Host files aren’t working? Check out these procedures
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more

Chances are you are trying to bind certain name strings to specific IP addresses to override other name resolution methods. However, the browser cannot find the host file or the recently made changes simply refuse to take effect. How do you get the hosts files to work properly again?
All changes to hosts should take effect immediately. You shouldn’t think of rebooting your browser, your PC or performing any extra steps. However, unexpected issues do arise from time to time.
So, if you’re not entirely sure how you can solve this problem, we’re going to help you out. Just as always, there are several ways to tackle the issue effectively. Let’s get started.
What can I do when Hosts files aren’t working?
1. Basic troubleshooting steps
- Make sure your hosts file is named correctly. Double-check that it is hosts and not host or anything related.
- The same goes for the extensions chapter. It should have no extension (hosts, not hosts.txt). If you have configured Windows to hide known extensions, uncheck the option.
- Other users running into the same issue confirmed the error was related to the line endings. Therefore, changing the line endings to Windows format could make a difference. Usually, it’s the white space that messes with things since it’s so difficult to notice.
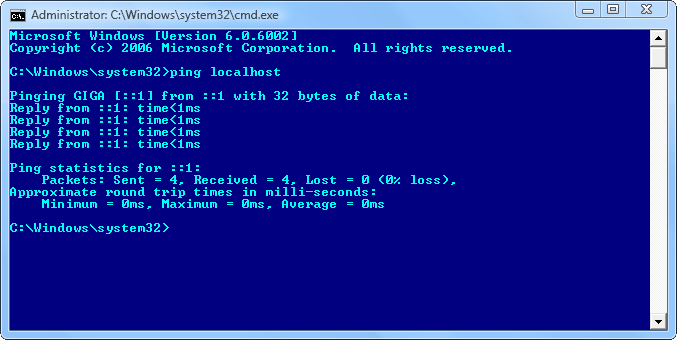
2. Drop the old data and ping localhost
If the changes are done correctly, you should see the results immediately. In spite of that, do keep in mind that Windows caches name resolution data. Therefore, the old records may still be used for a while.
Your next step should be to fire up a command prompt and type: ipconfig /flushdns to drop the old data. Try to ping localhost and see if it uses the correct IP (it should match what you put in the hosts file).
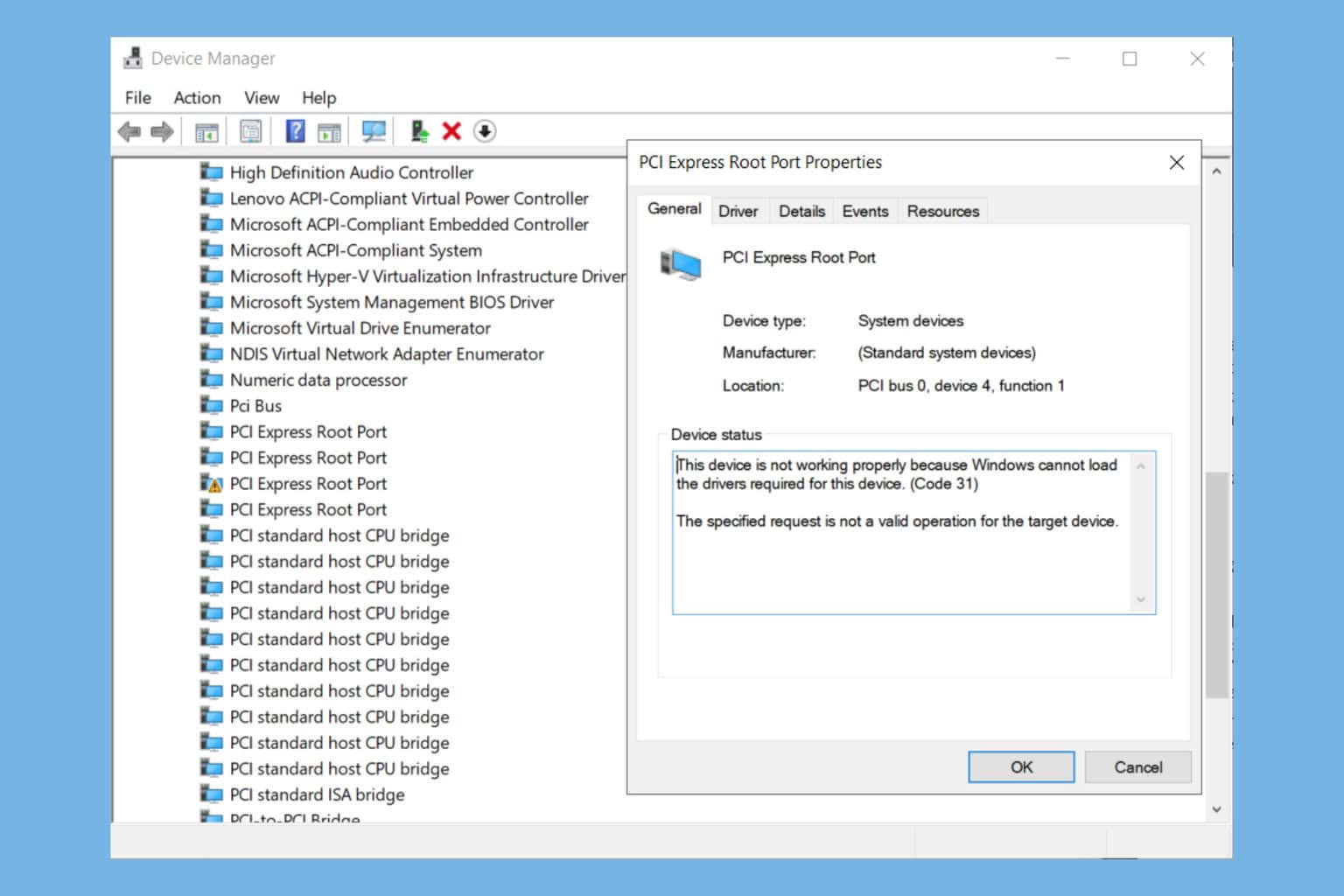
If it does, your hosts file is fine and the issue is elsewhere. If not, then you know for sure that the file is bad. Pay attention to where it goes. It might try ipv6, so the hosts file itself is broken. Remove everything from it and leave only your entry.
If you’re having trouble accessing Command Prompt as an admin, then you better take a closer look at this guide.
You can’t flush the DNS resolver cache? Check out this guide and learn how to do it.
3. Recreate the file with default permissions
