Can't run Windows 11? Windows 10 21H2 might be close enough
7 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- If you can't or won't try Windows 11 yet, Microsoft comes with an alternative.
- The next feature update for Windows 10 version 21H1 will be, of course, 21H2.
- Preview build 19044.1147 is available for testing only for some Windows Insiders.
- Some Insiders means those who were moved from the Beta Channel to the Release Preview Channel because their PC did not meet the hardware requirements for Windows 11.

If you still haven’t jumped on the Windows 11 bandwagon yet, there is some exciting news for you. Microsoft has decided to release a new version of Windows 10, called 21H2, which will be the next feature update for this OS.
As a part of this launch event, if we may call it that way, the Redmond-based tech company also releases Windows 10 21H2, build 19044.1147 (KB5004296).
A new update is coming to Windows 10
Speaking of this new preview build, which is 19044.1147, Microsoft stated clearly that it will only be available to some Insiders.
We are talking about the ones who were moved from the Beta Channel to the Release Preview Channel because their PC did not meet the hardware requirements for Windows 11.
Also worth knowing is that this build will be released via Microsoft’s seeker experience in Windows.
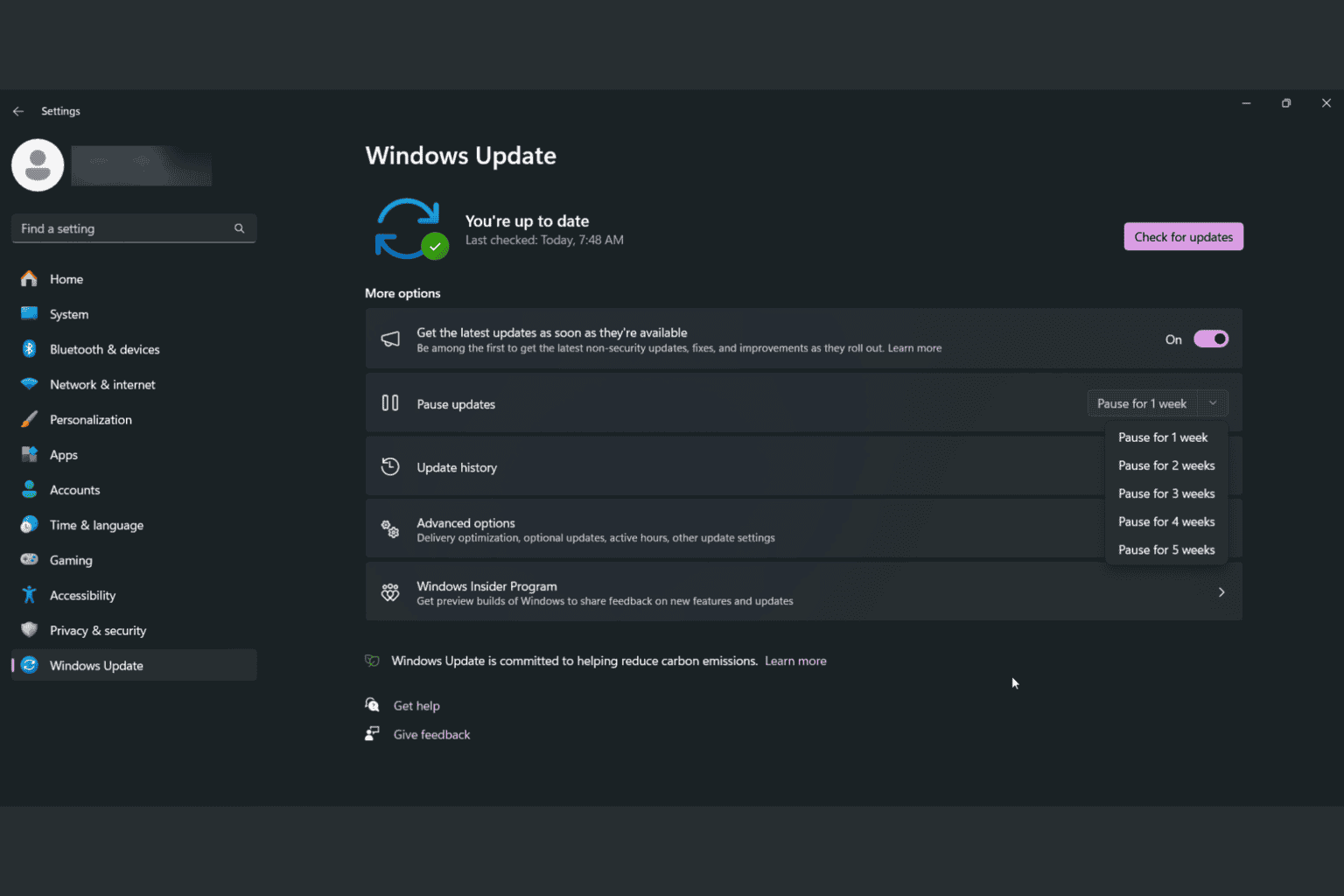
In order to install the new software, the above-mentioned Insiders will need to go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and choose to download and install 21H2.
