How to Create a Self-Signed Certificate in Windows 10
Use a command-line tool or third-party software
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- The process of adding an SSL certificate to your website is pretty straightforward, and this guide will help.
- We also discuss the 3 most efficient ways to either purchase an SSL certificate, use an open-source SSL, or create your own.
- One of the best ways to generate a self-signed certificate in Windows 10 is to do so via a command line.

Adding an SSL certificate to your website is a straightforward process. You can either purchase a third-party SSL certificate and renew it on a yearly basis or use an open-source SSL certificate and create a corn job to renew it every month.
However, for development and testing, you can explore the possibility of creating a self-signed SSL certificate in Windows.
Creating a self-signed certificate is an excellent alternative to purchasing and renewing a yearly certification for testing purposes. You can make use of OpenSSL to generate a self-signed certificate for this purpose.
In this article, we explore how to create a self-signed certificate in Windows 10. The later part of the article also explores how to deploy the self-signed certificate to client machines.
Quick Tip:
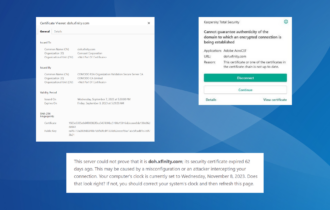
Although you can save some money if you create a self-signed certificate, it may lead to a permanent block of your website for some users. This is caused by the certificate error message and in most cases cannot be undone.
Besides that, the process is time-consuming and really not worth your time which also has a certain cost. We strongly recommend using a 3rd party SSL service provider.

GoDaddy SSL Certificates
GoDaddy is one of the best web hosting providers that also offers affordable SSL certificates.How can I generate a self-signed certificate in Windows 10?
1. Use OpenSSL to create a self-signed certificate
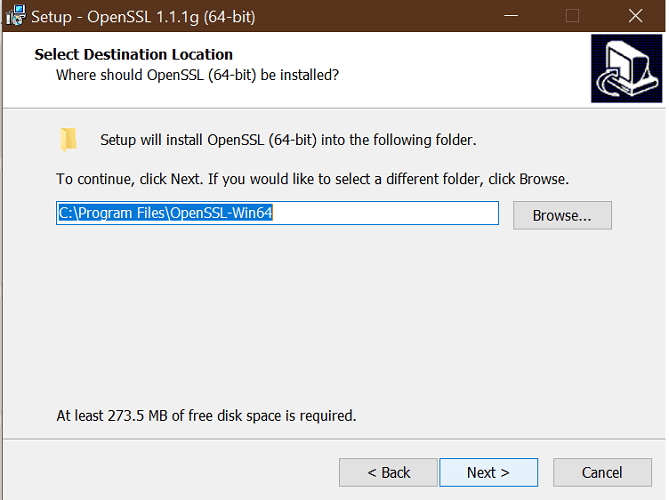
1.1 Install OpenSSL
- Download the latest OpenSSL windows installer from a third-party source.
- Run the installer. OpenSSL requires Microsoft Visual C++ to run. The installer will prompt you to install Visual C++ if it is already not installed.
- Click Yes to install.
- Run the OpenSSL installer again and select the installation directory.
- Click Next.
- Open a command prompt and type OpenSSL to get OpenSSL prompt.
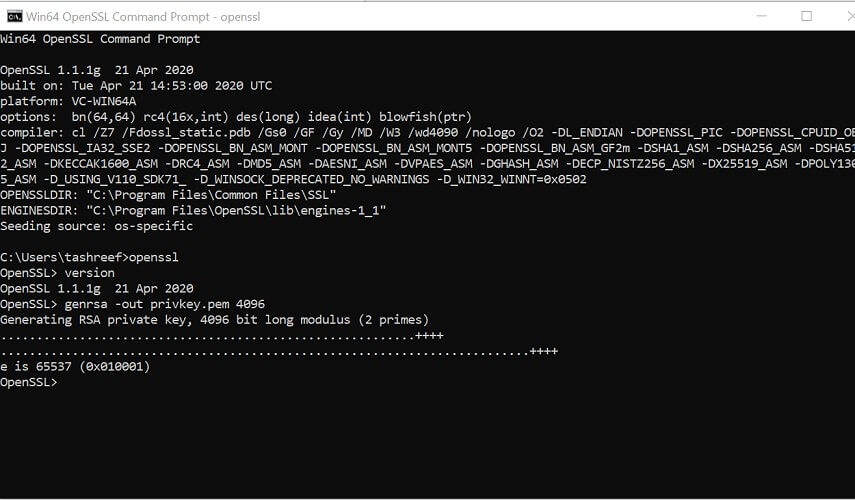
1.2 Create a public/private key file pair
- Make sure you have OpenSSL installed.
