How to Change BIOS Settings on Windows 11 [Easy Steps]
Hardware settings can only be changed from BIOS
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- To change BIOS settings on Windows 11, you need to hold the designated key while your PC boots.
- You can do that from the Recovery options in the Settings app on your PC.
- To enable AMD TPM on Windows 11, you need to access the firmware settings and change a few security options.
- Read our article to find out exactly how to do these things.
Changing your settings is sometimes necessary to ensure that your PC is working properly, and most settings can be adjusted from the built-in settings apps.
However, many hardware settings are inaccessible from the desktop, and the only way to access them is to enter BIOS and modify them from there.
Windows 11 didn’t change the modality to reach BIOS, and it’s almost the same as on the previous versions of the OS.
If you want to know how to change BIOS settings on Windows 11, then be sure to keep reading to find the best ways to do it.
What does BIOS do?
BIOS is a chip on your motherboard with motherboard firmware and settings stored on it, and it’s in charge of initializing your hardware during the boot and starting the boot loader.
Besides the initialization, it is also used to configure your hardware, system, security, and boot settings. In addition, you can use it to overclock your hardware or discover the best BIOS settings for gaming.
To learn more, we suggest visiting our what is BIOS article for more in-depth information.
How does BIOS work?
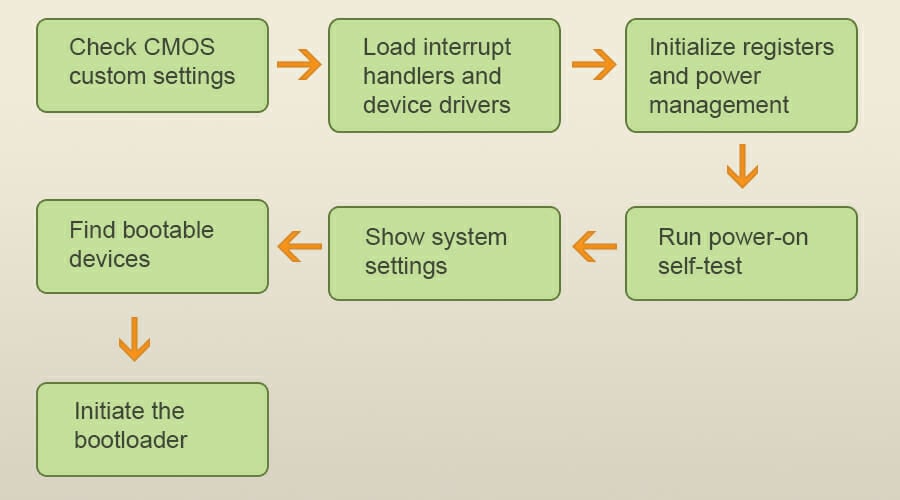
When you press the Power button on your PC, the first thing that BIOS does is check the CMOS for custom settings.
Next, it loads the interrupt handlers and device drivers and initializes registers and power management.
After that, it performs a power-on self-test and checks if the required hardware works properly. If everything is in order, you’ll see your system settings, and BIOS will determine if bootable devices are available.
Once the bootable device is found, the booting sequence will initiate and start your operating system.
How can I change BIOS settings on Windows 11?
1. Access BIOS using the shortcut key during the booting process
This is the easiest way to access BIOS, but it’s not universal. Some motherboards use a different key, and you can do two things to find the right key.
- During the boot, look for the message saying Press Key to enter setup or any similar message. In most cases, pressing this key will allow you to enter BIOS.
- Check your motherboard manual and find the shortcut key.
