What is my Proxy & How do I Find it?
Your gateway to fast and secure connection
5 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more

You’ve probably heard about proxies and their role in enhancing your privacy or just boosting your network performance. Well, we’ll be discussing how to find out your proxy and the various settings you can tweak for an improved overall performance.
Not everyone needs a proxy because its main purposes are to mask your browsing activities, performance improvement, security and sometimes, troubleshooting. It basically acts as your middleman between your internet and device for a specific purpose.
All these can be achieved without a proxy by using private browsers or VPNs but let’s take a closer look at situations that require a proxy.
What are the different types of proxies?
- Forward Proxy – This is the most common one and found on browsers. It works by being the first recipient of requests then forwards them to the internet. If the site is found to be malicious or a phishing site, you’ll receive a warning.
- SOCKS Proxy – This is the most versatile proxy as it operates on a transport layer and handles different protocols. Since it handles a variety of protocols, it also requires authentication so that only authorized users can have access. You can learn more about how to set up SOCKS proxy in our detailed article.
- HTTP and HTTPs proxies – Both are used for web filtering but the HTTPs is used for encrypted data and ensures its security during transfer.
How do I find and set up my proxy?
1. Find your proxy
- Press Windows + S to open the Search menu, enter Internet Options in the text field, and click on the relevant search result.
- Navigate to the Connections tab and click on the LAN settings button.
- You will find the proxy address and other information listed under the Proxy server.
You can also check your proxy online using free sites like the Whatismyproxy site.
 NOTE
NOTE
2. Set up a proxy server
2.1 Automatic setup
- Click on the Search text box in the taskbar, type proxy, and select Proxy settings.
- Toggle on the Automatically detect settings.
- If you have a preferred proxy URL, then enable Script Address, paste the URL, and click Save.
2.2 Manual setup
- Press the Start Menu icon and select Settings.
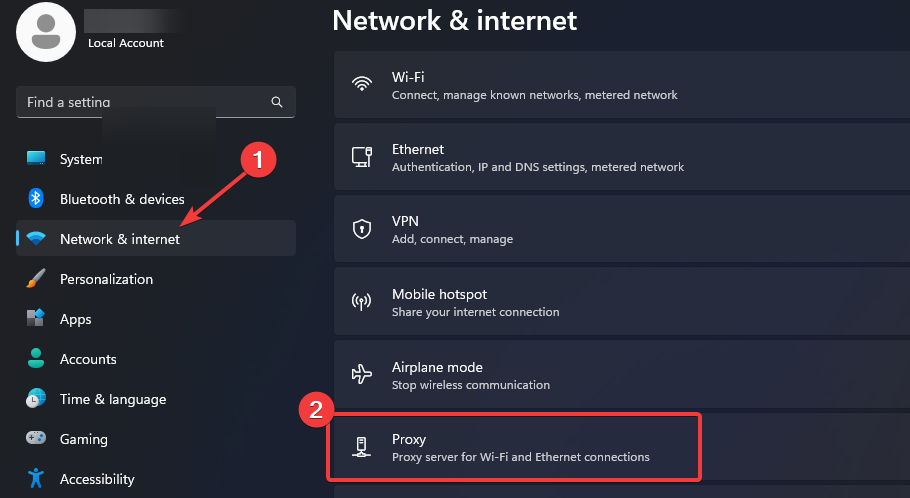
- Click on Network & Internet on the left pane, then scroll down and click Proxy on the right pane.
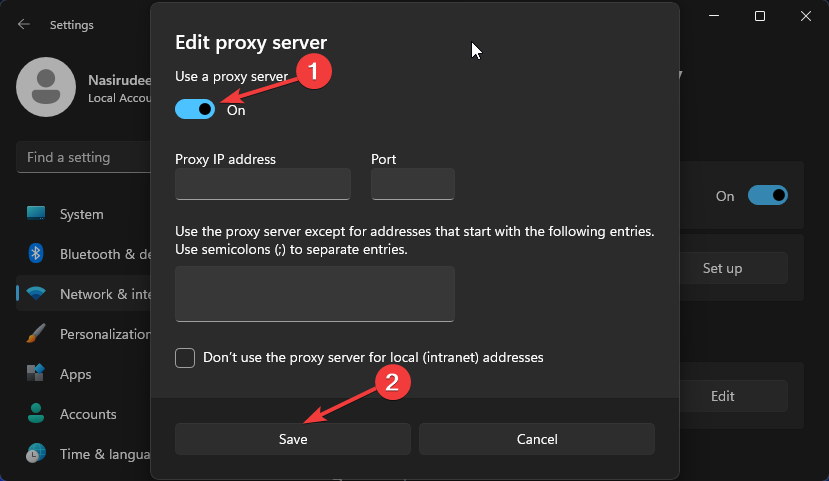
- Select Edit next to Use a proxy server option in the Manual proxy setup section, toggle on Use a proxy server, enter the IP address and Port if available and click on Save.
