How to Change Domain Controller IP Address
Easy methods to change the IP address of a domain controller
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- The domain controller authenticates a user using the data stored in the Active Directory.
- Changing the IP address of a domain controller can cause issues for the administrator.
- Thankfully, this guide gives you the safe method to change the IP address of the domain controller and change the system name.

Domain Controllers (DCs) are actively used for authenticating users and the devices connected to the domain.
Because of these works, they are best set up and left as is. This becomes important in terms of their hostname and network details.
Changing the IP of the domain controller may not be ever required but a time may come when you change it.
Moreover, domain controllers are assigned to a static IP address so they are reliable and discovered across the network without any issues.
While changing the IP address of the domain controller may cause certain issues for the administrator, because of its critical nature.
However, if the DC is not hosting any other roles, changing IP isn’t a big problem and can be done easily.
In this guide, we will show you exactly how you can change the IP of the domain controller safely and with no issues. Let us get right into it.
How do I find the IP address of my domain controller?
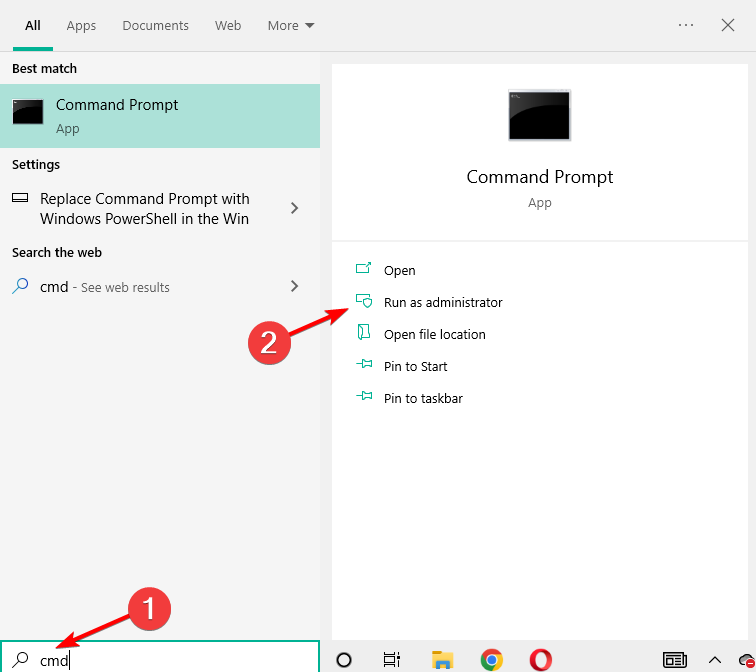
- Open the Start menu.
- Type Command Prompt and open it as an administrator.
- Execute the below command and press Enter.
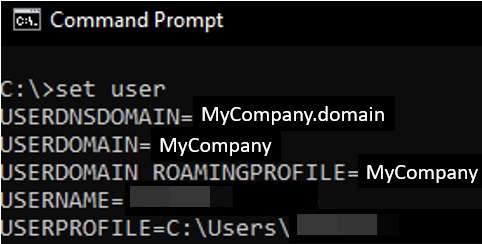
set user- If the USERDNSDOMAIN isn’t displayed then likely the server isn’t a domain member. You may want to consult with your Network Admin because it will be required in the later steps.
- You need the USERDOMAIN value for the DCDiag test.
- Type the below and press Enter.
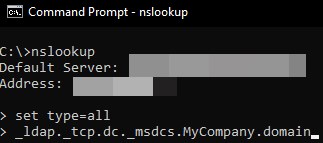
nslookup - Execute the below command and press Enter.
set type=all - Type the below command and press Enter.
_ldap._tcp.dc._msdcs.<DOMAIN_NAME>- Replace the <DOMAIN_NAME> with the USERDNSDOMAIN value you got in Step 3.
- This DNS query will display the SRV record of each domain controller.
- Check for hosts containing the same name or the same IP address. Notably, each entry should have a unique hostname and IP address.
- To exit out of nslookup, enter:
exit
Using the above steps, you would be able to find the IP address of your domain controller. The steps may look a bit too much but it is for those who know what they are doing.
How do I change the system name and IP address from the domain control network?
1. Rename the system name
1.1. Using System Properties
- Download the Remote Server Administration Tools.
- Launch the installer.
- Read and accept the license and click I accept.
- After the installation is complete, open the RSAT tool.
- On the start screen, click on Server Manager.
- Click on Change System Properties.
- Click on the Computer Name tab, and click Change.
- Hit the OK button to acknowledge the renaming.
- Under Computer Name, type the name you wish.
- Click OK.
1.2. Using Netdom
- Open the Start menu.
- Run the command prompt as an administrator.
