What is CPU Virtualization & How to Enable it in BIOS?
It is quite easy to enable CPU virtualization on a PC
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- CPU virtualization can be useful for utilizing the available resources efficiently.
- A virtual machine can run a different operating system than the one running on the main CPU.
- You can easily enable it via the BIOS menu, as this guide explains.
Virtualization is a technique that creates multiple versions of various system resources, including your CPU, server, storage, etc. For example, CPU Virtualization lets you use a single CPU like two different CPUs. This is like running two other computers on a single machine.
In this guide, we will help you understand what CPU virtualization is and how you can enable it in the BIOS settings of your PC. Virtualization can help several organizations efficiently manage their resources and other benefits, which we will discuss in this guide.
What is CPU virtualization?
The basic meaning of virtualization is to create another version of an operating system or any other resource. This could be anything from a network source, server, storage, or CPU.
When you virtualize your CPU, you give the same powers of one CPU to be used in another system virtually.
Every virtual machine runs an independent OS and acts like a separate computer. But that is not true, as it runs on just a portion of the main CPU.
Virtualization software communicates directly with the CPU, and the software handles everything else in the computer.
The software then splits the communication into different sections, as if they were being transmitted via two separate CPUs. One of the main advantages of CPU virtualization is that it allows you to run two different operating systems in one CPU.
There are two primary types of CPU virtualization:
- Hardware-assisted virtualization: This type of virtualization relies on hardware features built into the CPU to provide isolation and performance benefits. Examples include Intel’s VT-x and AMD’s AMD-V technologies.
- Software-based virtualization: In this approach, virtualization is achieved through software emulation. This method can have higher overhead and lower performance compared to hardware-assisted virtualization but can be used on systems without dedicated virtualization support in the CPU.
Is CPU virtualization the same as multi-tasking?
Do note that one should not confuse CPU virtualization with multitasking. Also, it would be best not to read CPU virtualization with hyperthreading along the same lines.
Multitasking lets you run two or more two applications at one time. However, the focus of operation would always be on a single application. Every modern CPU enables you to multitask.
On the other hand, hyperthreading is where compatible CPUs run a program specifically meant to carry out two actions at the same time.
Different from both multitasking and hyperthreading is CPU virtualization. In CPU virtualization, a single CPU can act as multiple separate systems.
So, you can run two operating systems in one CPU—for example, MacOS on one and Windows OS on the other. With CPU virtualization, running Windows OS on a Mac or Linus PC is also possible.
CPU Virtualization benefits
- Saves cost: When you enable CPU virtualization, it allows you to set up multiple systems using a single CPU, thereby reducing the idle wait time.
- Optimal utilization of resources: One powerful CPU can be used to virtualize into different systems reducing the idle compute time and enhancing the optimal utilization of resources.
- Better in disaster recovery: When you have a virtualized environment, the recovery process would take a few minutes instead of hours on a single CPU because now you do not need to go through the hassle of setting up a new server, etc.
- Increase efficiency: IT managers can easily install, update and maintain all the virtualized computers easily, as all they have to do is do the needful in the main CPU.
- Eco-friendly: Setting up a virtualized environment helps reduce the number of physical servers, ultimately reducing the amount of power consumed. This will help reduce the carbon footprint.
For instance, a software development company can use virtual machines to simulate different operating environments for testing purposes. This can save costs and time, as developers can quickly switch between various operating systems and configurations without the need for multiple physical devices.
How can I enable CPU virtualization in BIOS?
