FAT32 vs NTFS: Which Format is Best for System Reserved Partition?
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Microsoft System Reserved Partition holds the Boot Configuration Database, Boot Manager Code, and Windows Recovery Environment.
- Different formats can be used for System Reserved Partitions, including FAT and NTFS.
- You can use Windows Disk Management Tools to configure System Reserved Partitions.

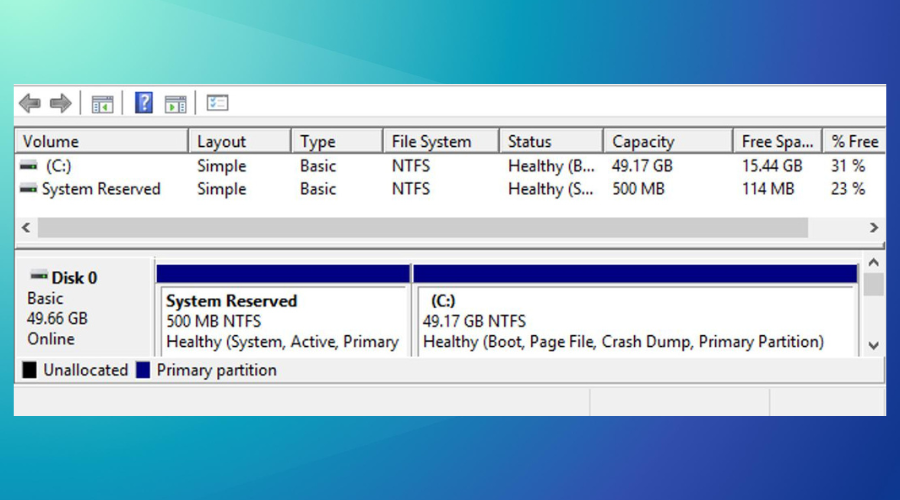
The System Reserved Partition fat32 or NTFS is a Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11 system partition. It is created during a clean install of the respective operating systems. Computers use the Fat32 and NTFS to store files.
The NTFS file system can store individual files of different sizes. However, the system reserved partition for Fat32 cannot store more than 4GB of individual file sizes.
What format is Microsoft Reserved Partition?
The Microsoft System Reserved Partition uses the NTFS format. Its primary purpose is to hold the Boot Configuration Database, Boot Manager Code, and Windows Recovery Environment. It also keeps space for startup files such as the BitLocker Drive Encryption.
Does the EFI partition have to be FAT32?
Computers adhering to UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) use the EFI system partition. Most of the time, its capacity is approximately 100MB to 500MB. It contains system utility programs, device driver files, boot loaders, and other data files.
The operating system loads these files at boot time when Windows starts. Therefore, you must format the EFI partition to FAT32. Always remember this when creating the EFI partition. If not, you might get an NTFS error. An example is Windows detected that the EFI system partition was formatted as NTFS when installing Windows OS.
Do you format system reserved partition?
You do not need to format a system reserved partition. As discussed above, these partitions play a crucial role when booting the Windows operating system or even during recovery. If you format the partitions, you will not be able to boot your operating system.
However, if they contain no boot components, you can use Windows disk management tools such as EaseUS Partition Master to format or even delete them.
Which is better, NTFS or FAT?
The most straightforward file system between the two is FAT. However, NTFS comes with increased security and multiple enhancements. So, for system reserved partition, FAT32 or NTFS?
- Security: NTFS allows users to set their permissions. FAT comes with only shared permission, creating a FAT security vulnerability.
- Fault tolerance: FAT will keep different copies of the files in case of file damage. NTFS repairs the damaged files automatically. This makes NTSA better for System Reserve Partition.
- Compression: You can compress your folders and files with NTFS. However, you cannot do the same with the FAT file system.
- Compatibility: The FAT file system is compatible with most versions of the Windows OS. The NTFS file system is compatible with Windows XP and later versions of the OS.