Event ID 1002: How to Fix This Application Hang Error
Get back your unresponsive apps and ensure good performance
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- On the surface, Event ID 1002 is a Windows 11 error that looks really difficult to solve because of how generic it is.
- The causes of this error could be almost anything from some random computer virus to an app that was badly installed.
- Fortunately, fixing this Event ID is pretty easy to do and can be done by running the right DISM commands.
Event ID 1002 is an error that occurs when an app just sort of hangs there. It doesn’t do anything, nor does it register any interaction before suddenly crashing.
This is actually a pretty common problem, and it can affect a wide variety of apps like Microsoft Outlook. And because it’s so common, there are a ton of fixes with this guide focusing on the best ones.
What causes Event ID 1002 to appear?
Before going into the weeds of the solutions, it’s important we break down what actually causes the problem in the first place.
Because Event ID 1002 is such a generic error, it’s pretty difficult to pin it down to exactly one. However, here are the likely culprits:
- Your computer is infected with malware: Fixing this will require you to use antivirus software, but the question is, which one? There are six particular antivirus tools, such as TotalAV, which reign supreme.
- Something on your Windows machine is corrupt: The problem either be corrupt files or an entire directory. Regardless of what it is, there are tools you can install to clean up your PC.
- Windows Firewall may be interrupting the process: If an app comes from a third-party source, your firewall may think it’s not legit. We recommend giving the app firewall permissions to bypass this.
How can I fix and stop Event ID 1002 from appearing?
There are a handful of things you can do before diving into the more complex solutions. This first batch can honestly be all done in a few seconds; several minutes at most:
- Restart your computer. This is the tried and true method of fixing the vast majority of problems on any Windows machine. Try this out and see if the problem is gone. Take immediate action if your PC is stuck on restarting.
- Disable your antivirus. As important as having an antivirus app is, it’s been reported that it can actually interrupt important processes.
- Reinstall the offending app. If there’s one particular app that’s constantly hanging, something may have gotten corrupted during the initial installation.
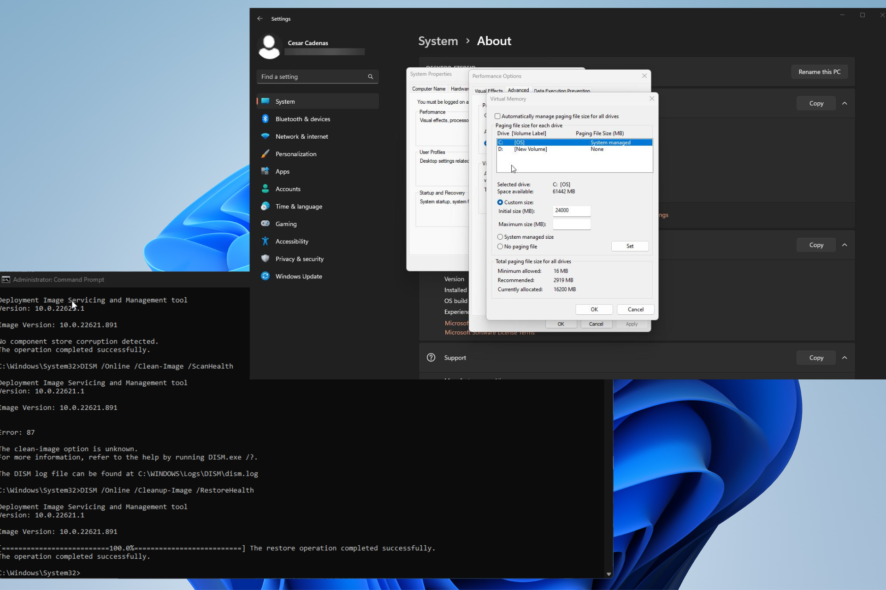
1. Adjust virtual memory in the Settings menu
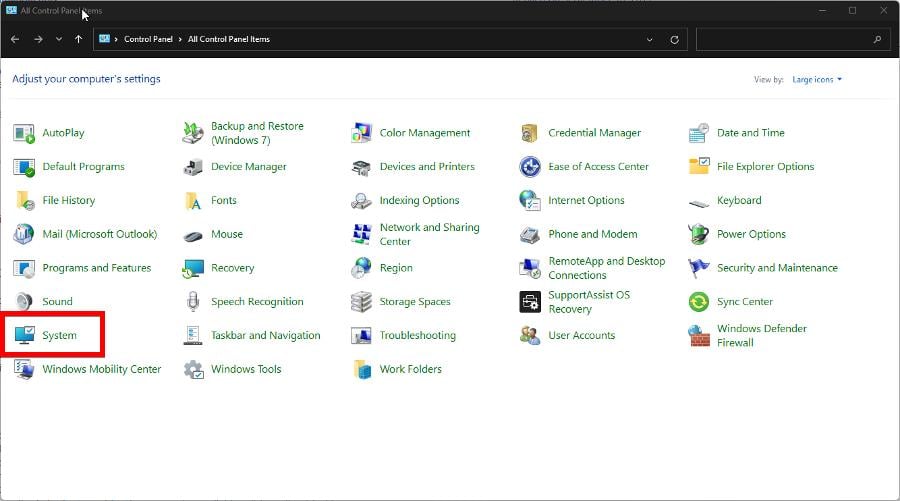
- Open the Control Panel and click System. Make the View By entry in the upper-right corner set to Large Icons.
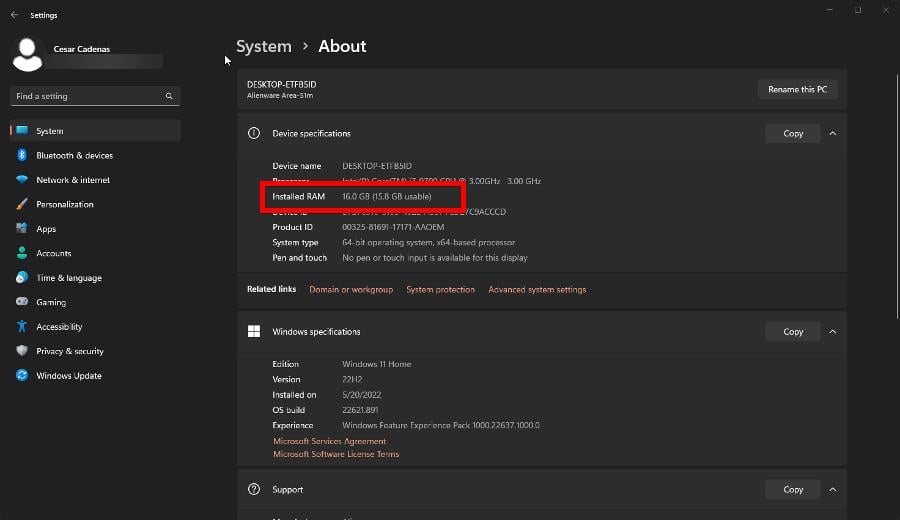
- In the new window that appears, take note of how much RAM you have installed on your computer. In this case, it’s 16 GB (16,000 MB).
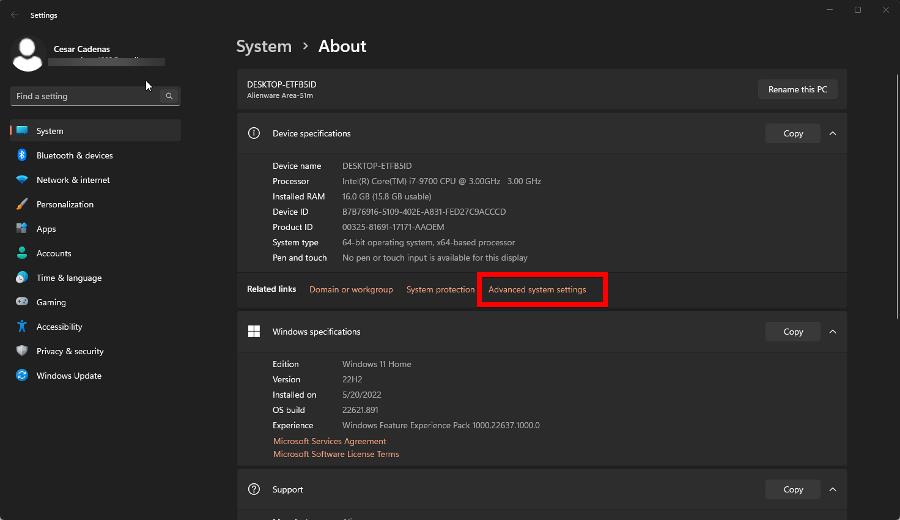
- Click Advanced system settings under Device Specifications.