2. Enter BIOS using the Settings app
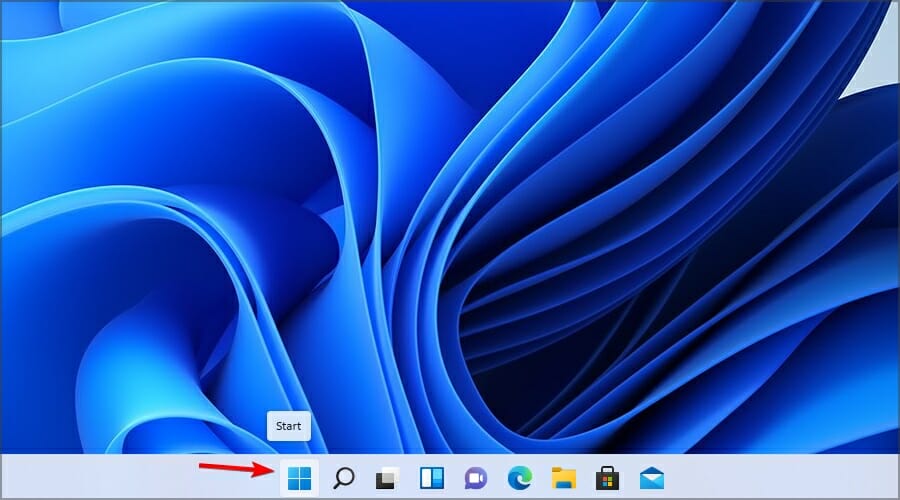
1. Click the Start icon in the Taskbar.
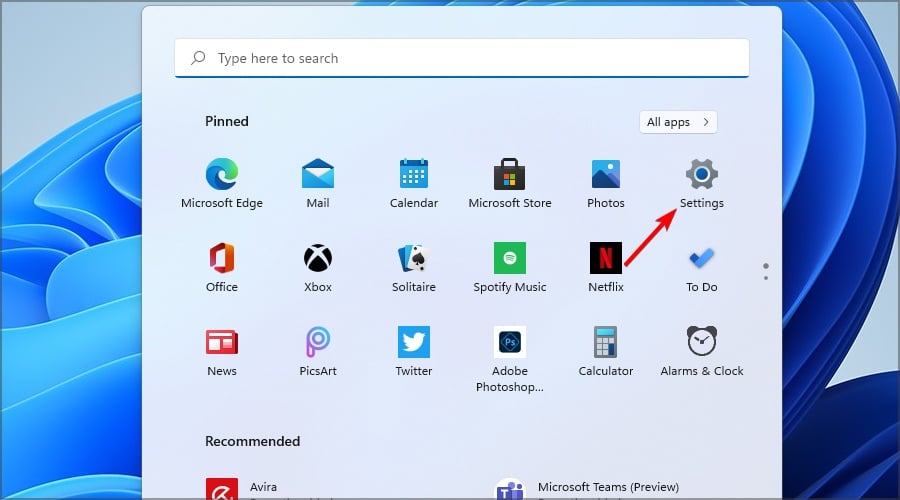
2. Now select the Settings app from the menu that opened.
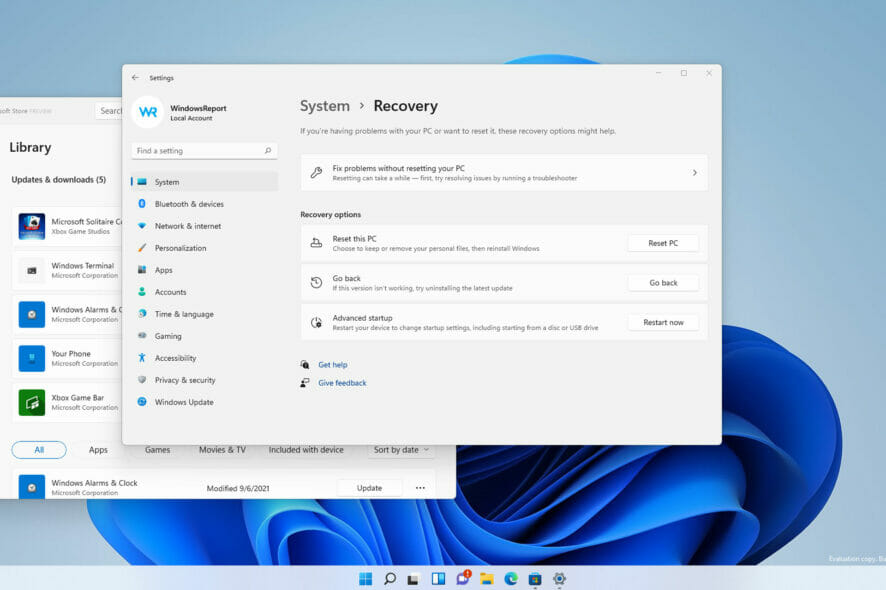
3. Go to the Recovery options.
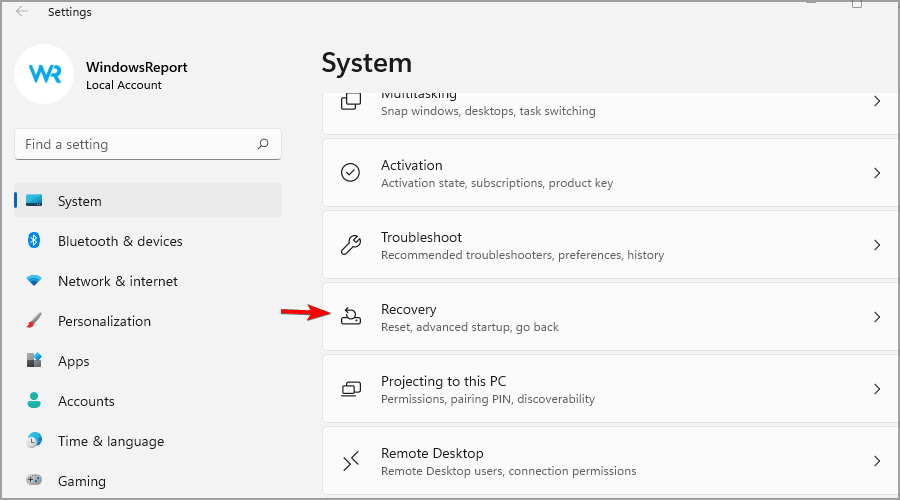
4. In the Advanced startup section, click on Restart now.
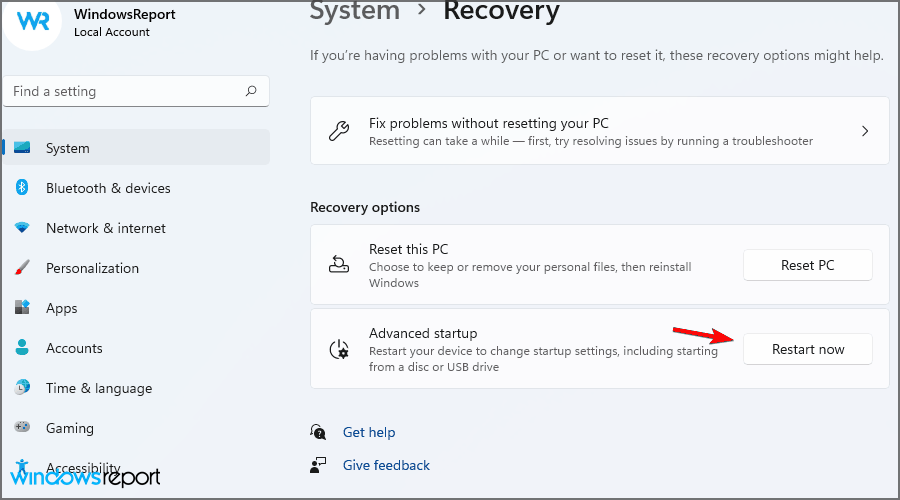
5. Select Restart now to confirm.
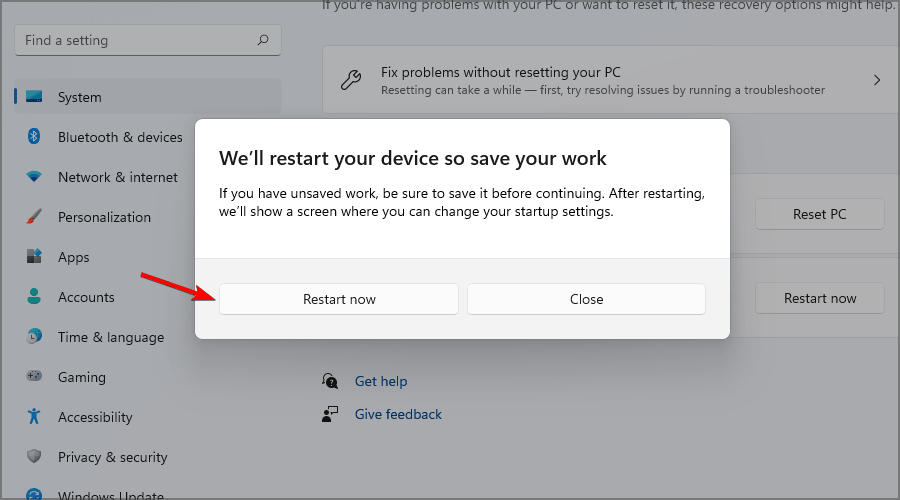
6. Go to the Troubleshoot center.
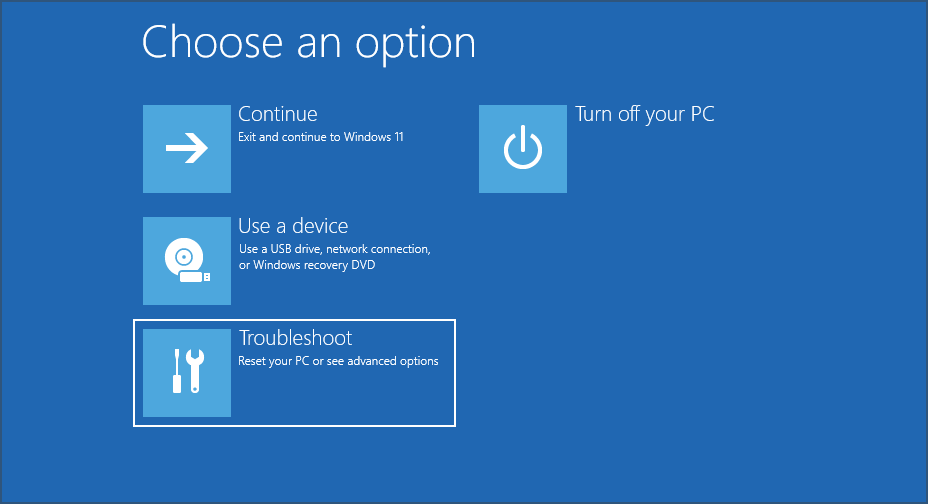
7. Select Advanced options.
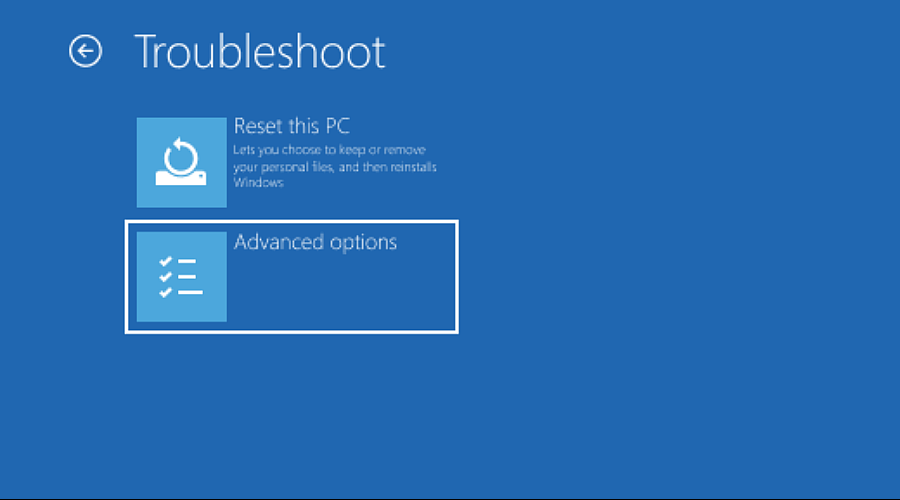
8. Now select UEFI Firmware Settings.
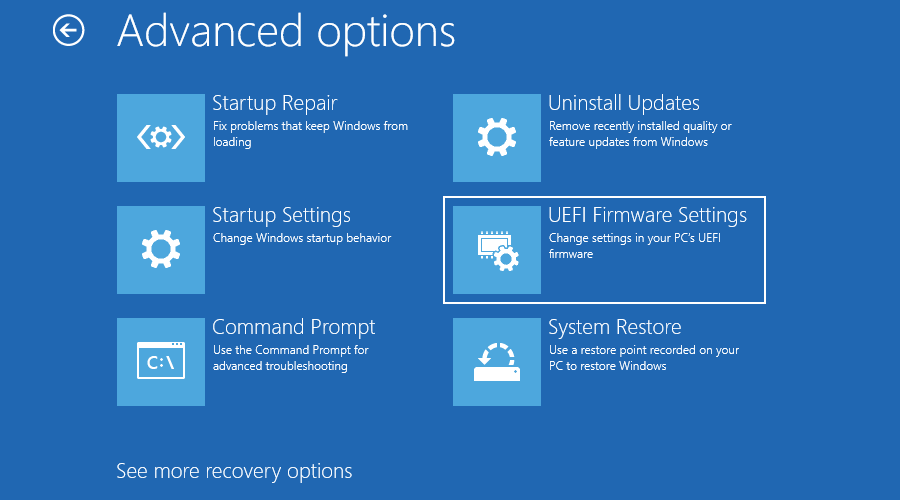
9. Finally, click Restart to confirm.
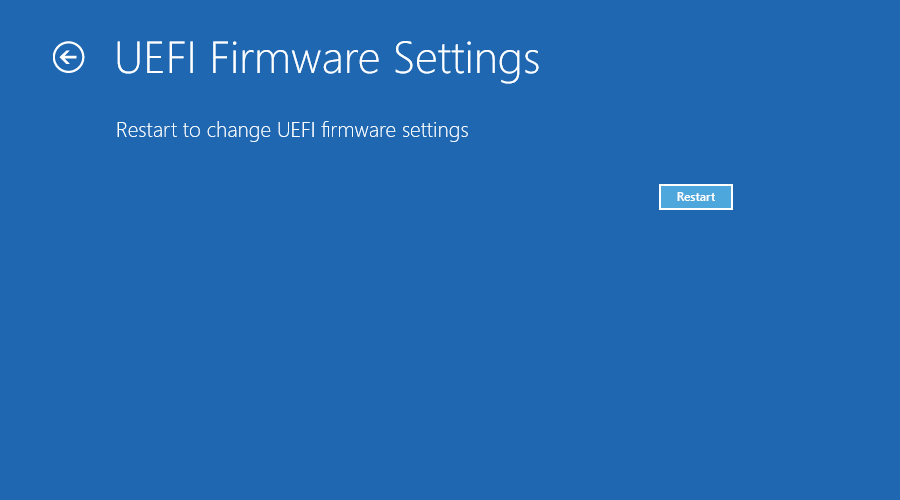
