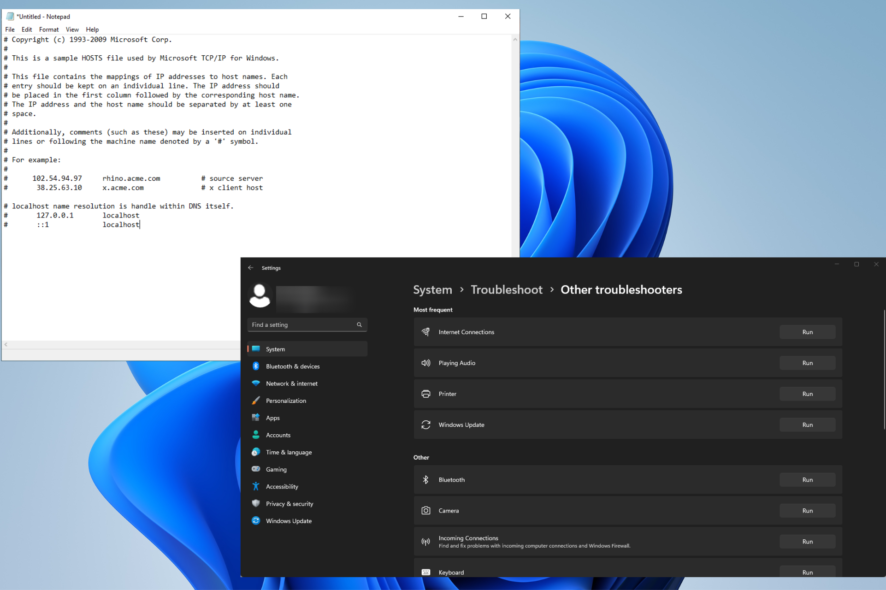
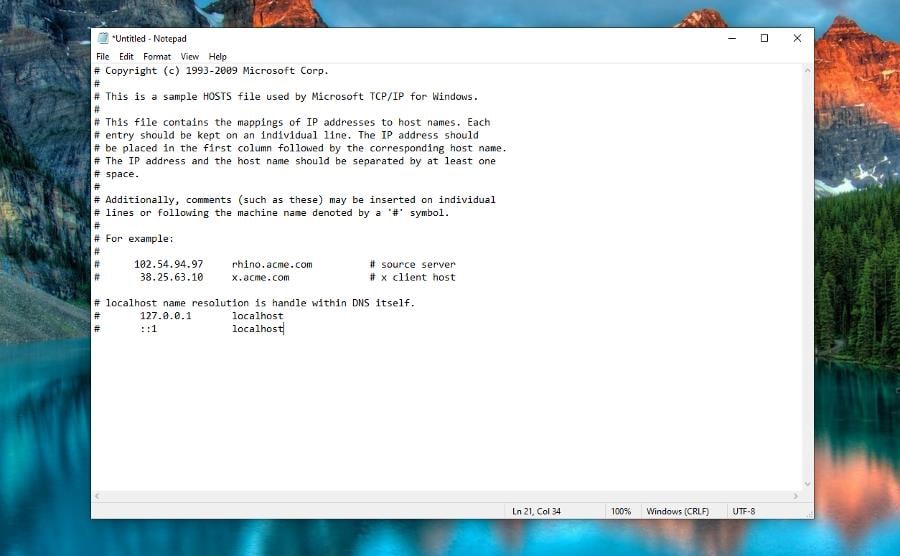
2. Reset the Hosts file to default
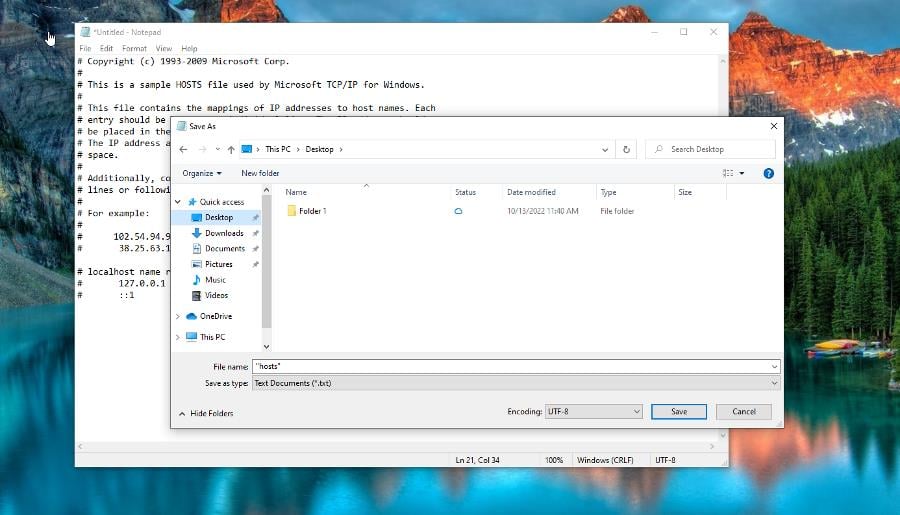
- On your Windows computer, open Notepad and enter the text you see in the image into the app.
