5 Ways to Fix Group Policy When It Keeps Reverting
Policy changes are a necessity and here's how to make yours stick
4 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Group Policy can be a powerful tool for managing your Windows environment, but it may also be a bit of a pain when it comes to troubleshooting.
- If your changes cannot be saved and keep reverting to previous settings, you could have a case of corrupt Group Policy settings on your hands.
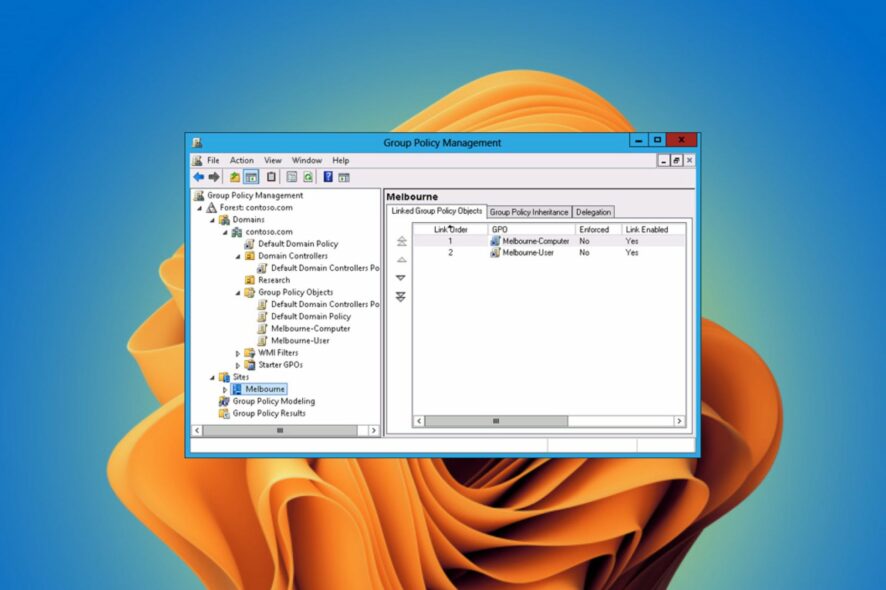
Have you encountered an issue where Group Policy keeps reverting? It turns out that this is a common issue. Group Policy settings in Windows are used to keep devices up-to-date and compliant with settings.
However, at times, Group Policy is stuck at applying, or the Local Group Policy keeps reverting your changes. This is no fun at all, but let’s look at ways to make your changes long-lasting, shall we?
Why do Group Policy settings keep reverting?
If you have been working with Group Policy for a while, you may have noticed that now and then, it seems like the policies don’t stick. After applying Group Policy changes, the next time you log in, the policies have reverted to their previous state.
Wondering why this happens? Here are a few reasons:
- Policies are not applied correctly – The most common cause of this issue is that policies are not applied correctly. If you have a lot of domain controllers, there can be delays in applying the policies due to replication. This can result in the policies being applied on one domain controller but not another.
- Incorrect permissions – To apply Group Policy, your user account must have permission to edit group policies on the target computer. If you don’t have permission to perform this operation, any changes made through group policies will be lost until they are applied again by an administrator account.
- Conflict in GPOs – The Group Policy settings you have created for your domain can be managed using a tool called the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). This tool allows you to manage the GPOs in your domain and view their settings. If there is a conflict between two GPOs in your network, GPMC will display an error message and revert the GPOs.
- Corrupt user profile – If your user profile is corrupted then this can cause issues with group policies. In order for group policies to work properly, all users must have their profiles configured correctly. If any of your users’ profiles are corrupt, then group policies won’t be applied correctly and will need to be reverted back to their default state.
So let’s look at how we can fix it.
How can I fix Group Policy when it keeps reverting?
Before you start troubleshooting Group Policy, it’s important to perform preliminary checks to ensure that the problem isn’t something else. To do this, follow these steps:
- The first thing you should do is check the time on your computer. If it’s off by more than a few minutes, it can cause problems with Group Policy.
- Ensure you are using an administrator account. For more insight, check out the difference between an administrator and a standard account.
- Boot Windows in Safe Mode and check whether the problem is resolved. This helps when a non-critical service or third-party process is the underlying cause.
- Create a new user account in Windows and set it as an administrator. The latter is just as important since it provides the required privileges to make changes on the PC.
If none work, head to the solutions listed next.
