How to Set Permissions in Active Directory for Users
Permission settings can be done with third-party management tools
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Active Directory permissions determine how much privilege you have to access and modify files, folders, and functions on the Active Directory.
- Administrators can set permissions in the Active Directory via the Group Policy Management Console.
- You may also use Active Directory management third-party tools to take care of the Active Directory permissions.
The Active Directory is a tool for managing remote computers by users with Administrative access and granting permissions to users. It allows users with permission access to privileges not allowed for other users. Hence, we’ll take you through how to set permissions in Active Directory users.
What are permissions in Active Directory?
Access to use and make changes in the Active Directory is limited to a specific set of people with privileges that allow them access to them. These access privileges are permissions in the Active Directory granted to users or groups that permit them to interact with objects.
Furthermore, there are Standard and Special types of permissions in Active Directory. Standard permission allows users to read, write, and have total control.
In addition, special permissions allow the user to modify object permissions or owners, change settings, etc. Check our guide about the best practices for Active Directory to apply now.
How do I set permissions in Active Directory for users?
1. Use the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)
- Press Windows + R key to open the Run dialog box, type gpmc.msc, and click OK to open the Group Policy Management console.
- Right-click on the Group Policy Objects icon and select New from the drop-down.
- Input a Name, set the Source Starter GPO option as none, and click OK.
- Right-click on the new GPO and select Edit GPO from the drop-down.
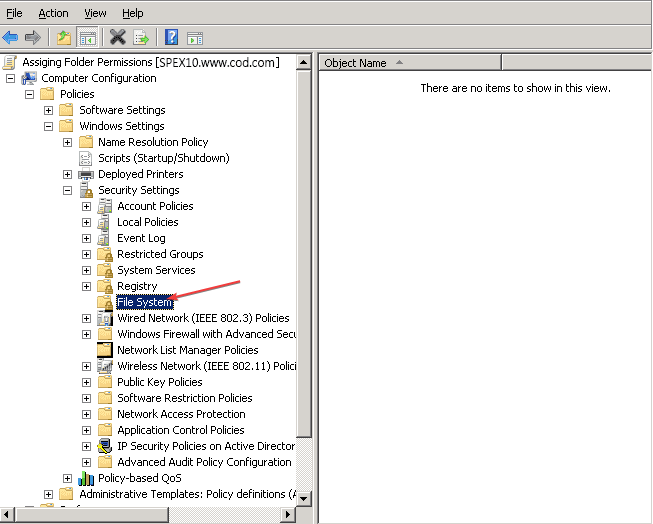
- On the Group Policy Management Editor window, go to the following path:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\ - Right-click on File System, then select Add File from the drop-down.
- Locate and click on the folder you want to assign permissions, then press OK.
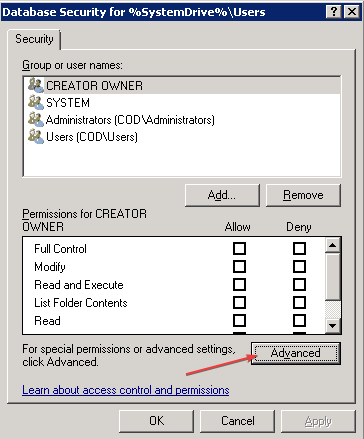
- On the Database Security page, click the Advanced button.
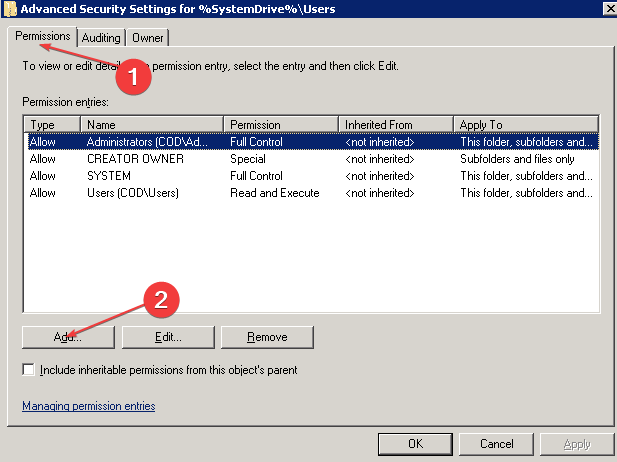
- In the Permissions tab, click Add to create and assign permission to a new user, select an existing user you want to assign permission to, and press Edit.