Some of the new features that revolve around security, management, and productivity, include:
- WPA3 H2E standards support for enhanced Wi-Fi security
- Windows Hello for Business supports simplified passwordless deployment models for achieving a deploy-to-run state within a few minutes
- GPU compute support in the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and Azure IoT Edge for Linux on Windows (EFLOW) deployments for machine learning and other compute intensive workflows
What other changes has Microsoft made through 21H2?
As with any update to an existing version, the tech company has to come with some new upgrades, features, or even services.
So, in order for Windows 10 to take the leap from 21H1 to 21H2, Microsoft has designed and applied the following changes:
- Fixed an issue with searchindexer. After you sign out, searchindexer continues to hold handles to the per user search database in the profile path, “C:\Users\username\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\\”. As a result, searchindexer stops working and duplicate profile names are created.
- Fixed an issue that prevents gaming services from opening certain games for desktop users.
- Fixed an issue that prevents you from entering text using the Input Method Editor (IME). This might occur, for example, after startup if you have set the power options to shut down a laptop by closing its lid.
- Changed the functionality for uploading new activity into Timeline. If you sync your activity history across your devices using your Microsoft account (MSA), you cannot upload new activity into the Timeline. You can still use Timeline and see your activity history (information about recent apps, websites, and files) on your local device. This does not affect Azure Active Directory (AAD) accounts. To view web history, Microsoft Edge and other browsers provide the option to view recent web activities. You can also view recently used files using Microsoft OneDrive and Microsoft Office.
- Fixed an issue that might cause the File Explorer window to lose focus when you are mapping a network drive.
- Fixed an issue that causes File Explorer to stop working after reaching 99% completion when you are deleting many files on a mapped network drive.
- Fixed a timing issue in the Group Policy Registry Telemetry that causes Group Policy extension processing to fail.
- Fixed an issue that repeatedly rebuilds the Windows Filtering Platform (WFP) filters. This issue occurs when a device is enrolled in a mobile device management (MDM) service and “MDMWinsOverGP” is set.
- Fixed an issue with an MDM service that fails to correctly apply certain junk mail rules.
- Fixed an issue that always reports the update build revision (UBR) as zero (0) on a device during enrollment to an MDM service.
- Fixed an issue that causes the enrollment of the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) certificate to fail with the error, “0x80090027 NTE_INVALID_PARAMETER”. This issue occurs when the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) provider (the Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider) stores the key.
- Fixed an issue with auditing events 4624 and 5142 that display the wrong event template when Dutch is the display language.
- Fixed an issue that causes System Integrity to leak memory.
- Fixed an issue that plays the sound for selecting something in a game loudly when you press the trigger button on a game controller.
- Fixed an issue that prevents power plans and Game Mode from working as expected. This results in lower frame rates and reduced performance while gaming.
- Fixed an issue in which “Network Internal Access” appears on the taskbar network icon on systems that access the internet from certain domains.
- Fixed an issue in which the Network Connectivity Status Indicator (NCSI) fails to detect internet connectivity after you connect to a virtual private network (VPN).
- Fixed an issue that causes printing to stop or prints the wrong output. This issue occurs when you print using a USB connection after updating to Windows 10, version 2004 or later.
- Fixed a rare issue that might degrade performance in applications that call Gdiplus.dll!GdipMeasureString in a tight loop with a new font on each call. This issue occurs after installing Windows updates released on and after February 2021.
- Fixed an issue that incorrectly routes some audio channels when streaming using certain fixed channel layouts.
- Fixed an issue that always displays devices that RemoteFX USB redirects as “Remote Desktop Generic USB Device” instead of the actual device name.
- Fixed an issue in which Set-RDSessionCollectionConfiguration does not set the camerastoredirect:s:value custom property.
- Fixed a Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) domain controller memory leak that is reported in Privileged Access Management (PAM) deployments.
- Fixed an issue that prevents you from accessing a network drive that maps to a Distributed File System (DFS) root after you sign out.
- Fixed an issue that prevents you from reconnecting to mapped network drives after you sign in and displays an access denied error. This issue occurs if you use the net use /deep option to create multiple drive mappings to different paths on the same encrypted file share.
- Fixed an issue that prevents access to files on a Server Message Block (SMB) share when you enable Access Enabled Enumeration (ABE).
- Fixed an issue that prevents the Windows Server service from starting if SrvComment is greater than 128 characters.
- Fixed an issue in the Windows Network File System (NFS) client that might prevent you from renaming a file after mounting an NFS share. This issue occurs if you rename the file using File Explorer but does not occur if you rename the file using command line.
- Fixed an issue with an unhandled Open File dialog critical exception. As a result, Microsoft Foundation Class (MFC) applications might close unexpectedly.
- Fixed an issue in which the Storage Sense page in Settings might incorrectly report the size of some storage devices that use the GUID Partition Table (GPT). The affected devices will incorrectly report in Storage Sense that the size is twice as large as the size reported in File Explorer. Note: This issue does not affect storage devices that use a master boot record (MBR).
Know that, once an Insider updates their PC to Windows 10, version 21H2, they will continue to automatically receive new 21H2 updates through Windows Update using Microsoft’s servicing technology.
If you want to check if you’re running Windows 10, version 21H2, just type winver into the Windows search box on the Taskbar. It should show as Version 21H2.
Have you already tried the new build? Share your experience with us in the comments section below.






User forum
2 messages