- Select File, then Save As.
- Go to Desktop, name the file as “hosts” (make sure the quotes are included) and click Save.
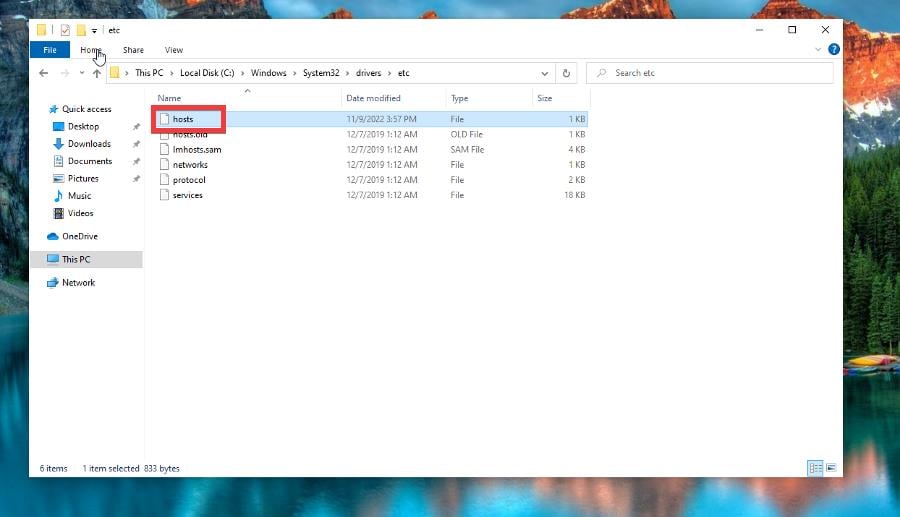
- Close Notepad and open File Explorer.
- Go to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc.
- Right-click the hosts file and rename it as hosts.old. The User Account Control may appear asking if you want to make changes. Click Yes.
- Drag and drop the new hosts file from the desktop to the folder. Click Continue if you need to provide administrator permission.
- Close File Explorer and you’re done.
3. Disable Cortana and Search
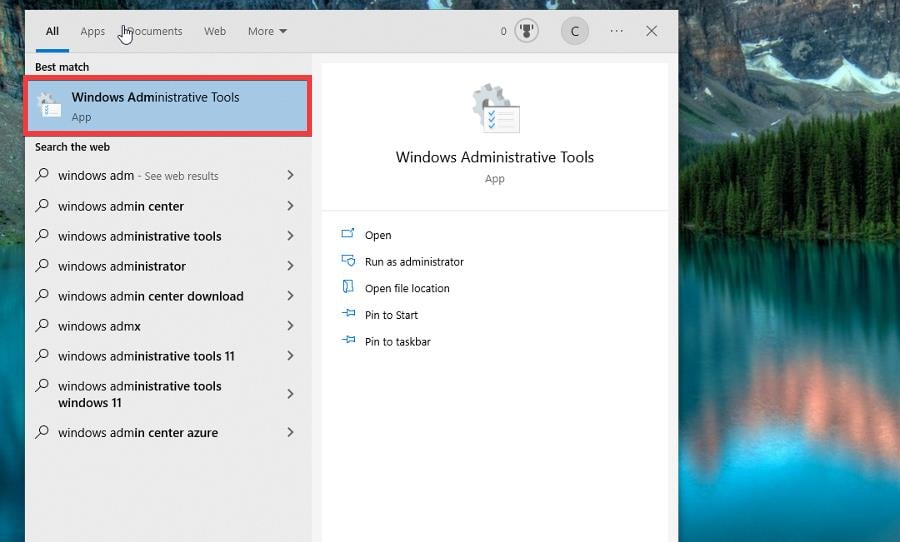
- In the Search bar, bring up Windows Administrative Tools. Select the entry that appears.