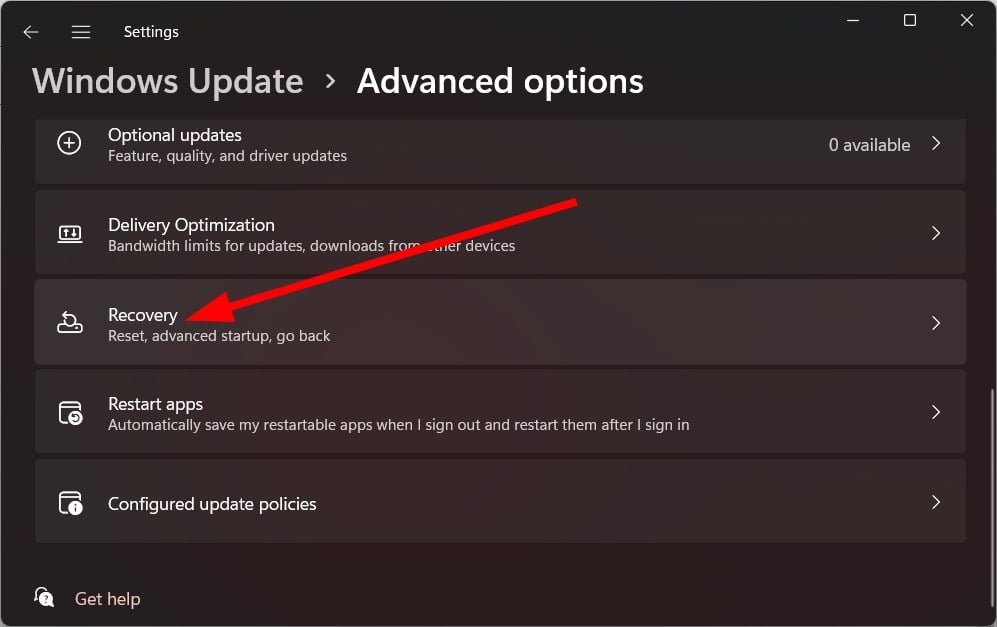
- Press the Win + I keys to open the Settings menu.
- Click on Recovery.
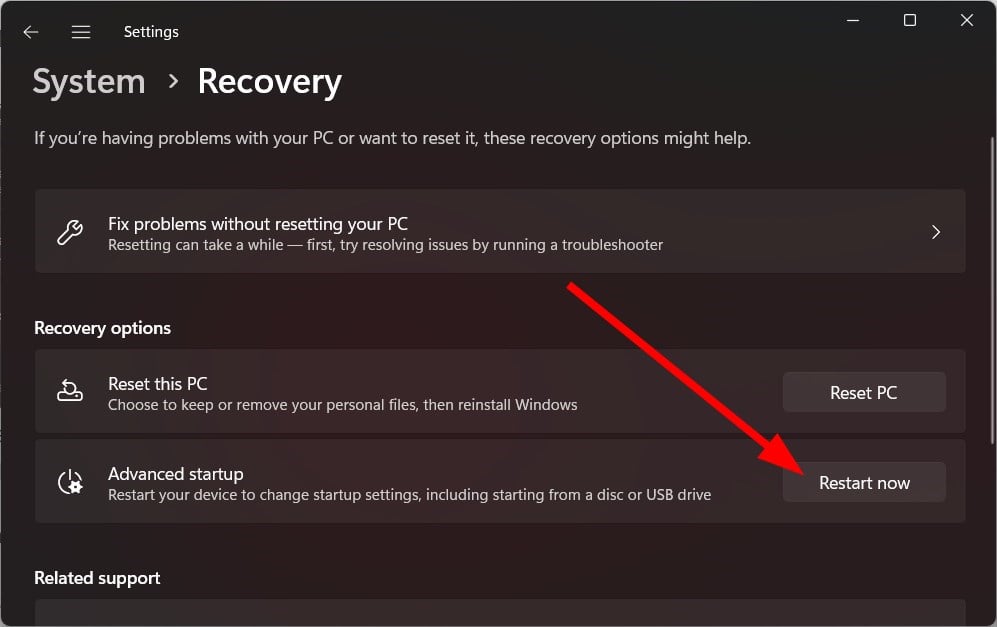
- Under Advanced startup, select Restart now.
