Windows 11 Data Deduplication: How to Install & Configure
Save big on storage space and hardware costs
8 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Data Deduplication is a process to clear storage by identifying and moving the unique chunks to the Chunk Store.
- It works seamlessly, and you may find deduplication savings as high as 80-95%.
- Deduplication does come with a set of critical drawbacks that most users remain oblivious to.

Data deduplication allows administrators to reduce the consumed space and save on data storage costs. While several ways exist to find and delete duplicate files, some prefer the conventional approach. That’s where Windows 11 Data Deduplication comes into the picture.
Also known as Dedup, Data Deduplication is the first choice of Windows system administrators. And the process is just quite simple, given you have a basic understanding of how things work on the OS. So, let’s find out!
How does Windows data deduplication work?
As the name suggests, Data Deduplication is the process of identifying duplicate chunks of data and then moving them using reparse point, which will redirect to the unique file copy.
Dedup is a multi-step process, from scanning the files, breaking them into chunks, identifying the unique ones, moving them to the chunk store, and then using the reparse point.
Remember, any changes here are registered unoptimized, and the process takes place the next time the Optimization job is run, typically once every hour. Though it sounds complex in theory, the process is automated and occurs in the background without requiring manual interference.
Also, as per Microsoft, configuring Data Deduplication can help reduce storage requirements by up to 95% in cases of high duplication. The average range for documents and similar files is 30-50%, while for virtualization libraries, it’s 80-95%.
The deduplication process has been developed considering two vital aspects. It does not affect the writing operations, and the programs accessing the file should be able to do so seamlessly, remaining completely unaware that these have been deduplicated.
What are the benefits of deduplication and compression?
Here are the primary benefits of Data Deduplication:
- Reduces storage requirements: By identifying and eliminating duplicate chunks of data, Dedup helps reduce the required storage space. This also clears up the disk for other pieces of data.
- Lowers incurred costs: With reduced storage requirements, the cost to maintain hardware also comes down significantly, ensuring that major corporations save big time.
- Simplifies data recovery: Data recovery can be complicated when duplicate files exist on the server, but with Data Deduplication enabled in Windows 11, the process will be both simple and quick.
- Enhanced network performance: Fewer duplicate files also translate to lesser data being transferred over the network, thus freeing up considerable network resources, and users, in turn, enjoy higher Internet speed in Windows 11.
How do I enable deduplication in Windows?
1. Data Deduplication in Windows 11
1.1 Search for duplicate files
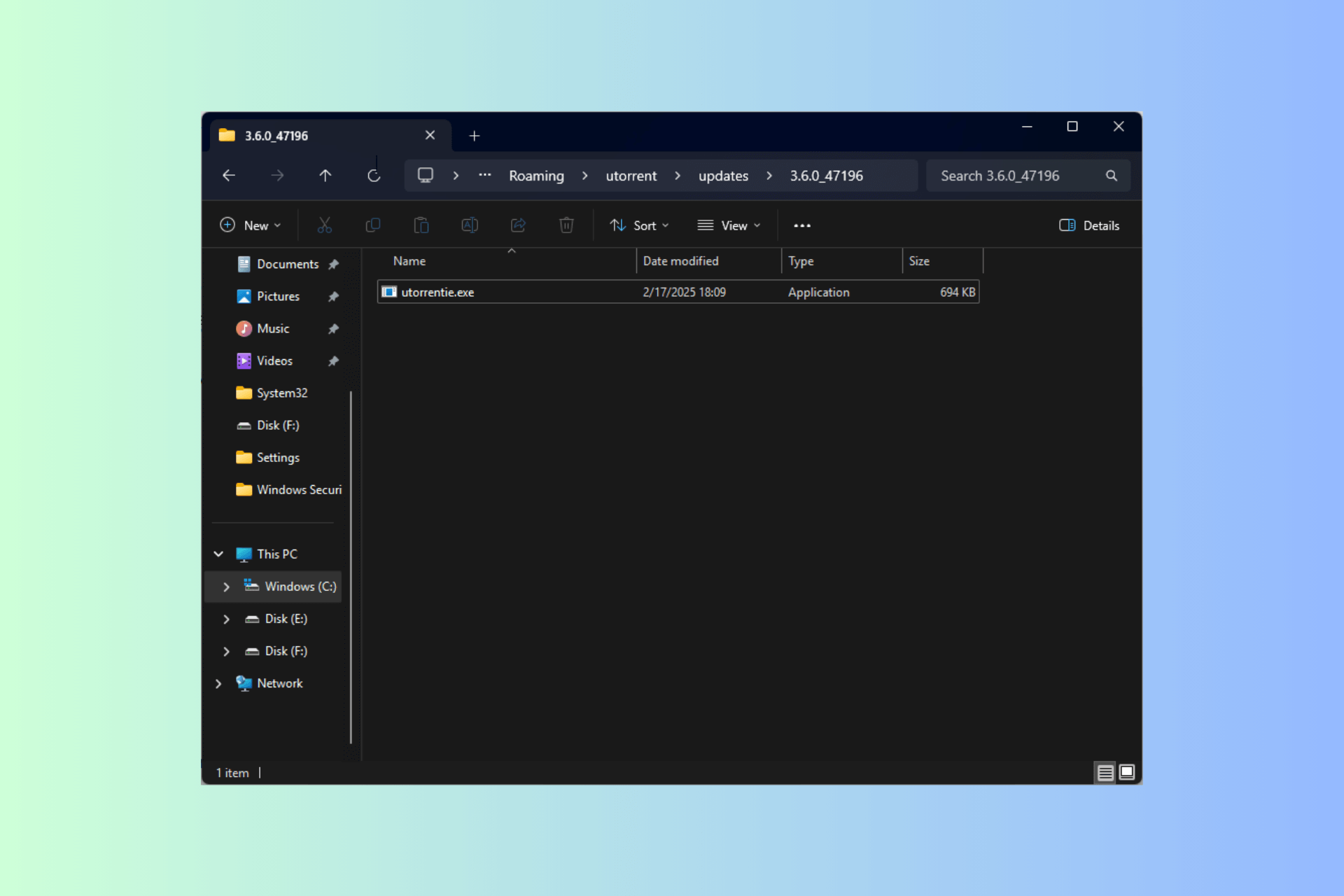
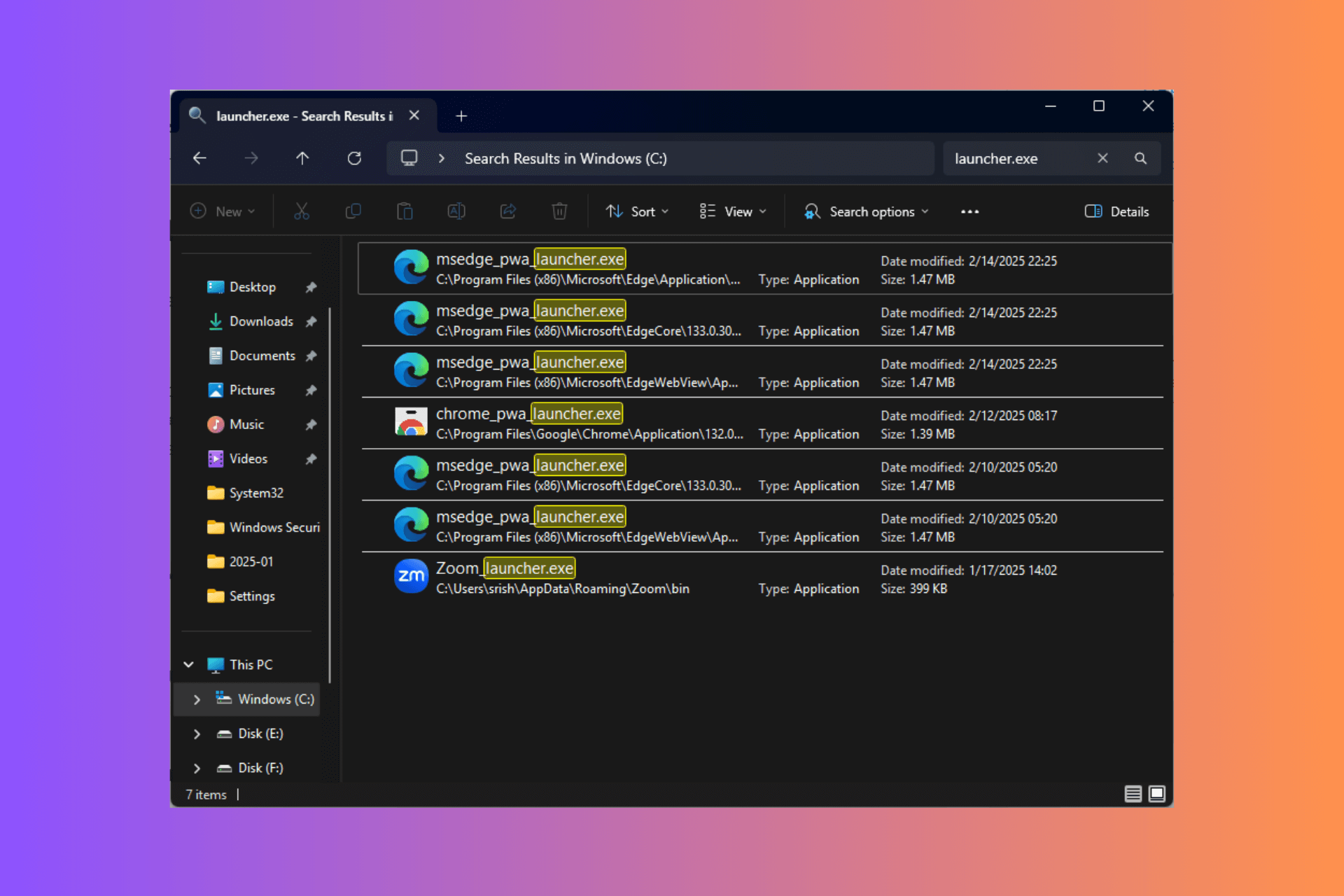
- Press Windows + E to open File Explorer, and navigate to the folder where you want to locate duplicate files.