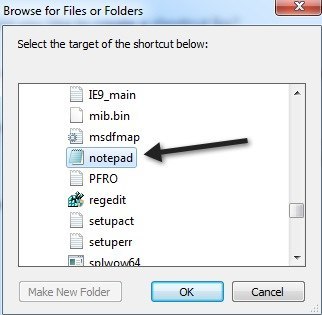
- Create a new text file on your desktop.
- Copy and paste the contents of your current hosts file into the new file in Notepad.
- Save it.
- Then, rename it to hosts.
- Copy the file to your %SystemRoot%System32driversetc. directory, and overwrite the old file.
If Windows continues to ignore the host file, recreate it with default permissions.
4. Add exceptions to proxy/disable the automatic configuration script
- Follow this path Internet Explorer > Internet Options > Connections.
- Alternatively, press Windows key and type Configure proxy server.
- Click LAN settings.
- If everything is blank and Automatically detect settings is checked, then you aren’t using a proxy.
- If you do use one, you could add exceptions by returning into Connections > LAN settings.
- Click Proxy Server / Advanced next.
- You may now add your exceptions to the Exceptions text box.
If you have a proxy configured, the automatic proxy server configuration scripts can override the hosts file. One solution here is to configure it not to do this.
If you’d want, you can also disable the automatic configuration script. Just make sure to uncheck Use automatic configuration script.
Proxy server issues are pretty annoying. Make them a thing of the past with the help of this guide.
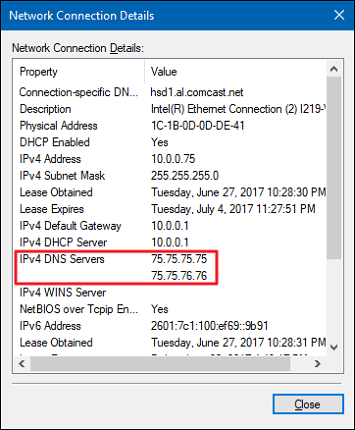
5. Check DNS address
- Enter into Network connections properties.
- Go to TCP/IP settings.
- Change the first DNS server to 127.0.0.1 (localhost).
- Make sure the second remains your actual DNS IP.
You could also try doing a few changes in the DNS address department. They aren’t a must but may help if something is badly configured.
6. Create a new hosts file
- Open Windows Explorer as Administrator.
- Delete the hosts file.
- Open Notepad as Administrator too.
- Then, create a new hosts file.
Are you still experiencing the same problem? In that case, another effective solution is to create a new hosts file. Start from scratch, then add entries.
It comes a time when you try to migrate your website from one host to another. You clearly want to make sure the website is working properly before changing the domain’s settings, yet those hosts files don’t work.
Although there is no quick fix to this problem, you can try out the above suggestions. Moreover, you can share your views, feedback, and other queries related to hosts files in the comments area below.
READ NEXT: