Fix: VMware Workstation and Hyper-V are Not Compatible
Insufficient memory can cause Hyper-V's incompatibility with VMware
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- VMware not compatible with Hyper-V error can occur when the Hyper-V role is enabled as a secondary virtual machine creator.
- VMware needs a 4GB RAM or more because your PC needs to run its systems also.
- One of the possible fixes for the incompatibility issue is to uninstall Hyper-V in the GUI.
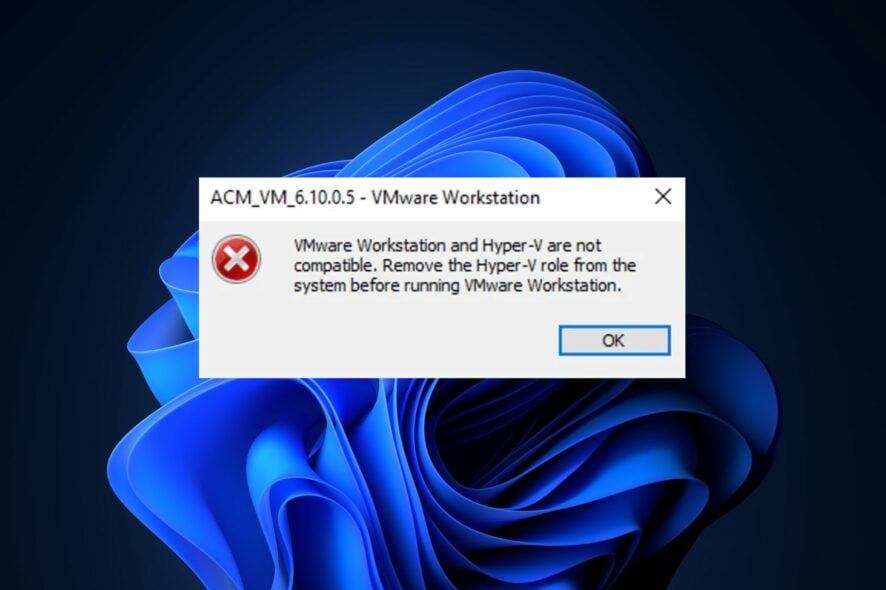
It can be quite annoying if you get the Hyper-V not compatible with VMware error after installing a virtualization application on a Windows machine.
This error is almost inevitable because Windows 11 cannot run another Virtual Machine creator alongside Hyper-V. Regardless, fixing the VMware and Hyper-V incompatibility issues is still possible.
Why is VMware not compatible with Hyper-V?
Whenever the Hyper-V role is enabled, the virtualization extensions are not exposed to type 2 hypervisors installed on a Windows machine, hence the incompatibility issue. However, other factors responsible for this error are:
- Outdated or low-bit processor: VMware workstation and Hyper-V may not be compatible if you use an outdated processor for Windows Server 2012. Regardless of the Hyper-V feature you wish to use, a 64-bit processor of second-level address translation (SLAT) is a requirement for newer hardware.
- Insufficient Memory: To run multiple Virtual Machines simultaneously, you’ll need enough memory of at least 4 GB of RAM or more for the host and other Virtual Machines.
- Hyper-V is a Virtual Machine creator: Hyper-V is also a Virtual Machine creator and cannot run with another VM due to competition for resources. You may have to disable Hyper-V in Windows 11 in such cases.
What can I do if VMware is not compatible with Hyper-V?
You should ensure to perform the following preparatory checks before engaging in any troubleshooting or settings tweaks:
- Ensure you have about 60GB and above of hard disk storage.
- Your computer should have a minimum RAM of 4GB.
- Get to know how to locate the files & folders and their respective functions.
- Ensure that your processor is compatible with a 64-bit processor and supports AMD, Intel, and Qualcomm processors.
Having checked these and the issue persists, proceed to the advanced fixes below.
1. Uninstall Hyper-V in the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Click the Start button, input cmd, and launch the Command Prompt.
- Run the following command to open System Information to check if Hyper-V is installed and press Enter:
msinfo32.exe - If Hyper-V is installed, proceed to uninstall it with the next steps.
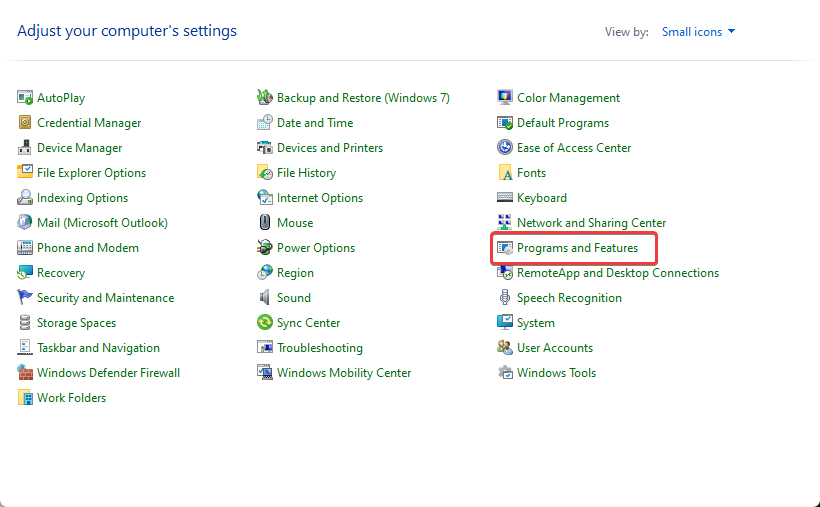
- Open Control Panel and click Programs and Features.
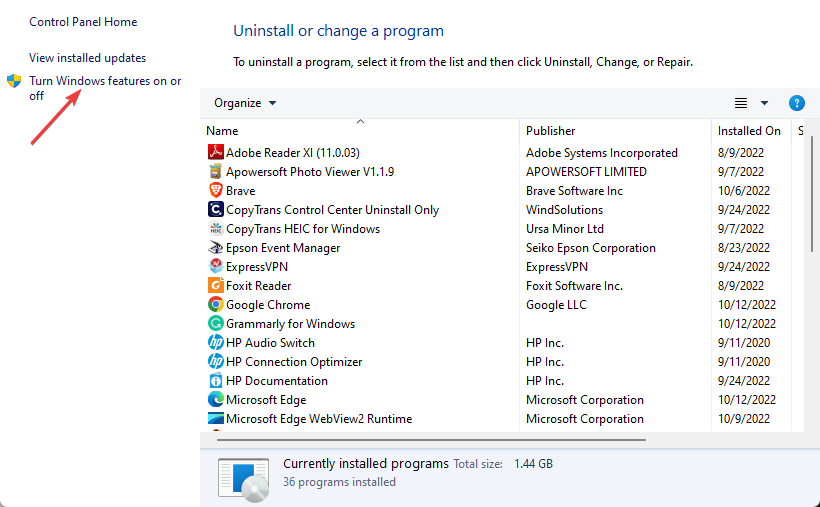
- Then, click Turn Windows features on or off.
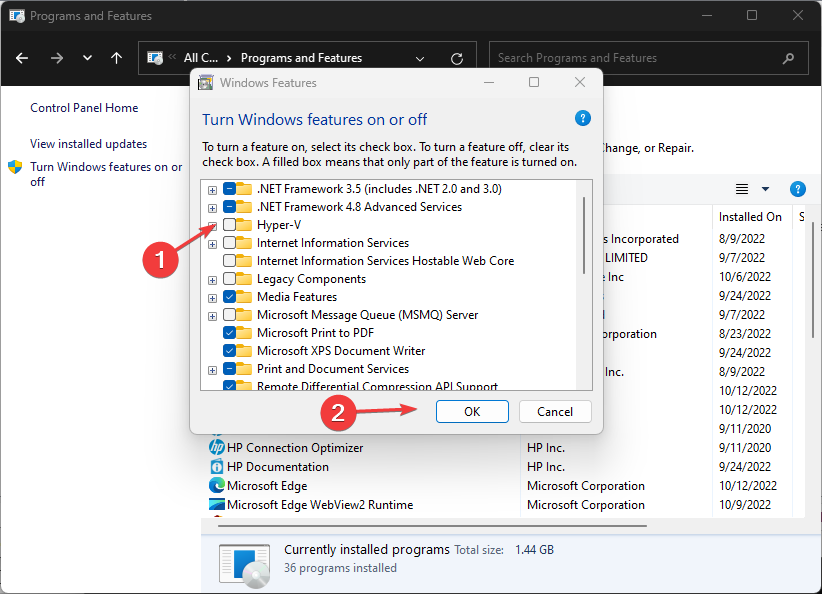
- When the Windows features page opens, deselect the Hyper-V checkbox, and click OK.
- Restart the computer.
You can follow similar steps for Windows Server 2016. However, should you later need to re-enable Hyper-V, you can check our guide on how to Install Hyper-V in Windows 11.
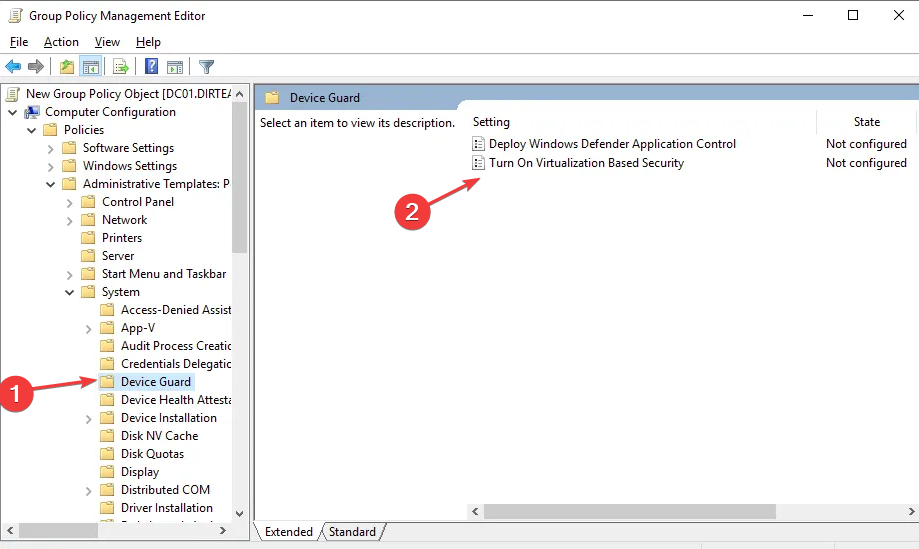
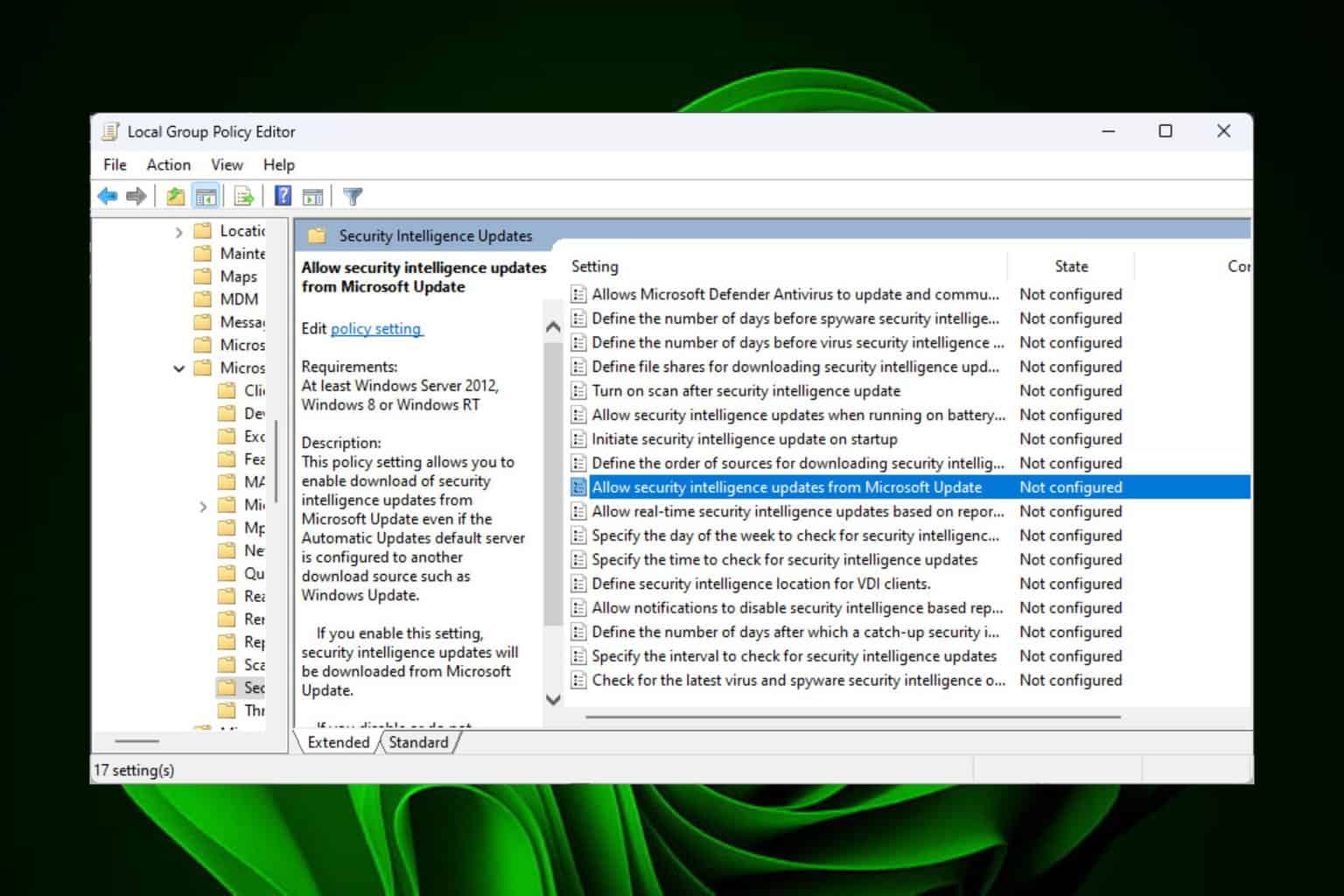
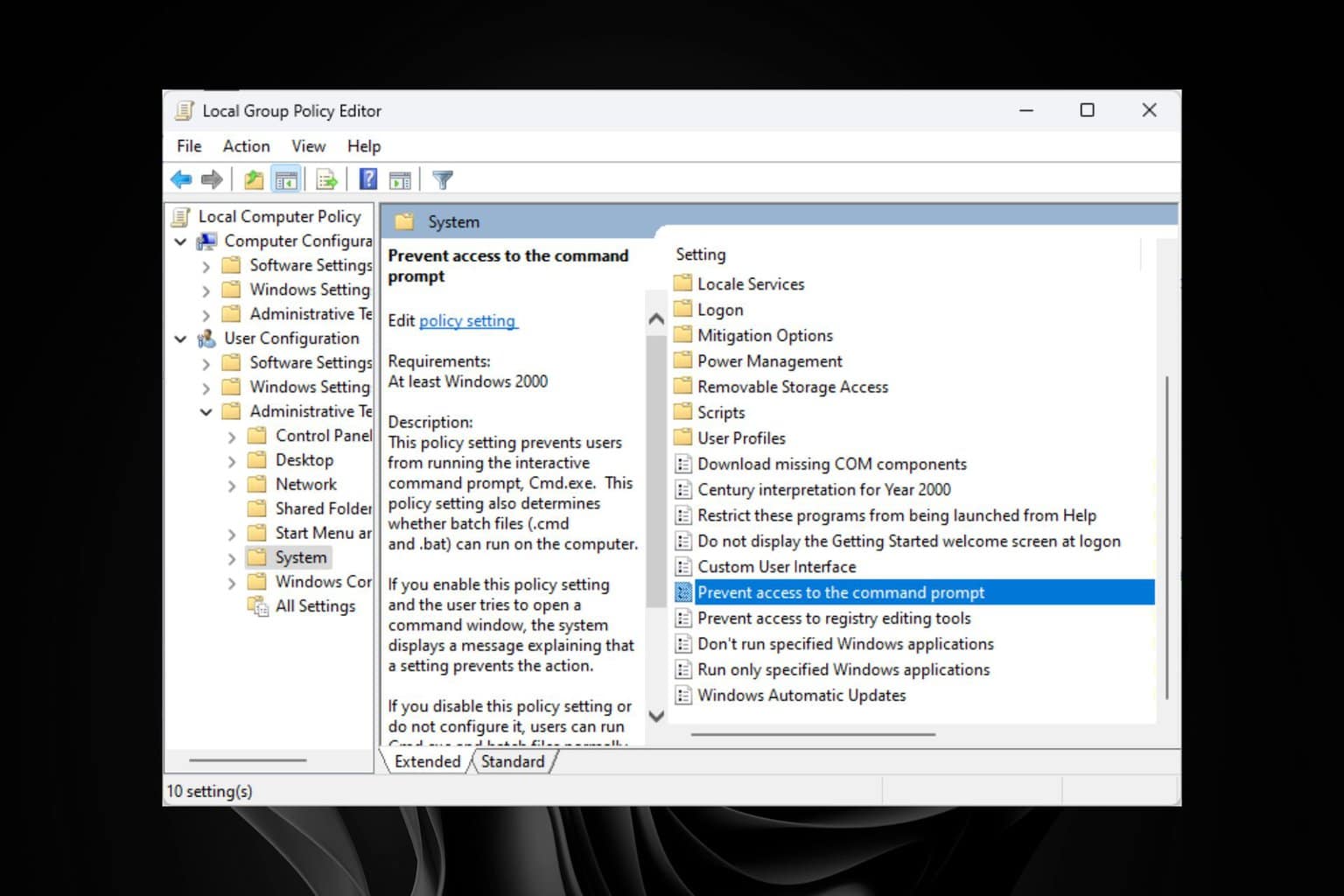
2. Turn off Virtualization Based Security
- Press the Windows + R keys simultaneously, input gpedit.msc and click OK or hit Enter.
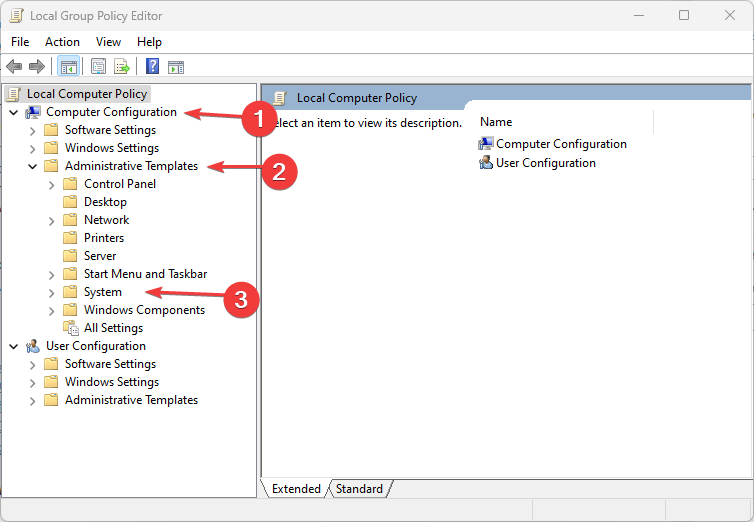
- Go to Local Computer Policy, then click on Computer Configuration.
- Select Administrative Templates and click on System.
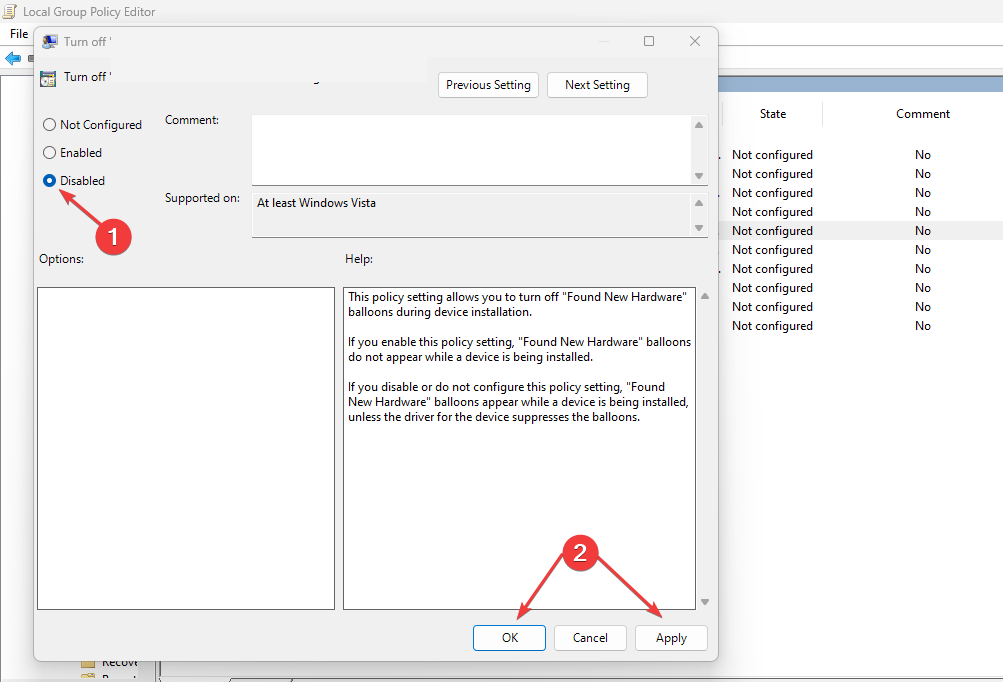
- Then, click on Device Guard and double-click Turn On Virtualization Based Security (the status of this setting should show Not configured by default).
- A window should open, select Disabled and click OK to save the settings, then close the window.
Alternatively, if you can’t seem to access Virtualization-Based Security, you can read how to disable VBS on Windows 11 PCs and find some relevant solutions.
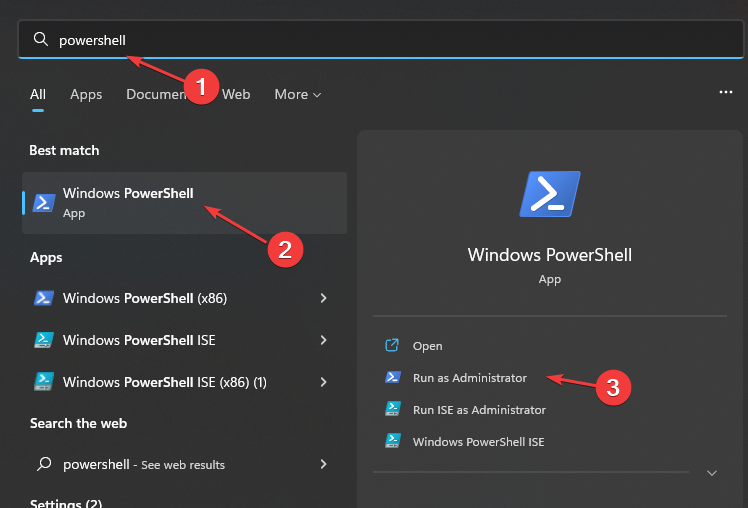
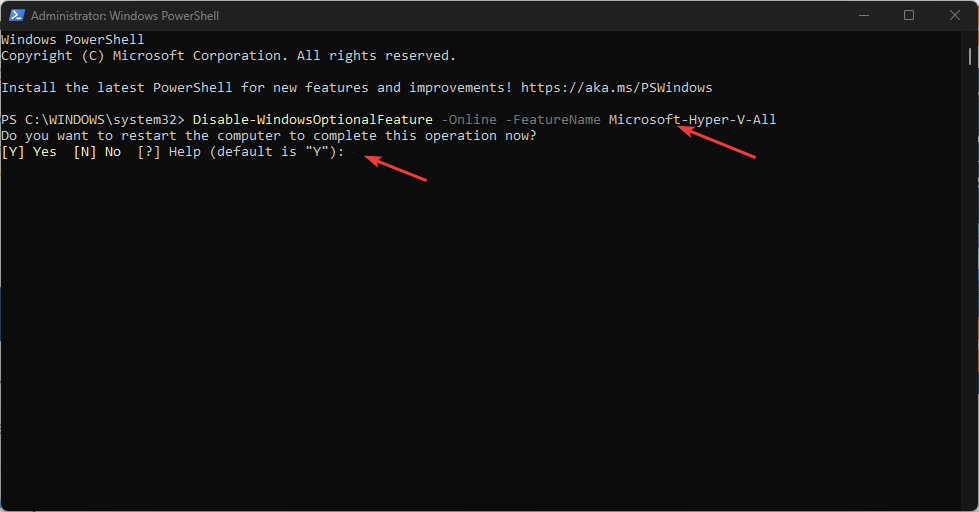
3. Disable Hyper-V using PowerShell
- Press the Windows key, type Powershell, right-click on PowerShell and select Run as Administrator.
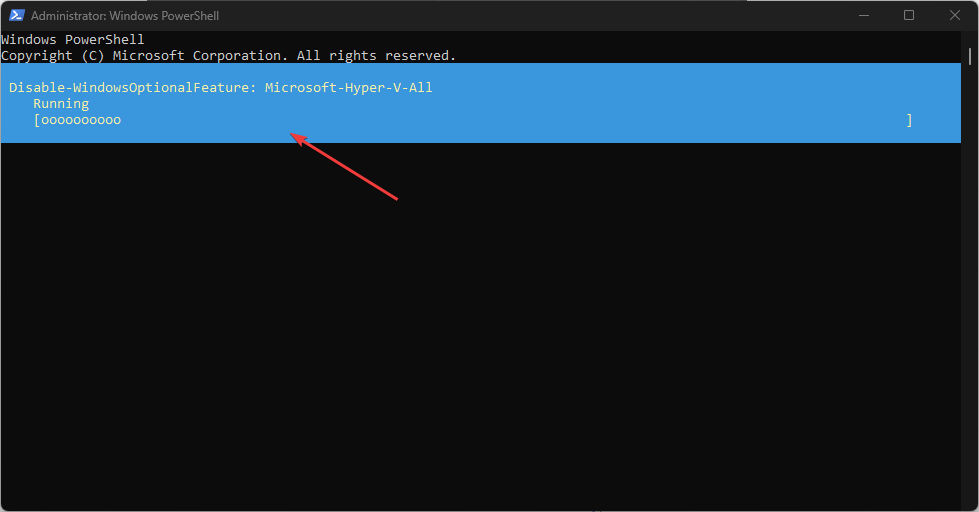
- Type the following shell command in the PowerShell window and hit Enter:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V-All - PowerShell will initiate the Hyper-V disabling process.
- If it is successful, you will be asked to restart your PC, type Y to confirm, and your PC will restart to apply the changes and enable a new feature.
If you want to re-enable Hyper-V in PowerShell, you can read through our guide on enabling Hyper-V in Windows 11.
You can also check our detailed guide on what to do if VMware workstation and Hyper-V are not compatible with Windows 11.
However, if the Hyper-V to VMware compatibility problems persists, you should consider checking our article to fix Windows 11 Hyper-V errors.
If you have new queries or suggestions about other fixes that have worked for you, kindly drop them in the comments section. We will appreciate your input.