- On the Permission Entry for Users window, view the list of permissions you can choose, then check the box for Allow or Deny against a Permission.
- Click the drop-down button against the Apply onto option, then select where you want to apply the permissions.
- Press OK to save the permissions settings.
The above steps will assign the selected privileges to the user and allow access to the selected folder or credentials without requesting permission.
2. Set Permissions for Delegated Authentication
 NOTE
NOTE
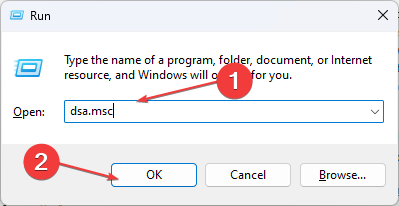
- Press Windows + R key to open the Run dialog box, type dsa.msc, then press OK to open the Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Right-click the user, group, or organizational unit (OU) to delegate, then click the Delegate Control button.
- Click Next on the Delegation of Control wizard and click Add.
- On the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box, enter the username or group name you want to grant permissions to configure delegated authentication.
- Click Check Names to verify that the user or group has been created in Active Directory, click OK, then click the Next button.
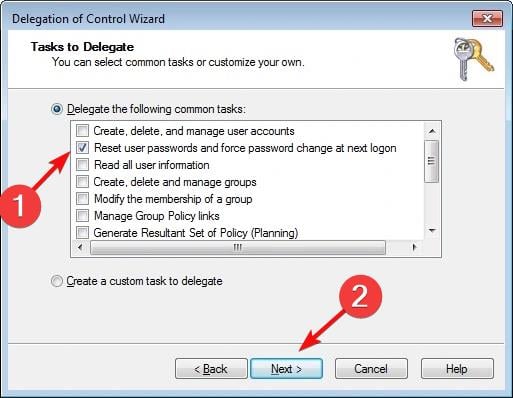
- Select the Delegate the following common tasks option, then select the Reset user passwords and force password change at the next logon option.
- Click Next, then click Finish.
- Right-click on the modified user or group and select Properties from the drop-down.
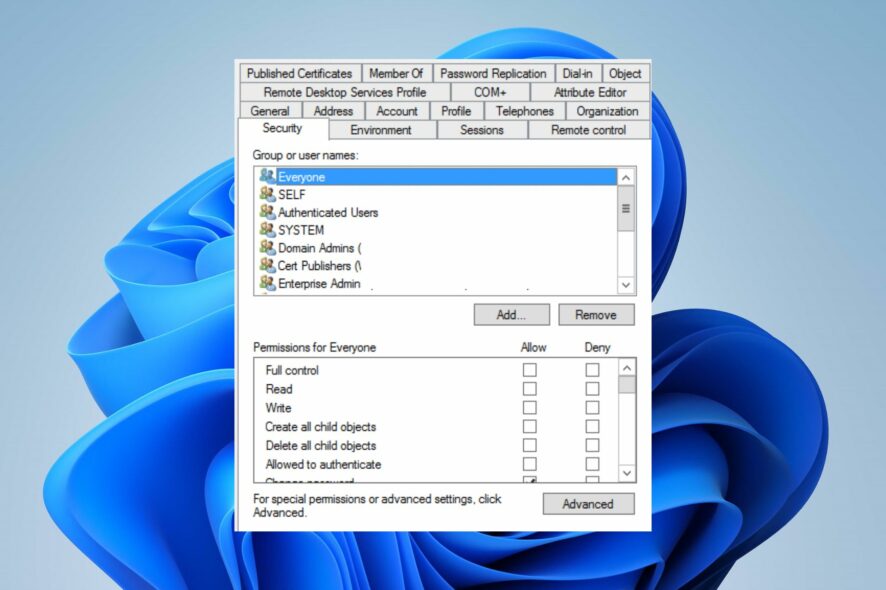
- Select the Security tab, and then click Advanced.