1. Refresh policy settings
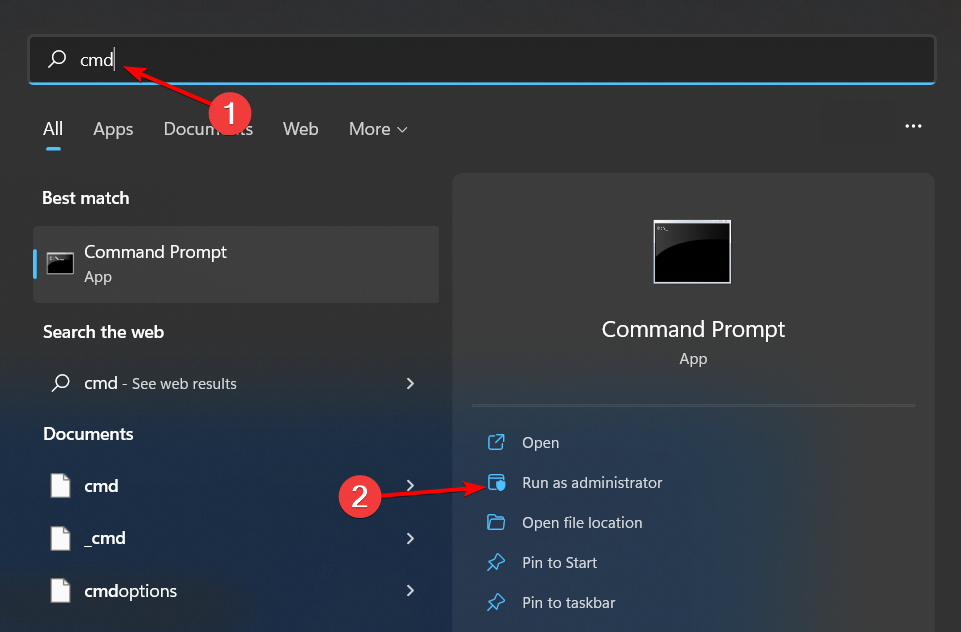
- Hit the Windows key, type cmd, and select Run as administrator.
- Type in the following command and press Enter:
GPupdate/force
2. Reset Group Policy Editor
- Hit the Windows key, type cmd, and select Run as administrator.
- Type in the following commands and press Enter after each one:
RD /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicyUsers" && RD /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicy"gpupdate /force - Restart your PC.
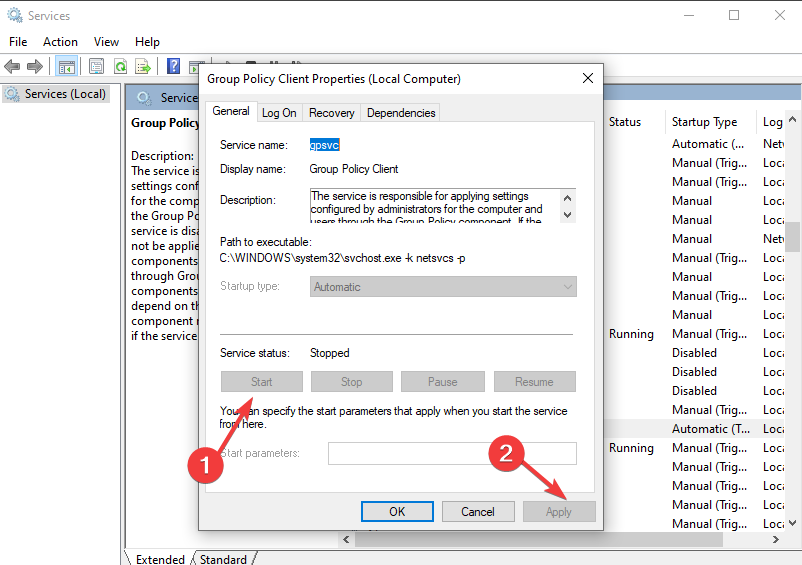
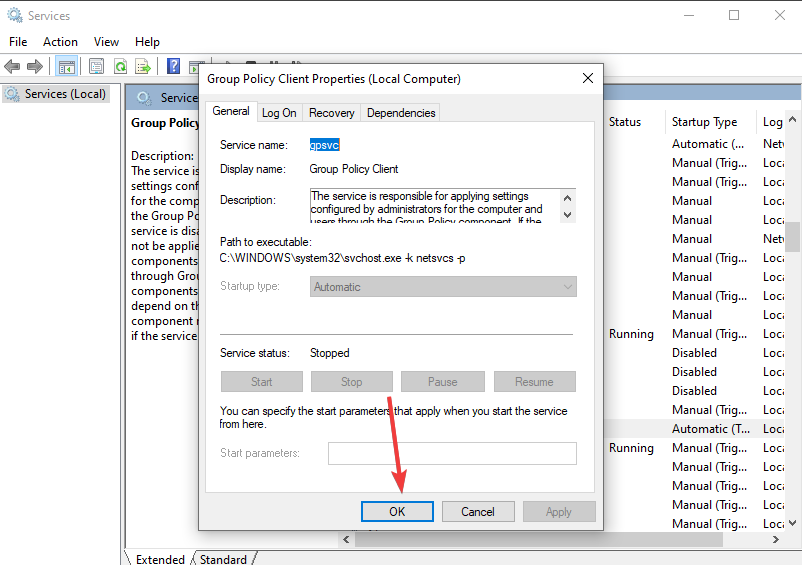
3. Restart Group Policy Service
- Press the Windows + R keys simultaneously to open the Run command.