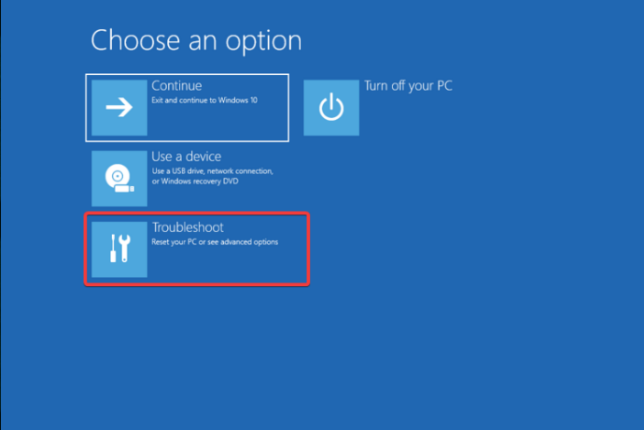
- Choose the Troubleshoot option.
- Select Advanced options.
- Select UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Choose Restart.
- Click on the button that flashes on your screen to enter BIOS. The keys could be different. It is most usually F2, F8, F10, or Del.
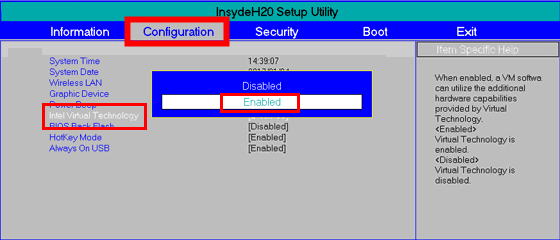
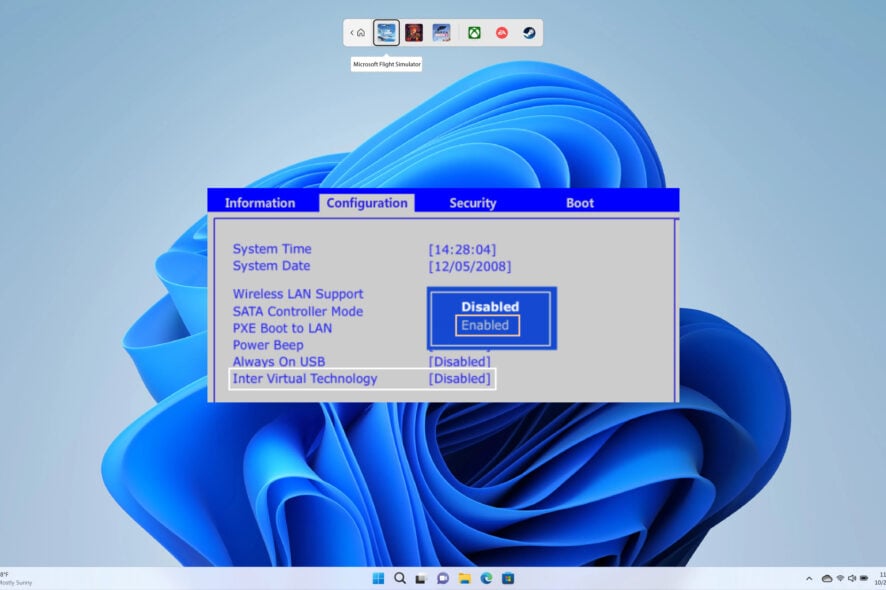
- Use the arrow keys to select Configuration.
- Select Virtualization Technology.
- Select Enable.
- Press F10 to save the changes and exit.
That is it from us in this guide. The above steps let you turn on CPU virtualization on your PC. If you get an error where VT-X is disabled in the BIOS for all CPU modes, you should check out our guide to fix the problem.
Also, if Hypervisor is not running on your PC, you can refer to the solutions in our guide to resolve the problem.
We also have a guide that explains the 3 efficient ways to disable Hyper-V in Windows 11. So you should check out our guide if you want that.
Feel free to know your thoughts on this guide and whether you successfully enabled CPU virtualization on your PC or not.