- Open Command Prompt and create a new directory on your C drive:
C: >cd Test - Now go to the new directory:
C: Test> - Now you need to type the path of the OpenSSL install directory followed by the RSA key algorithm.
C: Test>c:opensslbinopenssl genrsa -out privkey.pem 4096 - Run the following command to split the generated file into separate private and public key files:
C: Test>c:opensslbinopenssl ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f privkey.pem
Once you have the public/private key generated, follow the next set of steps to create a self-signed certificate file on a Windows system.
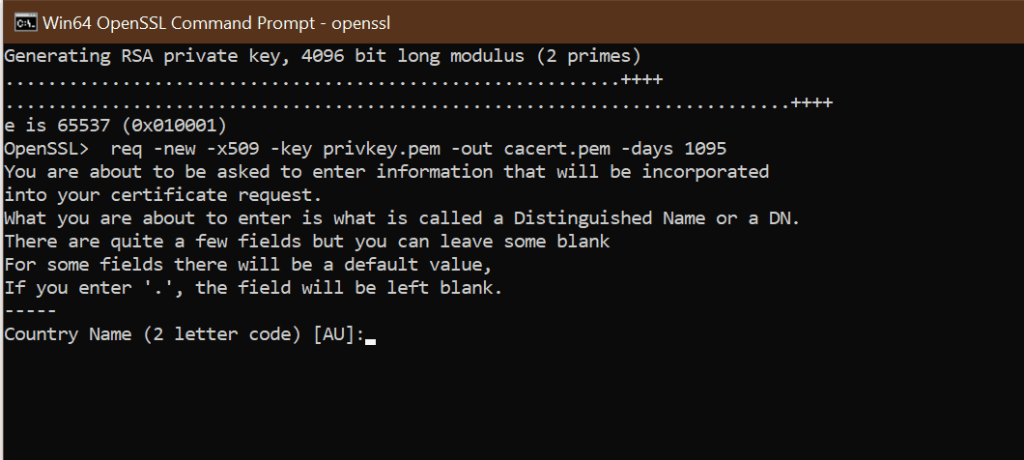
1.3 Generate a self-signed certificate
- Open a Command Prompt window.
- Go to the directory that you created earlier for the public/private key file.
C: Test> - Enter the path of the OpenSSL install directory, followed by the self-signed certificate algorithm:
C: Test>c:opensslbinopenssl req -new -x509 -key privkey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 1095
- Follow the on-screen instruction.
- You need to enter information about your organization, region, and contact details to create a self-signed certificate.
If you would rather use PowerShell to create a self-signed certificate, follow the next set of steps instead.
2. Generate a Self-Signed Certificate on Windows using PowerShell
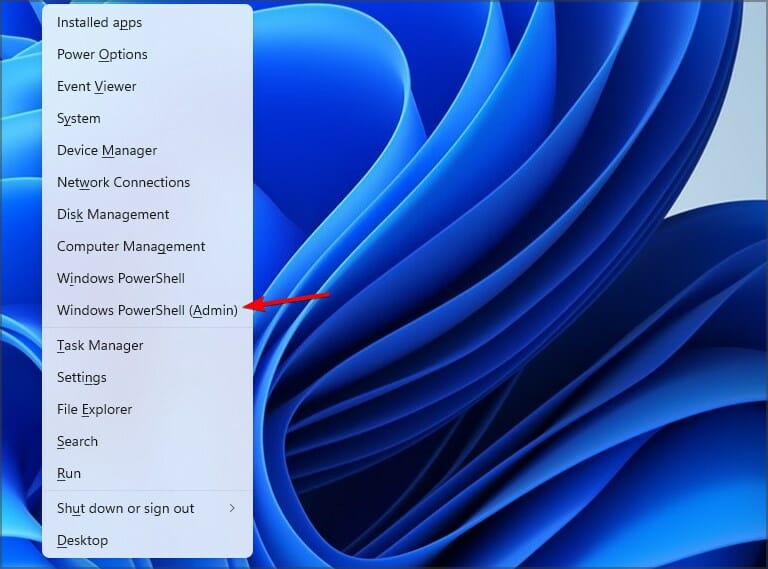
1. Press the Windows key, and type Powershell in the search box. Right-click on the PowerShell app and select Run as Administrator.