- Type in services.msc, then press Enter.
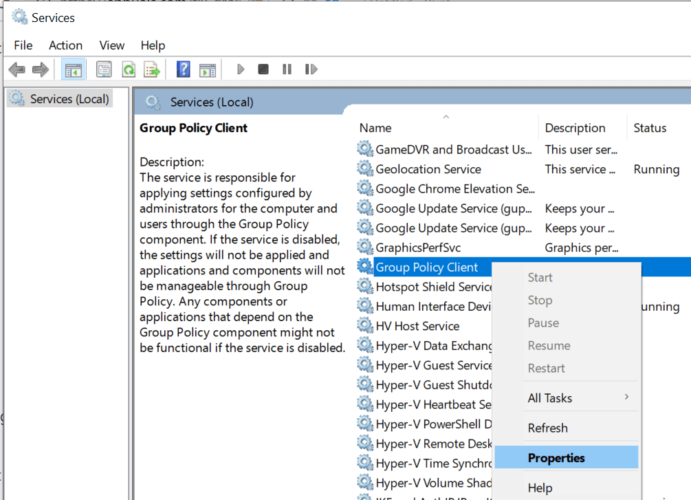
- Navigate to the Group Policy Client, right-click and select Properties.
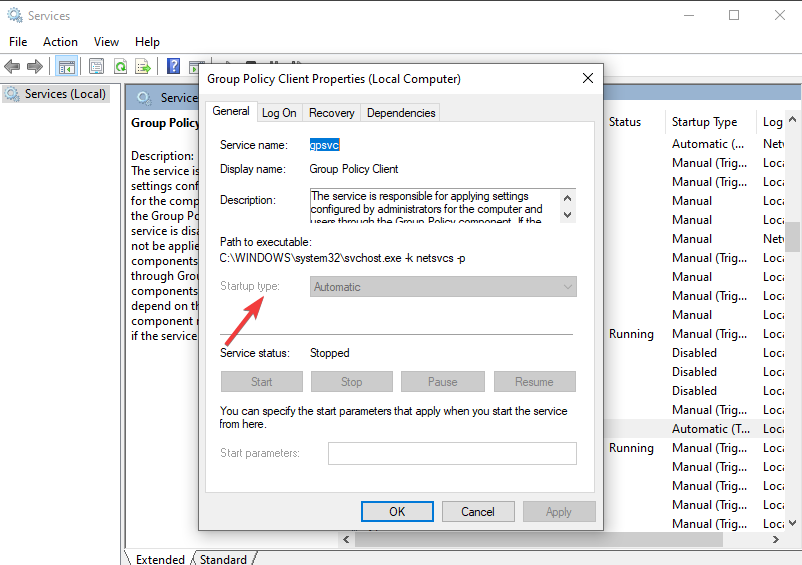
- Select the General tab and change the Startup type to Automatic.
- Click on Start, then Apply.
- Hit OK to save the changes.
4. Use GPMC to troubleshoot
GPMC is a great tool for managing Group Policy in your network environment. If you have already installed it but aren’t using it regularly, spend some time learning how to use it properly — it will make managing Group Policy much easier.
One such way is that it can gather information and help troubleshoot why Group Policy keeps reverting and other related issues.
You may also encounter an issue where Group Policy is slow in generating reports, but we have covered how to boost speed in our detailed guide.
Also, check out what steps you should take if you find out that your version of Windows doesn’t have the Group Policy Editor.
Let us know whether you have been able to resolve this issue in the comments section below.



User forum
0 messages