STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE 0xC0000218 [Solved]
Performing startup repair is the simplest fix

The STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE BSoD (Blue Screen of Death), with error code 0xC0000218, appears when Windows can’t load a critical Registry file/hive required for booting.
This usually happens due to corruption in the Registry, corrupted system files, outdated or buggy drivers, and a malfunctioning memory module or storage drive.
Before you head to the solutions, reboot the PC, disconnect non-critical hardware, and remove any overclocking, if configured.
How can I fix the STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE Windows blue screen?
1. Perform a startup repair
- On the error screen, turn off the PC, then power it on, and as soon as Windows starts loading, hold the Power button to turn it off. Repeat this thrice, and on the fourth attempt, Windows should enter Automatic Repair.
- Let the scan run and if it then reads, Automatic Repair couldn’t repair your PC, click on Advanced options.
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Again, click on Advanced options.
- Click the Startup Repair option.
- Select your user account from the list.
- Enter the password for the selected user account, click on Continue, and let Startup Repair run and fix issues preventing Windows from loading.
- Once done, try booting Windows and check for improvements.
When faced with the STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE Windows blue screen error, the easiest solution, and the one recommended by Microsoft, is to run Startup Repair. It basically fixes issues preventing Windows from loading, including problematic Registry hives!
2. Run the SFC and DISM scans
- Enter the Recovery Mode in Windows, and click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Advanced options.
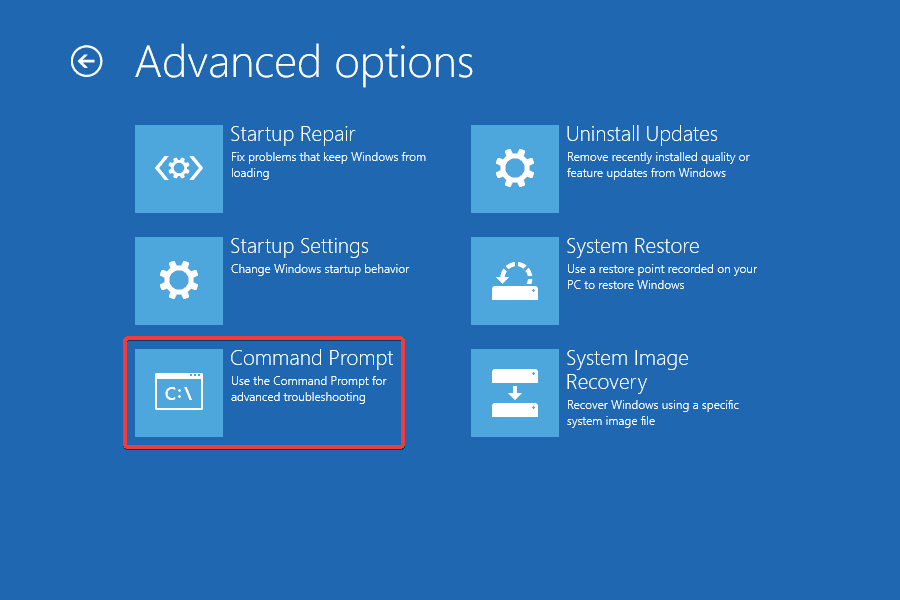
- Click on Command Prompt.
- Select the primary user account from the list and then enter the password for it.
- Once the Command Prompt opens, paste these DISM commands individually and hit Enter each:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Now, run this SFC scan command:
sfc /scannow - After the scans are run, boot Windows normally and verify whether it now loads without triggering STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE.
Corrupted system files are a common reason behind the blue screen error. To fix this, you must run the DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) and SFC (System File Checker) scans, which will replace all problematic files with their cached copies stored on the PC!
3. Perform a system restore
- Enter the Windows RE (Recovery Environment), and click on Troubleshoot.