- Open the Registry Editor in the Administrative Tools folder.
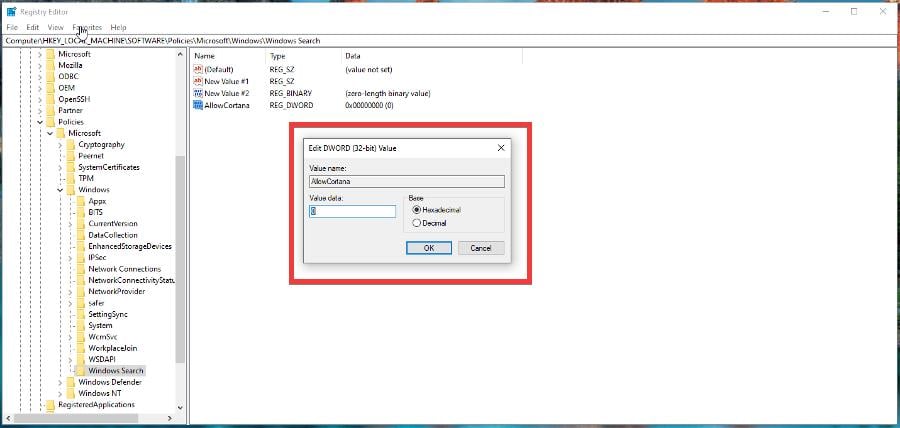
- In the top bar, type in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Search.
- Right-click AllowCortana and select Modify. Set the value data to 0 and click OK.
- Do the same thing to DisableWebSearch.
If you get a log viewer and read a 1014 log, you may see “t-ring-fallback.msedge.net”. It looks like this relates to Microsoft Edge, but it doesn’t. It more closely relates to Search and Cortana.
After disabling those two, check if the 1014 error is gone.
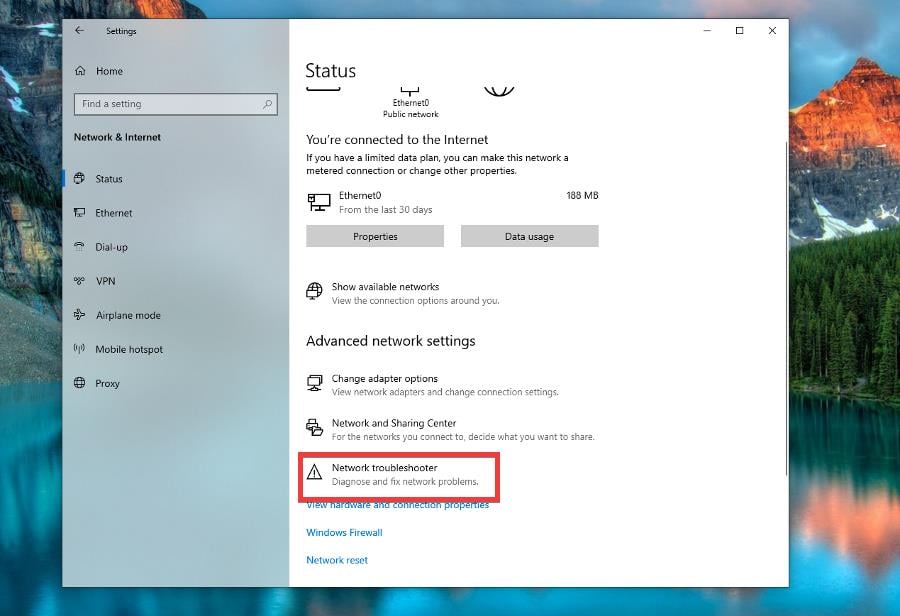
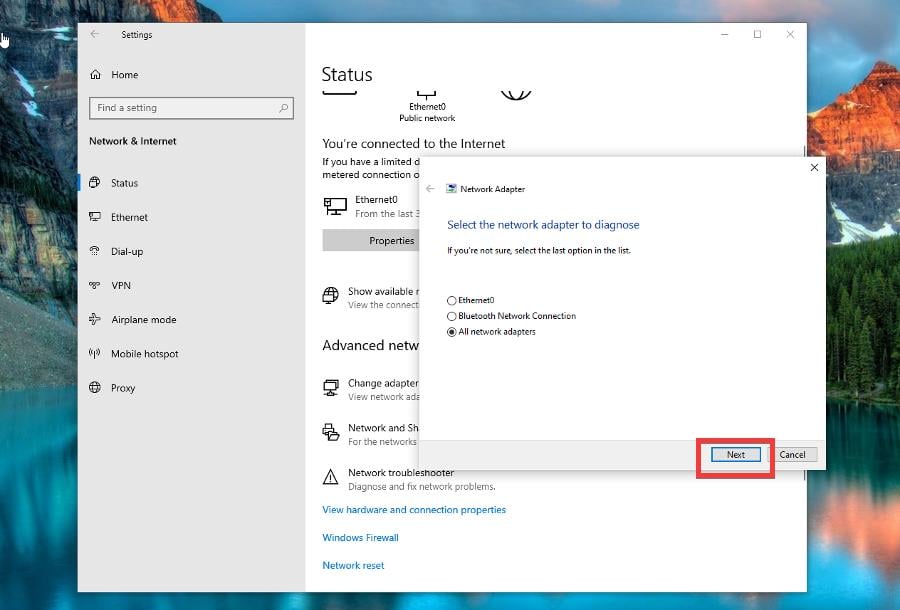
4. Fix Wi-Fi connection issues
- On Windows 10, open the Settings app, click Network & Internet, then Status on the left-hand side.
- Select Network troubleshooter.
- Select which network adapter you want to diagnose. Click Next.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to solve the problem.
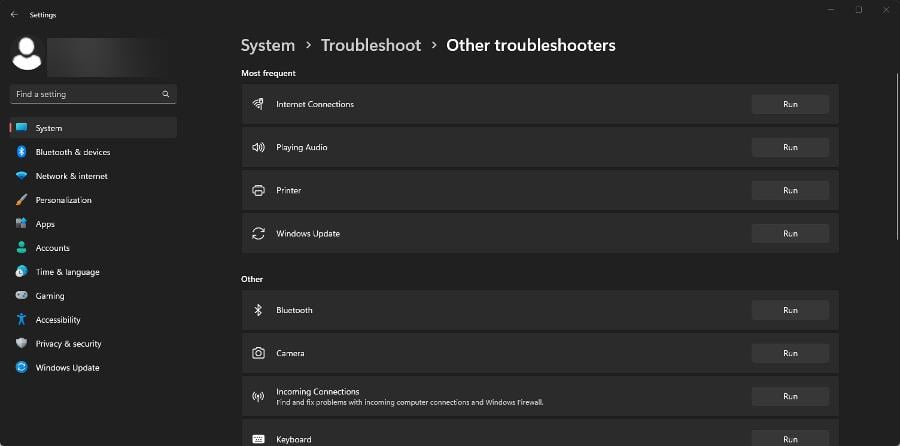
- On Windows 11, open the Settings app, select System on the left-hand side, and click Troubleshoot.
- Select Other troubleshooters. Click Run next to Internet Connections as well as any other problematic areas. Follow the direction on the screen to fix the 1014 problem.
What causes Event ID 1014 to appear on my Windows computer?
According to an old Microsoft TechNet post from 2011, there are four main reasons why this error appears. From those four, we’ll point out the more likely culprits and add some of our own.
- The TCP/IP Offload has been enabled on a network adapter. This is a technology that offsets CPU processing to the adapter and frees up the CPU so it can do another task, but can cause problems.
- Your router and PC are on different Wi-Fi channels. Admittedly, this problem is pretty rare since modern routers will change automatically but older models might not.
- Your computer’s drivers are out of date and it’s important that you update them as soon as possible.
- There’s some kind of problem with your router and we recommend performing a power cycle. We have a guide on a similar 1014 error with instructions on how to safely power cycle.
- Your internet service provider (ISP) is dealing with an outage. If this is the case, there’s nothing you can do but wait until your ISP fixes the problem.
Are there other Event ID errors that I should know about?
There are two particular Event ID errors that are particularly notorious. The first is Event ID 7000 which occurs a service on your computer doesn’t have the right credentials to run.
This is the result of an error with the Service Control Manager and has different variations of it like 7023. Solutions include restarting the offending service and using the Group Policy Editor to make adjustments.
The other error is Event ID 1000 which causes software to suddenly close. Culprits for this error involve malware and old versions of Windows OS.
To fix Error 1000, we recommend updating your drivers, reinstalling the problematic app, or performing a clean boot.
Feel free to comment below if you have any questions about all of these Event ID errors. Also, leave comments about what reviews you’d like to see or information on other Windows software.




User forum
1 messages