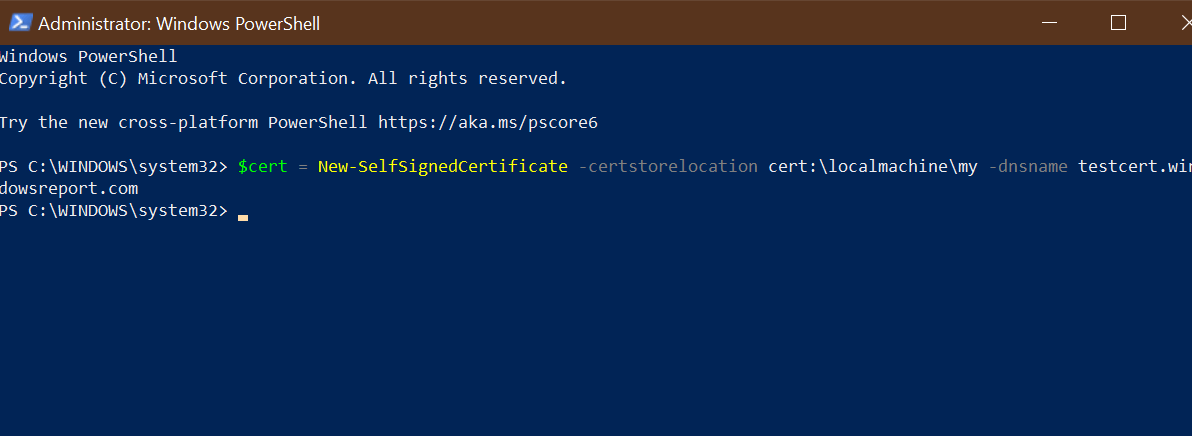
2. Run the New-SelfsignedCertificate command, as shown below:
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -certstorelocation cert:localmachinemy -dnsname testcert.windowsreport.com3. This will add the certificate to the locater store on your PC. Replace testcert.windowsreport.com with your domain name in the above command.
4. Next, create a password for your export file:
$pwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String ‘password!’ -Force -AsPlainText5. Replace Password with your own password.
6. Enter the following command to export the self-signed certificate:
$path = 'cert:localMachinemy' + $cert.thumbprint Export-PfxCertificate -cert $path -FilePath c:tempcert.pfx -Password $pwd7. In the above command replace c:temp with the directory where you want to export the file.
8. You can import the exported file and deploy it for your project.
Another great option to generate a self-signed certificate on Windows 10 is to use a command-line tool such as Powershell.
With it, you don’t need to download any third-party software. You just need to input the appropriate command line in Powershell, and the tool will do the job for you.
How to add my self-signed certificate into the curls ca file on Windows 10?
- Once you have created a self-signed certificate and installed it, you may want cURL to trust the certificate as well.
- The later versions of cURL don’t include a trusted listed a .pem file. You can download the .pem file and type the following command in the php.ini file.
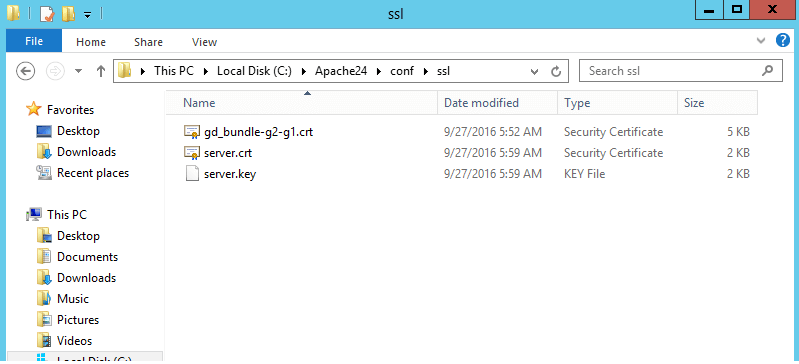
curl.cainfo = "C:xamppphpcacert.pem" - Once done, you need to get cURL to trust your self-signed certificate. To do this, open your server.crt file. The file is created when you created your self-signed certificate.
- Copy all the content of the server.crt file and then add it to the cacert.pem file.
Creating a self-signed certificate using OpenSSL can be done using the Command Prompt or PowerShell. Being able to create your self-signed certificate allows you to create a temporary certificate for in-development projects that require an SSL certificate.
We hope you managed to generate a self-signed certificate on your Windows 10 PC. Let us know in the comments section which method you prefer to use.

User forum
0 messages