- Execute the below command and press Enter.
netdom computername <Current computer name> /add:<New Computer Name>- <Current Computer Name>: Enter the current, or primary, fully qualified DNS name of the computer that you are renaming.
- <New Computer Name>: Enter the full qualified DNS name for the computer you are renaming.
- Type the below command to assign the new name to your PC and press Enter.
netdom computername <CurrentComputerName> /makeprimary:<NewComputerName> - Restart your PC.
- After the PC reboots, open CMD.
- Execute the below command.
netdom computername <NewComputerName> /remove:<OldComputerName>
We have shown you two methods to change the system name, i.e. one using system properties and the other one using Netdom.
Do note that whichever method you choose, you have to update the FRS object and Update the DFS Replication member object.
2. Update the FRS member object
- Open the Start menu.
- Open Windows Tools.
- Select Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Click Advanced Features in the View menu.
- Expand the domain node, System, File Replication Service, and Domain System Volume (SYSVOL share).
- The objects below Domain System Volume (SYSVOL share) are the FSR Member objects, find the object that shows the old name of the domain controller.
- Right-click the FRS Member object and click Rename.
- Type the new name of the domain controller.
3. Update the DFS Replication member object
- Open the Start menu.
- Open Windows Tools.
- Select Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Click Advanced Features in the View menu.
- Expand the domain node, System, DFSR-GlobalSettings, Domain System Volume, and Topology.
- Locate the <DomainControllerName> object showing the old name of the DC.
- Right-click the msDFSR-Member object and click Rename.
- Enter the new name of the domain controller.
4. Change the IP address of domain controller
1. Press the Windows key on your keyboard or click on the Start button on your taskbar to open the Search menu.
2. Type cmd in the search box and right-click on the first result, then select Run as Administrator.
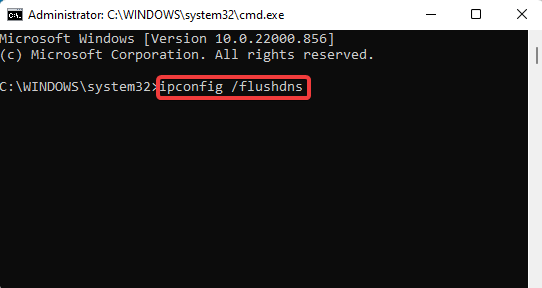
3. Write the below command and press Enter to remove any cached DNS entries created by the local DNS server:
ipconfig /flushdns4. Execute the below commands one by one and press Enter:
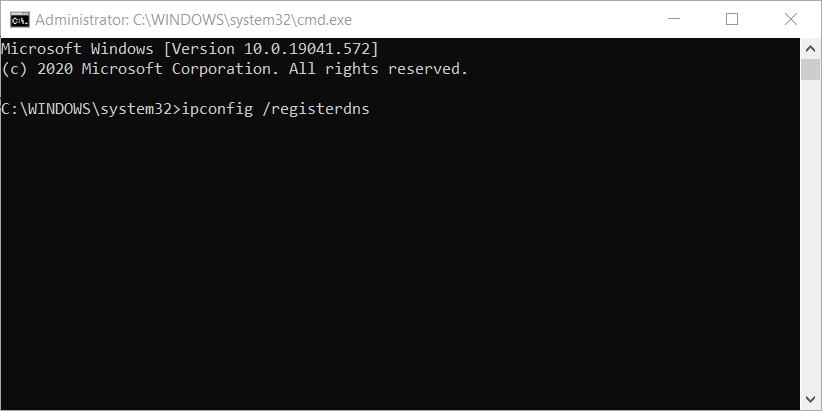
Net Stop DNSNet Start DNSNet Stop LogonNet Start Logon5. Now run the below command to ensure the new IP address is registered by the DNS server:
ipconfig /registerdns6. Finally, run the below command to update the Service Principal Name (SPN) records:
dcdiag /fix
The Domain Controller’s IP can be easily changed via the built-in command tool known as Command Prompt or cmd. All you need to do is input a few commands in it, and the tool will do the job for you.
Is a domain controller the same as Active Directory?
We won’t give you complex terminologies as we want you to understand terms easily. An Active Directory is like a database. It stores information of users and computers as objects.
On the other hand, the domain controller is a service that runs Active Directory and uses the data stored by the AD for authentication and giving access to the user. Notably, a DC or domain controller manages the security policies of Windows NT or Windows Server.
So, the easiest way to remember the difference between Active Directory and DC is that Active Directory handles your identity and security access, on the flip side the Domain Controllers authenticate your authority.
That is it from us in this guide. We hope that we gave you the complete information on how you can change the IP of the domain controller. Let us know in the comments below if you come across any issues while following the above steps.



User forum
0 messages