How to Hide Local Drives Using Gpedit.msc, Registry Editor and Disk Management
The easiest way to hide the drives is by using the Group Policy Editor
3 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Ever wanted to hide specific drives on your Windows computer to keep your data secure or just to declutter your File Explorer? Using gpedit.msc and other methods, you can easily hide local drives without much hassle.
How do I use Gpedit.msc to hide local drives?
1. Hide drives using Local Group Policy Editor
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
- In the Local Group Policy Editor, go to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > File Explorer.
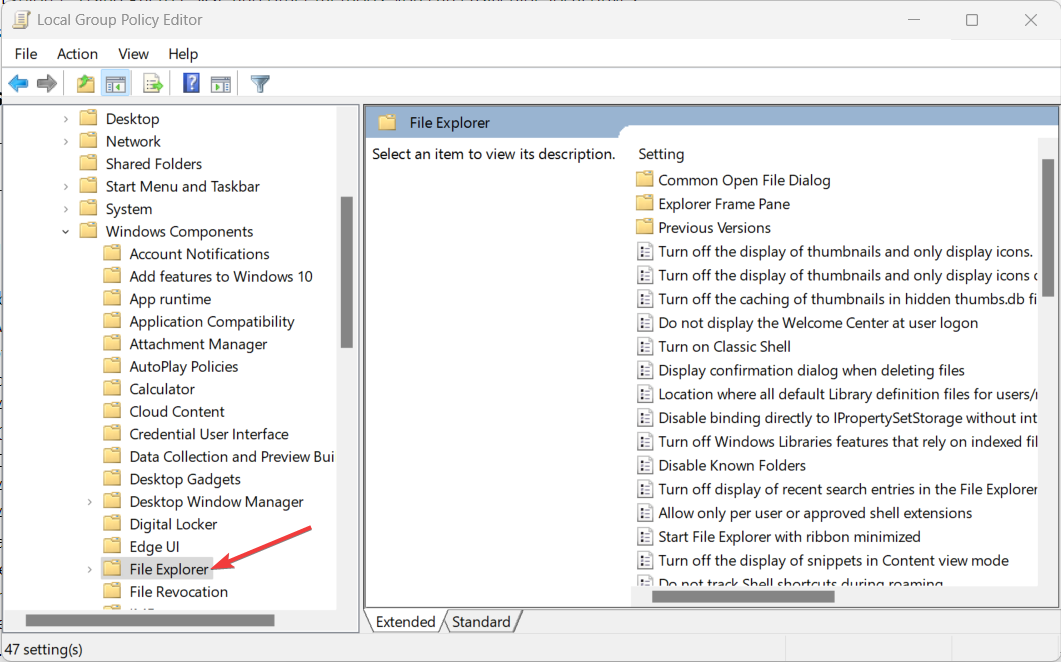
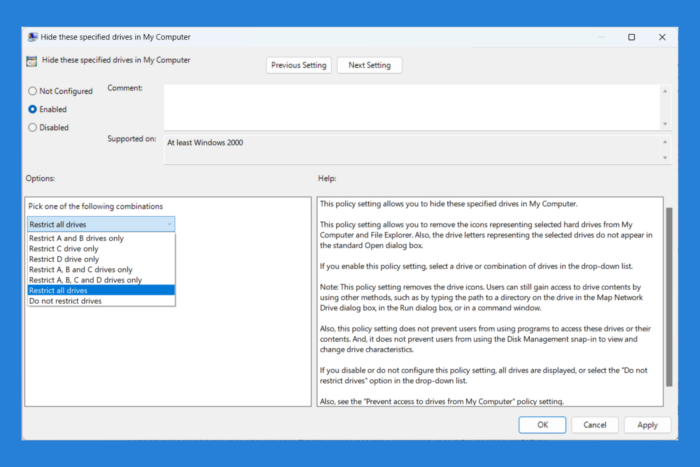
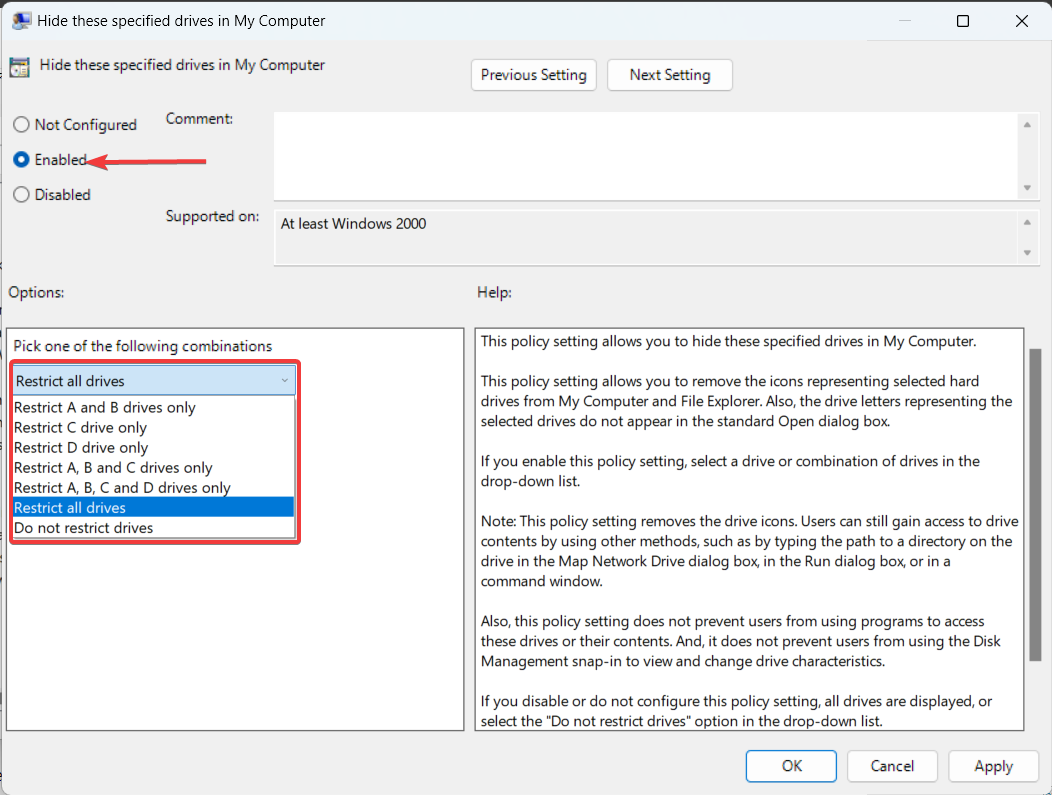
- Find and double-click on the policy named Hide these specified drives in My Computer.
- In the window that appears, select the Enabled option.
- Under the Options section, use the drop-down menu to select the drives you want to hide. Available options include:
- Restrict A and B drives only.
- Restrict C drive only.
- Restrict D drive only.
- Restrict A, B, and C drives only.
- Restrict A, B, C, and D drives only.
- Restrict all drives.
- Do not restrict drives.
- Click Apply and then OK.
- To check if the procedure worked, open File Explorer and check that the specified drives are no longer visible.
This method hides the drives from appearing in File Explorer. However, users can still access the drives through other means such as the Run command.
2. Hide drives using Registry Editor
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type regedit and press Enter.
- Navigate to the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer - Right-click on Explorer, select New, and then DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name the new DWORD as NoDrives.
- Double-click on NoDrives and select Decimal as the base.
- Enter the value corresponding to the drive you wish to hide:
- A = 1
- B = 2
- C = 4
- D = 8
- E = 16
- F = 32
- Close Registry Editor and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
This method effectively hides the specified drives and makes it harder for users to access them unintentionally.
3. Hide drives using Disk Management
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
- Right-click on the drive you want to hide and select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
- Click the Remove button and confirm the action by selecting Yes when prompted.
- Open File Explorer and check if the drive is visible.
This method removes the drive letter, effectively hiding the drive from standard user interfaces.
You may also use third-party tools such as AOMEI Partition Assistant to hide your drives. It has a graphical interface, which might be preferred by less technical users.
By following any of these methods, you can successfully hide local drives on your Windows machine, enhancing your data security and preventing unauthorized access.
You might also be interested in reading our guide on how to hide files and folders on Windows 11, because it’s much easier than hiding a whole drive.
Was our guide helpful? Let us know in the comments below.

User forum
0 messages