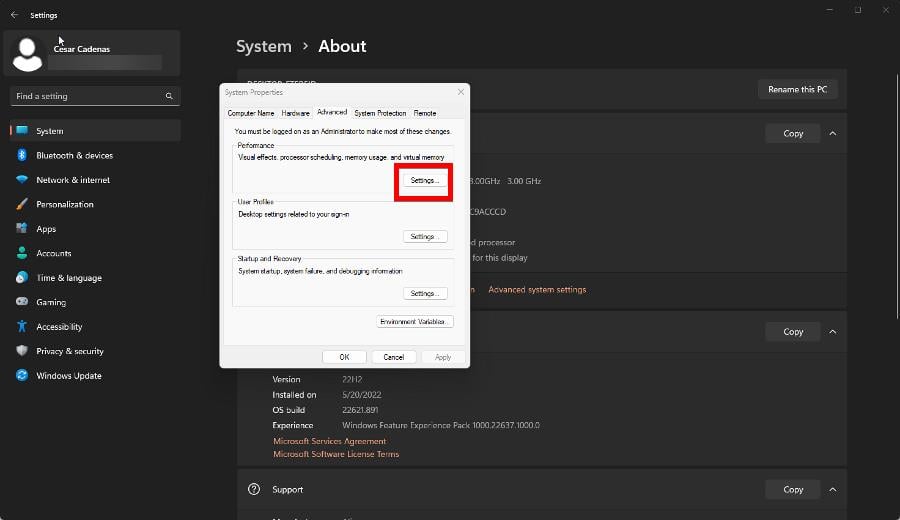
- Go to the Advanced tab, then click Settings under Performance.
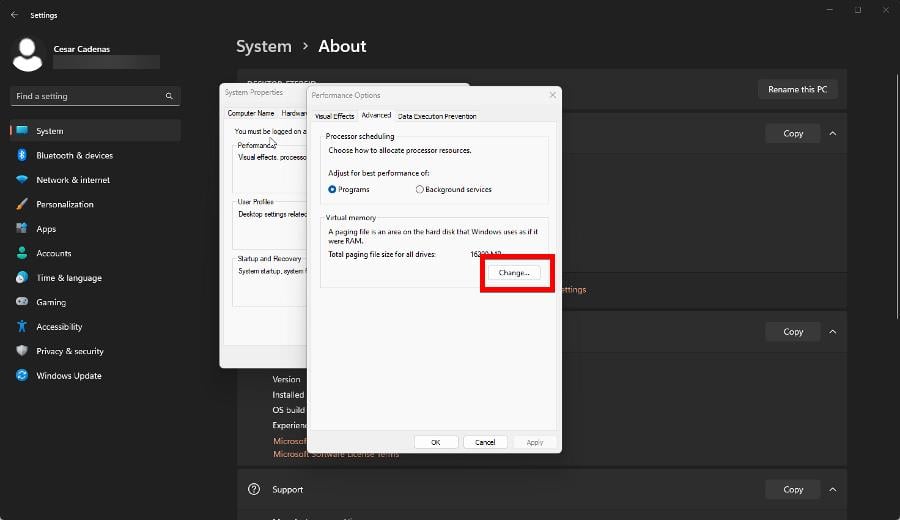
- Go to the Advanced tab in this new window, then click the Change button under Virtual Memory.
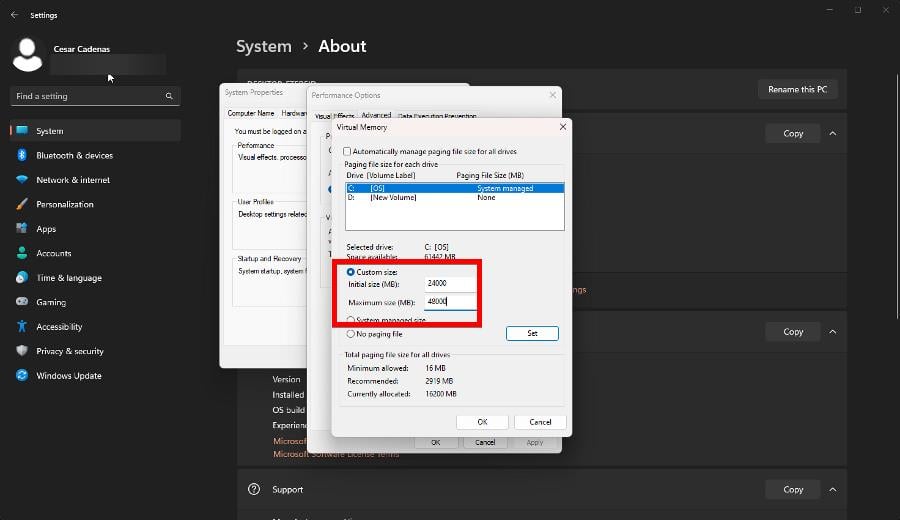
- In this new window, deselect the box next to Automatically manage paging file size for all drives in if it’s enabled.
- Click Custom size. You will now have to enter the megabyte amount for the paging file.
- Enter the amount of RAM you have times 1.5 in Initial Size. In this example, it’s 24,000MB.
- For Maximum, enter triple the amount of RAM.
- Click OK, then restart your computer.
2. Run ipconfig commands in the Command Prompt
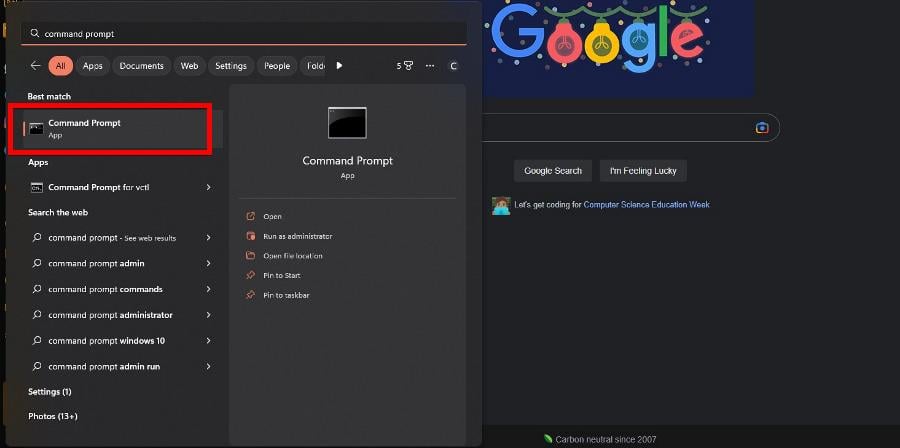
- Bring up the Command Prompt on Windows Search and select Run as administrator.
- Type in the following commands, and after each one, press Enter:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
This particular solution is mainly meant for DHCP-enabled computers. You can still use it on other types of machines to see if that works.
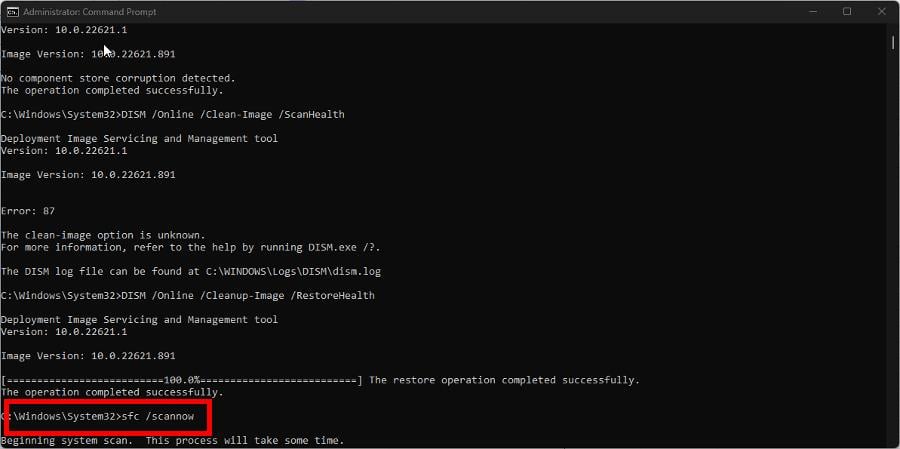
3. Run SFC and DISM commands to clean up
- Open Command Prompt again and run it with the same administrator permissions as before.