10. After the restart, Windows should boot directly to BIOS. From there, you can make all the BIOS changes you want.
There is a method to enter BIOS on Windows 11 without having to use a keyboard shortcut. Instead, you can access BIOS via Settings.
When should I update my BIOS?
This is a relatively simple but somewhat dangerous procedure. To learn more about the process, we recommend reading our BIOS update guide.
Now that you know the basics, should you update to the new version as soon as it’s available? The short answer is no; as long as your PC is working properly, there’s no need to update.
These types of updates usually fix minor bugs and add support for newer hardware, so if your PC isn’t affected by this specific bug, there’s no reason to update your BIOS.
Some updates bring support for newer CPUs, and if you’re planning to upgrade your PC and get a new CPU, then an update is mandatory. If you’re having issues with specific hardware, an update might help in some instances.
Remember that this isn’t a risk-free process, and if the update goes wrong, you might cause permanent damage to your PC and make it unable to boot, so update your BIOS only if necessary.
What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
UEFI stores the data in a .efi file on a dedicated partition, while BIOS relies on an EPROM chip. Another advantage is the GUI interface with mouse support, faster boot time, TPM, and Secure Boot support.
To learn more about TPM, we suggest visiting our TPM and Windows 11 guide. UEFI also has discrete driver support that holds this information in its ROM and better support for larger drives.
When comparing the two, the UEFI is an obvious improvement, and almost all modern motherboards use it.
We also have a guide on how to update BIOS in Windows 10 that you can check out.
If you want to change BIOS settings on Windows 11, first, you need to access it, and you can do that using any of the methods mentioned in this guide.
The quickest way to do that is to use the keyboard shortcut during the boot, and this is the method that the majority of users prefer.
However, if this method isn’t working for you for some reason, you can always boot to BIOS using the Advanced startup options. And don’t hesitate to also check out our article on how to remove BIOS password on Windows 11.
What is your favorite method to boot to BIOS? Let us know in the comments section below.