How to Enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS [For Different Versions]
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- TPM is a Windows 11 requirement, so it's important to know how to enable TPM 2.0 from BIOS.
- The process is simple and it's almost the same for both AMD and Intel devices.
- By enabling this feature, you'll enhance the security of your PC and protect it from malware.

TPM is a security feature and a Windows 11 requirement that has been a center of controversy because it’s required if you want to install the latest OS.
Luckily, most modern PCs support this feature, but many users with older PCs don’t have it. As a result, their PCs are ineligible for the Windows 11 upgrade.
When it comes to those computers that support it, users don’t know how to enable it properly, and we can’t blame them since this setting is hidden in BIOS.
In our older guides we showed you how to enable TPM in BIOS ASRock and today you’ll discover how to enable this feature on other motherboard brands.
How does TPM work?
TPM is a physical chip on your PC designed to protect the computer. By using it, you’ll ensure that only approved software can boot it, so it will protect your PC from bootloader malware.

In addition, this device is used for full-disk encryption, and it holds the cryptographic key needed to access your drive.
To learn more about it, we suggest reading our Windows 11 and TPM article for in-depth information.
What are the different types of TPM?
There are several types of TPM, and discrete TPM is the most secure choice since it’s separated from other hardware.
Many manufacturers use the integrated version that is added to other chips. Firmware-based versions are also popular, and they run in a trusted execution environment on your CPU.
Hypervisor TPMs are designed to run in an isolated exclusion environment inside of a virtual machine. The last type is software version, but they are considered vulnerable.
To learn about different versions, we suggest reading our TPM 1.2 vs 2.0 guide for a side-by-side comparison.
How can I enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS?
1. Enable TPM 2.0 in ASUS BIOS
For Intel motherboards
- While your system boots, keep pressing Del.
- Navigate to the Advanced section.
- Head over to PCH-FW Configuration.
- Locate PTT and set it to Enable.
- Select OK when the notice appears.
- Now press F10 to save changes.
- Restart your PC.
For AMD motherboards
- Keep pressing the Del key while your system boots.
- When you access UEFI, go to the Advanced section.
- Now head over to the AMD fTPM configuration section.
- Locate TPM Device Selection, and set it to Firmware TPM.
- Press F10 to save changes and restart your PC.
2. Enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS on Dell
- While your device boots, keep pressing the F2 key.
- Expand the Security section.
- Select TPM 2.0 Security.
- Make sure that TPM On is checked and Enabled is selected.
- Save changes and restart your PC.
3. Enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS on HP
- Keep pressing F10 while your PC boosts.
- Once you enter BIOS, head over to the Security tab.
- Locate TPM State and set it to Enabled.
- Save changes and restart your computer.
4. Enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS on Lenovo
- Keep pressing F2 to enter BIOS while your system boots.
- Once you enter, go to the Security section.
- Locate Intel Platform Trust Technology or AMD Platform Security Processor and set it to Enabled.
- Press F10 to save changes.
- Restart your PC.
How to check if my PC has TPM?
- Press Windows Key + X and select Device Manager from the list.
- Expand the Security devices section.
- If the devices in this section are enabled, it means that your PC has TPM support.
To check if TPM is enabled, do the following:
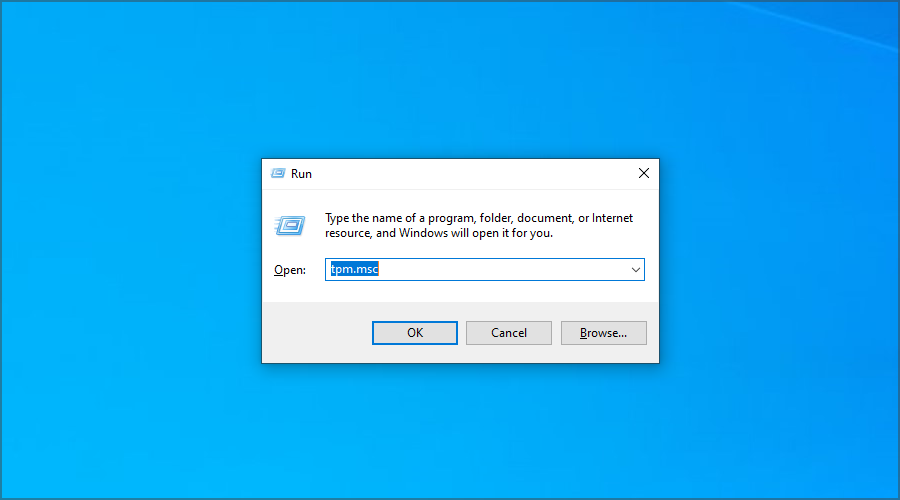
- Press Windows Key + R.
- Type tpm.msc and press Enter.
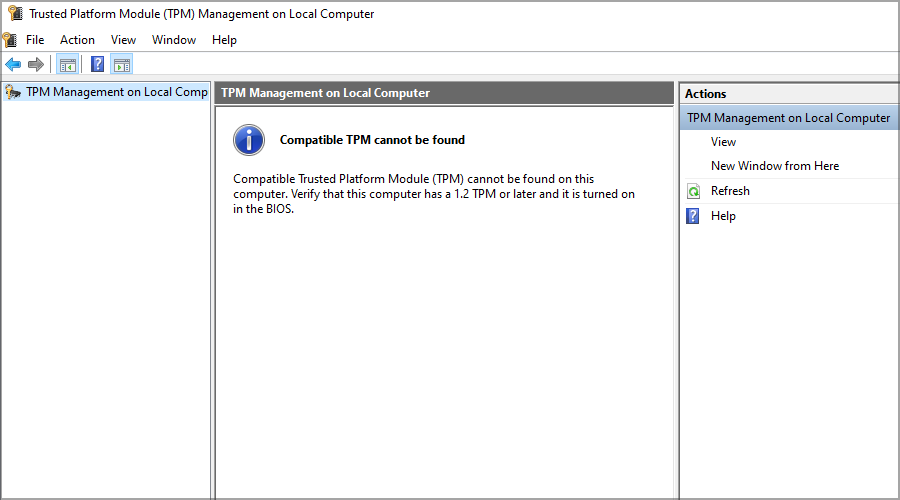
- In the new window, you should see if your TPM is enabled.
Does Windows 11 require TPM?
Yes, the OS requires TPM to install, and this has sparked a lot of controversy among users because not all older devices support this feature.
However, there are ways to install Windows 11 without TPM, but if you choose to do that, your PC might be susceptible to malware attacks.
In this guide, we showed you how to enable TPM 2.0 in BIOS on different motherboard brands. As you can see, the process is quite similar, regardless of the brand you’re using.
However, do keep in mind that CPU manufacturers use different terminology for TPM, so keep an eye out, especially if you’re using Intel.
Did you manage to enable TPM using the instructions from this guide? If so, feel free to let us know in the comments section below.













User forum
0 messages