- Type the following commands, and after each one, press Enter:
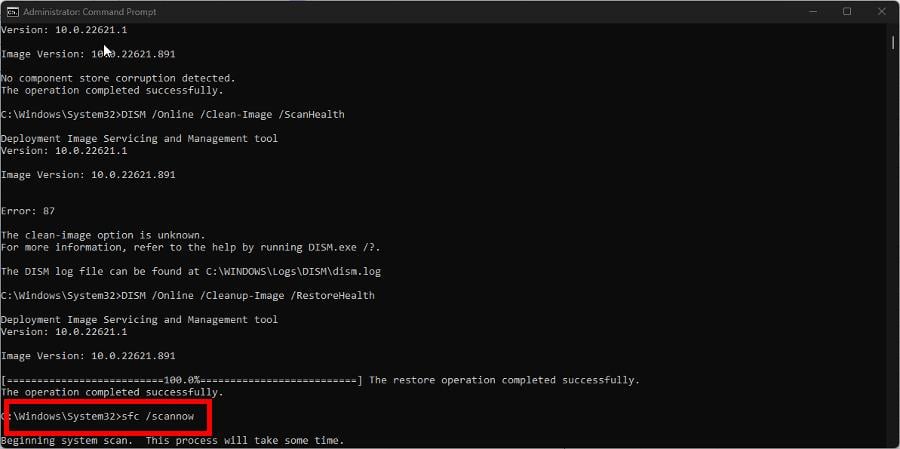
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealthDISM /Online /Clean-Image /ScanHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Once done, enter the following command to finish up:
sfc /scannow
Another great method is to run this scan using a third-party tool that specializes in system file checking.
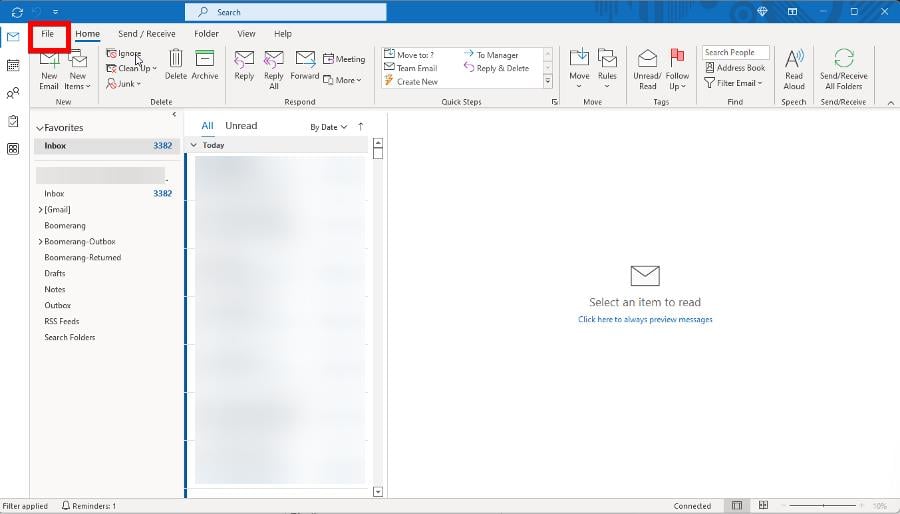
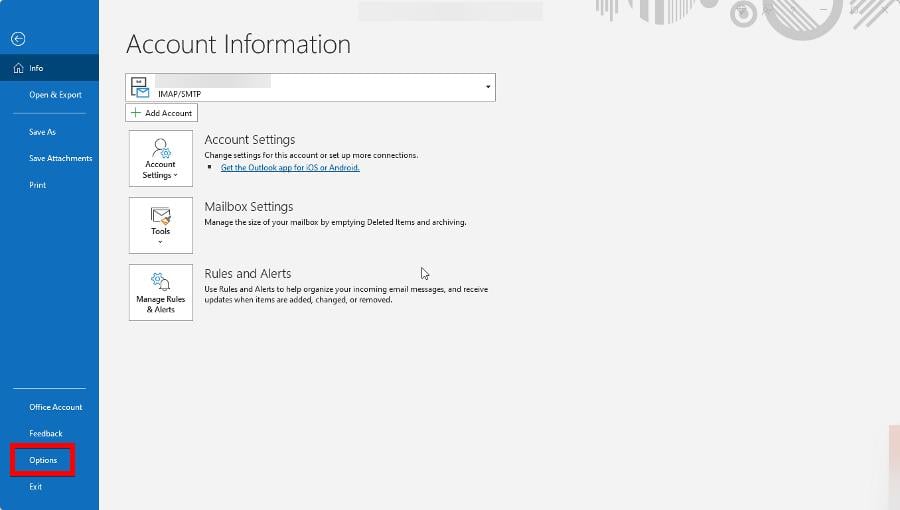
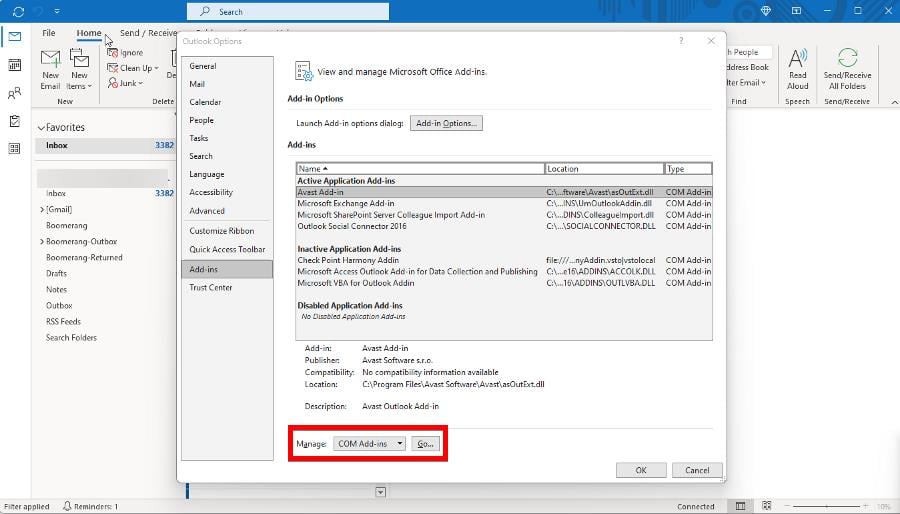
4. Disable Add-ins on Outlook
- Open Outlook and click File in the upper-left corner.
- Click Options in the bottom left.
- In the Outlook Options window, click Add-ins on the left.
- Click the Go button next to the Manage section.
- Highlight one of the Add-ins and select Remove on the right.
Microsoft Outlook gets a specific solution to itself because it’s known to commonly have the hanging problem, and the other fixes don’t always work. We also recommend reinstalling Outlook.
What are other Windows 11 Event IDs and how can I fix them?
Windows 11 has a variety of Event IDs for specific errors. One of which is Event ID 1000, which is very to 1002 because of its generic nature.
It appears whenever apps crash, but it’s exactly what causes it. Either way, we recommend scanning the registry and reinstalling the Microsoft NET Framework to fix this problem.
Then there’s Event ID 7023, which is caused by the Connected Devices Service terminating and causing a system crash. You can run an SFC scan, as seen in this guide, or perform a clean boot to address this.
Feel free to comment below if you have questions about other Windows 11 errors. Also, leave comments about guides you’d like to see information on other Windows 11 Event IDs or features.