- Click the Add button on the Advanced Security Settings.
- On the Permission Entry wizard, click Select a principal, enter the username or group name granted the reset permission, then click OK.
- Select Descendant User objects on the Applies to the field to show the list of permissions allowed for the user account.
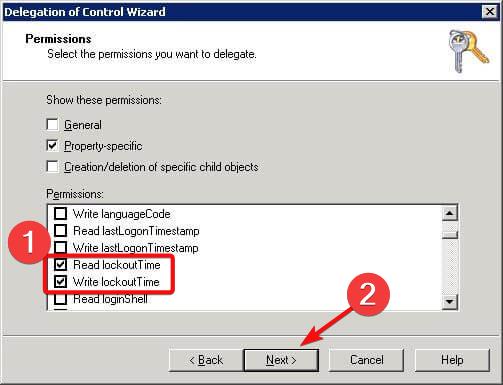
- Scroll down, enable Read lockoutTime, and Write lockoutTime, then click OK.
- Click OK to end the setup.
The above steps grant the user account permission to change the passwords of all the user objects in the administrative directory.
Read our guide on enabling Active Directory users and computers in Windows 11 if you can’t access it with step 1.
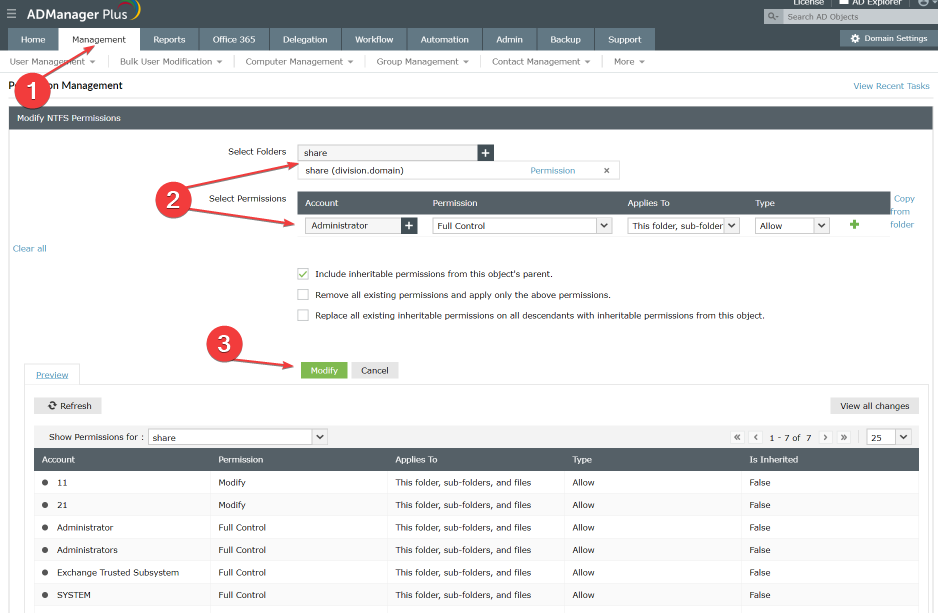
3. Use a reliable third-party tool
- Sign in to ADManager Plus.
- Navigate to AD Mgmt, select File Server Management, then click on Modify NTFS permissions.
- Choose which folders you want to enable a user or group to access.
- Go to the Accounts tab and choose the users or groups you want to grant permission to access the folder.
- Click the Modify button to save the permissions changes.
Administrators can use third-party Active Directory management tools to manage permissions delegation to objects in the Active Directory.
Our best recommendation for a third-party Active Directory permissions management tool is
ManageEngine ADManager Plus.

ADManager Plus
Manage all your endpoints and their permission with a complete solution that makes it all easier!We hope that our guide offered you comprehensive information on how to set permissions in Active Directory users.
Further, you can check how to install Active Directory on Windows Server if you don’t have it already installed.
Also, we have a detailed guide on how to demote a dominant controller on Windows Servers in a simple way and a guide on An account with the same name that exists in Active Directory error.
In conclusion, these are the best ways to set permissions in Active Directory. Should you have further questions or suggestions, kindly use the comments section.