- Now, enter the file name in the search bar near the top-right corner and wait for the results to populate.
- Select the duplicate file here and then click on Delete or hit the Del key.
- Choose the appropriate response in case a confirmation prompt appears.
- You can similarly perform a search and delete the other duplicate files.
This is by far the simplest method to delete duplicate files in Windows 11 without using the Data Deduplication methods or a third-party tool. It works the same way in the previous iteration, allowing users to remove duplicate files in Windows 10.
1.2 Sort files by name to identify duplicate files
- Press Windows + E to open File Explorer, and head to the folder that has duplicate files.
- Click on the View menu, and select Details from the list options.
- Now, choose Name from the Sort menu to list the files in alphabetical order.
- Any duplicate files will be listed right under the original ones making it easier to identify them.
- To remove them, select one and hit Delete. You can also select multiple files in one go by holding the Ctrl key.
If you are unsure about the name of the duplicate file, there’s always to option to sort them and get the duplicate ones listed next to the original. Though this is way harder than Microsoft’s solution, and if you feel the same, there are a few Data Deduplication tools for Windows 11.
1.3 Use a third-party tool
- Download CCleaner on your PC and launch the software.
- Select Tools from the navigation pane on the left, and click on Duplicate Finder.
- Select the drive in which you want to find the duplicate files, and click Search. You can also customize the settings here for a modified search with different parameters and exclusions.
- Once the duplicate files are found, choose the ones to remove, and then click on Delete Selected.
- Click OK in the confirmation prompt.
That’s it! When the manual methods seem a bit too exhaustive, dedicated and reliable third-party tools like CCleaner come to your rescue.
These simplify the job and help find and delete duplicate files across the PC within seconds without installing Windows Server and enabling Data Deduplication.
2. Data Deduplication in Windows Server
2.1 Installing Data Deduplication
- Launch the Server Manager on your PC, and click on Add roles and features.
- Click on Next to proceed.
- Choose Role-based or Feature-based installation and click Next.
- Double-click on File and Storage Services, expand File and iSCSI Services, then select Data Deduplication and proceed.
- Choose the appropriate response on the next few windows, and click Install when you see Confirm installation selections.
- Wait for the installation to complete.
2.2 Setting up Data Deduplication
- Expand Local Server from the navigation pane in Server Manager, and select File and Storage Services
- Now, choose Disks under Volumes if the former is not initialized yet.
- Right-click on the drive, select New Volume, choose the appropriate options, and then enable Data deduplication.
- If you want to enable Data Deduplication on a drive that’s already initialized, go to Volumes, right-click on the drive, and select Configure Data Deduplication.
- Now, choose the appropriate option from the Data deduplication dropdown menu, choose a time period for files to be checked, add any excluded extensions or folders, set Deduplication Schedule, and click on OK once done. You could also go with the default settings.
- You can now either wait for Data Deduplication to run automatically as per the configured schedule or start it manually.
2.3 Running Data Deduplication from PowerShell
- To run manually, press Windows + R to open Run, type powershell, and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
- Paste the following command while replacing Drive Letter with the one you want to perform the deduplication on, and then hit Enter:
Start-DedupJob -Volume Drive Letter :\ Optimization - It will now list the progress of deduplication, and the same should reflect in Server Manager.
- Once done, you can view the Deduplication Savings.
This is how you can install and set up Data Deduplication on Windows Server within minutes. As we mentioned earlier, the process is simple and quick.
Besides, if you find Configure Data Deduplication greyed out, make sure you have not selected the system drive, usually C:, because you can’t enforce the deduplication process on it.
What are the disadvantages of Data Deduplication?
Like anything else, Data Deduplication in Windows does come with a set of cons, basic factors that will affect the normal workflow or the data being worked upon. Here are a few drawbacks of Data Deduplication:
- Not useful when duplication is low: We often are enticed by the massive storage space savings from enabling Data Deduplication, but that’s not always the case. For many, the duplication is quite low, and the process doesn’t yield significant results.
- May affect performance: Although Data Deduplication ensures that reading and writing operations for the file remain unaffected, there are times when users report Windows taking a long time to open these files or work on them.
- Chances of files incorrectly being identified as duplicates: Though rare, there is always the chance of a file being incorrectly flagged as duplicates during deduplication. And this will lead to a loss of data.
- Increased probability of data corruption: When any part of the process malfunctions or the referencing is not configured correctly, there’s a high likelihood of data corruption. It will render the file useless unless you take measures to fix file corruption.
- Doesn’t work on encrypted data: Encryption and deduplication don’t work together. And encrypted data on the PC or the server won’t see any deduplication savings.
That’s all on Data Deduplication in Windows 11 and the Server edition of the OS! You can now easily enable the feature or clear duplicate files using the manual approach. But you won’t need as much effort to remove duplicate drives in Windows 11.
Before you leave, find some quick ways to remove duplicate files in Google Drive and clear duplicate photos in the iCloud library.
For any queries or to share your thoughts on the subject, drop a comment below.


























User forum
0 messages