If you’re not sure what server to use, there are hundreds of free public proxy servers but beware of the associated security risks and performance metrics as they’re usually overloaded.
3. Reset proxy settings
- Press Windows + S to open the Search menu, enter Command Prompt in the text field, and click on Run as administrator.
- Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
- Now, paste the following command and hit Enter to reset the proxy settings:
netsh winhttp reset proxy
4. Force disable proxy
- Create a restore point or backup the registry before making any edits.
- Press Windows + R to open the Run command, type regedit, and hit Enter or click the OK button.
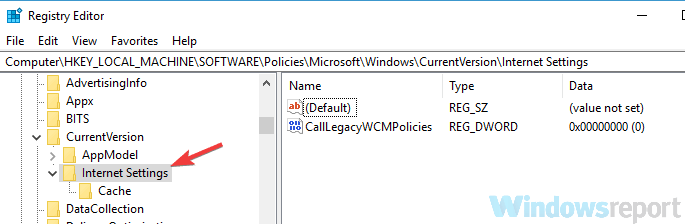
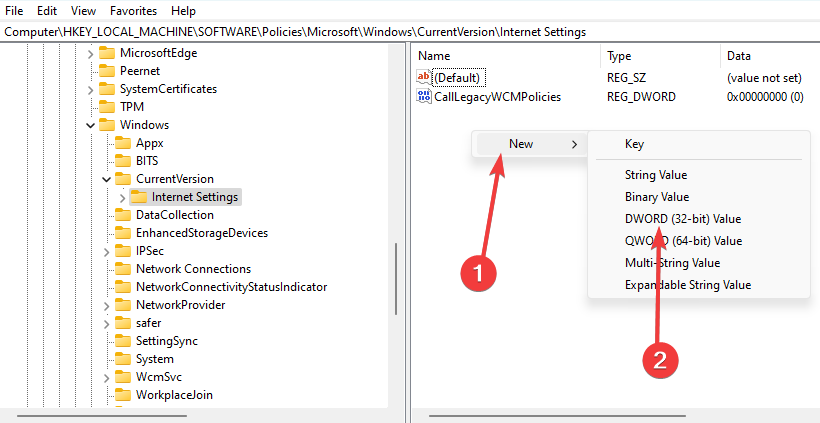
- Navigate to the path below:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings - Double-click the ProxySettingsPerUser DWORD and set its value to 1.
- If the DWORD isn’t available, right-click the right pane, choose New, DWORD (32-bit) Value, and name it ProxySettingsPerUser.
- Now double-click it and set its value to 1.
- If the above does not work, make the following changes in the same location:
- Change ProxyEnable value to 0
- Change ProxyHttp1.1 value to 0
- Remove ProxyOverride key
- Remove ProxyServer key
- Restart your PC for the changes to take effect.
This process comes in handy when your proxy keeps turning on and you need it disabled.
What are the benefits of a proxy?
- Anonymity – If you’re using public Wi-Fi, a proxy can help mask your real IP address and prevent tracking websites from tracing any online activities to you for targeted ads.
- Bypass geo-restrictions – Some media content is only available in select locations so a proxy can help you access this restricted content.
- Faster load times – A proxy monitors your activity and caches your frequently visited sites by reducing the load time. This can also save you some data if you’re on limited bandwidth.
- Security – Some proxies can prevent data interception when you’re browsing and protect you from malicious attacks. This is done by filtering out suspicious websites while fetching so they won’t appear in your results.
As much as proxy servers have their benefits, they also run into issues from time to time. You may get the something is wrong with your proxy server. Needless to say, you need proxy server tools for the best performance.
That’s a wrap but do let us know how you use your proxy and in what situation you frequently need it for in the comment section below.















User forum
0 messages