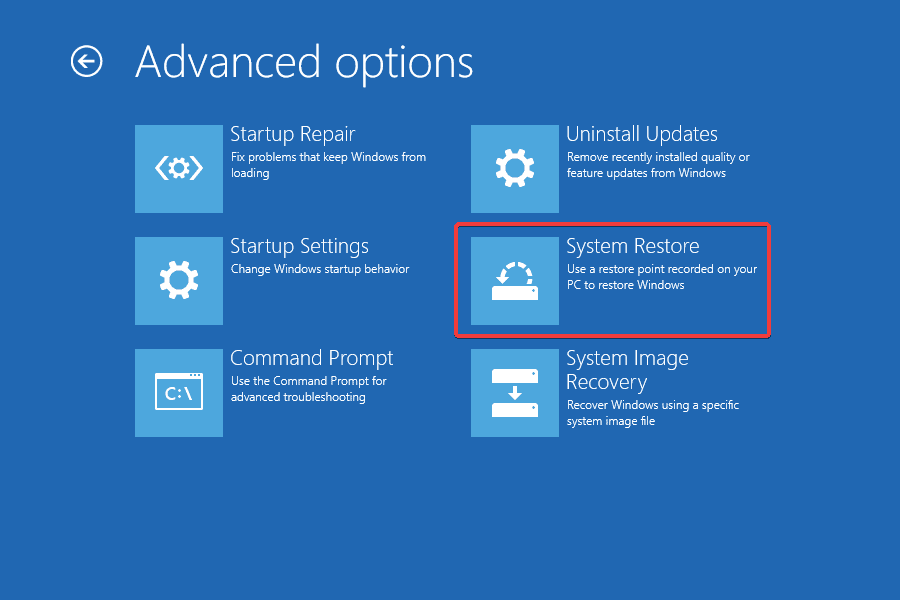
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click on System Restore.
- Select the primary user account and enter the password for it, if prompted.
- Click on Next to proceed.
- Select a restore point created before the issue first appeared, and click on Next.
- Verify the restore details and click on Finish.
- Click Yes in the confirmation prompt.
- Wait for the system restore to complete. It may take 15-45 minutes.
- Once done with the restore, boot Windows normally and verify whether the error STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE 0xC0000218 is fixed.
4. Uninstall conflicting drivers
- Boot Windows into Safe Mode from the recovery environment.
- Press Windows + X to open the Power User menu, and select Device Manager.
- Look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark or the ones that recently had a driver update, right-click on them individually, and select Uninstall device.
- Tick the checkbox for Attempt to remove the driver for this device, and click on Uninstall.
- After uninstalling the drivers, exit the Safe Mode, boot Windows normally, and check for improvements.
5. Repair disk issues
- From the Windows Recovery Environment, click on Troubleshoot, and then Advanced options.
- Click on Command Prompt, select the user account, and enter the password for it.
- Now, paste this command and hit Enter:
chkdsk /r - If asked to schedule the scan for the next reboot, press Y and hit Enter to confirm.
- Now, restart the computer and let Check Disk repair issues with the storage drive.
In several cases, it was seen that issues with the storage drive, primarily parts where Registry files were stored, triggered the STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE blue screen in Windows. Here, running Check Disk will allow you to repair the drive and fix issues like bad sectors.
6. Check for problems with RAM
In my experience, problems with the RAM are just as likely to be the underlying cause behind STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE. So, you will have to run the built-in RAM-repair tool, Windows Memory Diagnostic, from the Safe Mode in Windows.
When that doesn’t work, I recommend using Memtest86+, an advanced RAM-testing tool that runs checks on individual memory modules and detects even the smallest of problems. If issues are detected, replace the malfunctioning module and check for improvements.
7. Reinstall Windows
If the STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE BSoD persists, the last option is to reinstall Windows from scratch. Since there’s a chance of data loss, I recommend you move critical files from the PC to external storage in Safe Mode.
To reinstall Windows, connect a USB flash drive to another PC > go to Microsoft’s official website > download the Media Creation Tool > use it to create a bootable Windows USB > plug the flash drive into the affected PC > change the boot order to the USB drive > load the Windows setup and proceed with the reinstall.
One of these solutions must have helped with STATUS_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE in Windows. If the problem remains unresolved, the hardware is, most likely, malfunctioning, and in this case, it’s best that you visit a local repair shop and get the hardware components inspected for faults.
Before you leave, discover all the causes of BSoD and take suitable measures to prevent it from reappearing!
We covered a similar registry issue in our ERROR_CANNOT_LOAD_REGISTRY_FILE article, so don’t miss it.
For any queries or to share more fixes with our readers, drop a comment below.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more













User forum
0 messages