We Couldn't Update the System Reserved Partition [Windows 11 Fix]
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- The System Reserved Partition typically stores your device’s boot and encryption information. If it gets too populated, then you are bound to encounter some errors.
- If you are running a new Legacy install, bypassing the Windows 11 requirements, the partition may be too small.
- Fixing SRP-related errors can easily be done with the system’s built-in tools or third-party software.
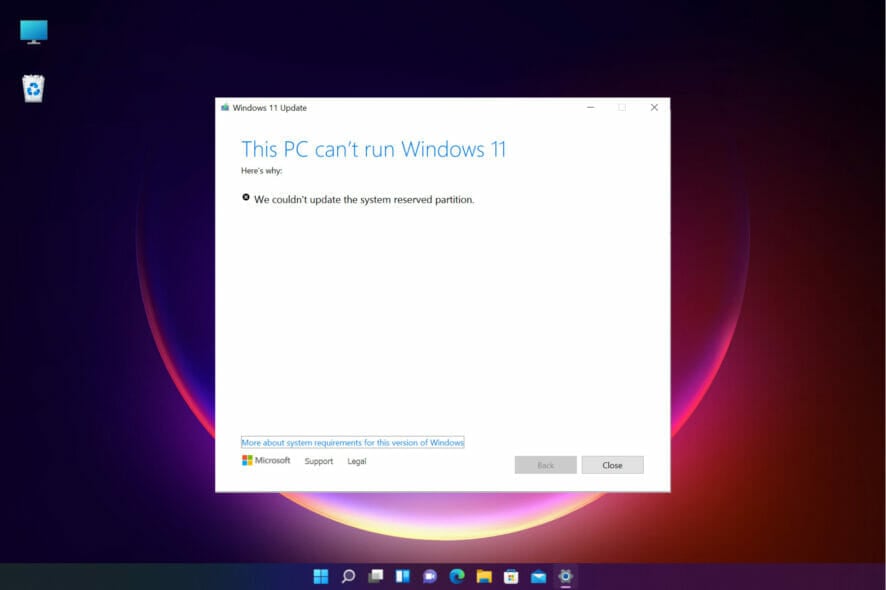
When updating Windows 11 or upgrading from Windows 10 to Windows 11, you might encounter the error We couldn’t update system reserved partition.
This might be accompanied by error codes 0xc1900104, 0x800f0922, or 0xc1900201.
What is causing the System Reserved Partition error?
This may be caused by a full System Reserved Partition (SRP) that can’t be written into anymore.
Additionally, some third-party security and antivirus applications write into the SRP and can quickly fill it up. Dual-booting with Linux could also be the reason for the error.
Also, if you are running a new Legacy install, bypassing the Windows 11 requirements, you may have a System Reserved Partition with only 50 MB, too small.
What is the Function of the System Reserved Partition?
The SRP is a hidden partition in the system drive that contains crucial boot and system recovery information.
The data includes boot manager code and boot configuration data as well as the startup files used for BitLocker Drive Encryption. In Windows 10, recovery environment data is also stored in this partition.
 NOTE
NOTE
What can I do if Windows 11 couldn’t update the system reserved partition?
1. Find out what is your partition type
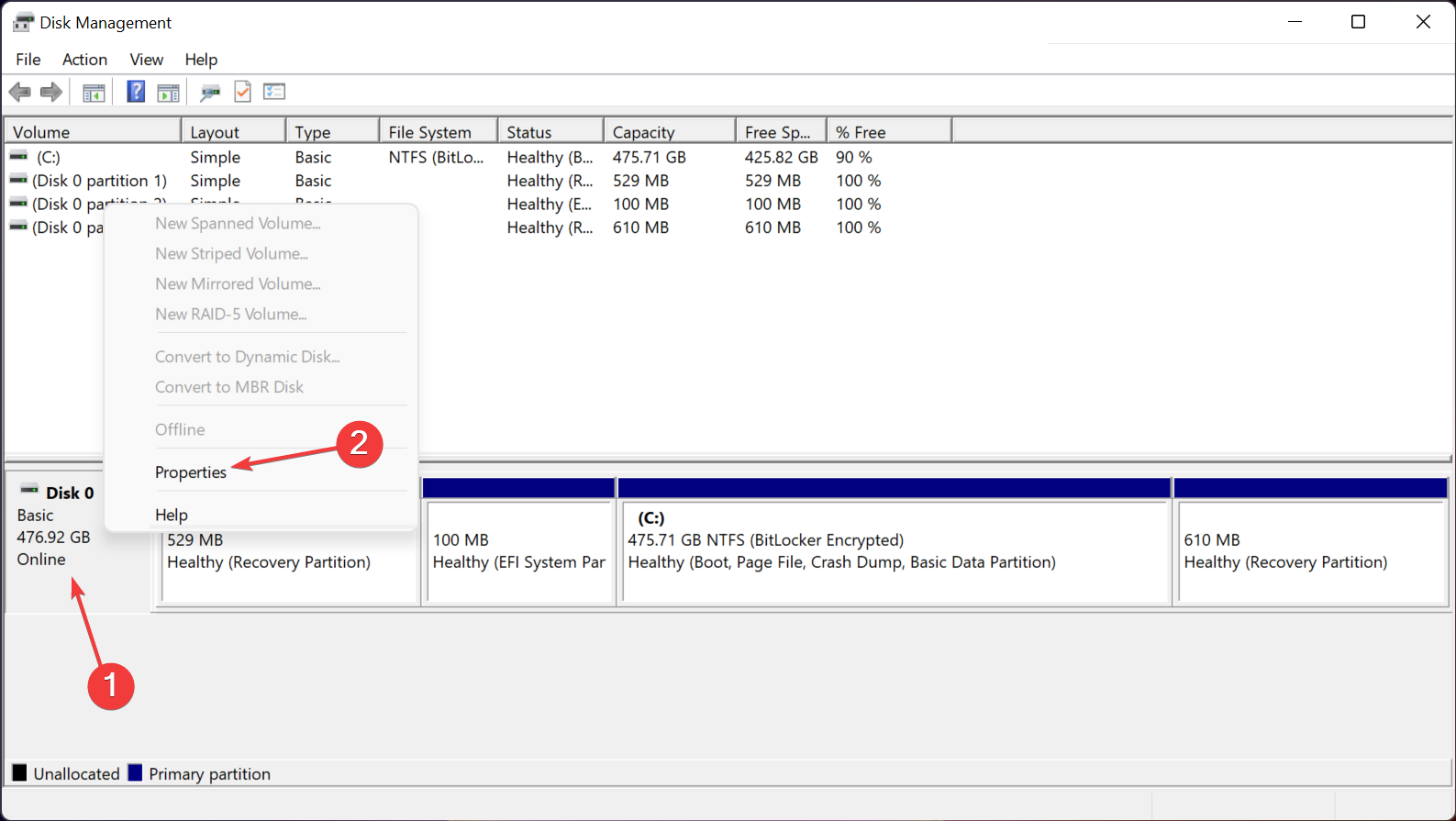
- Right-click the Start button and select Disk Management from the list.
- Now, right-click your main partition and select Properties.
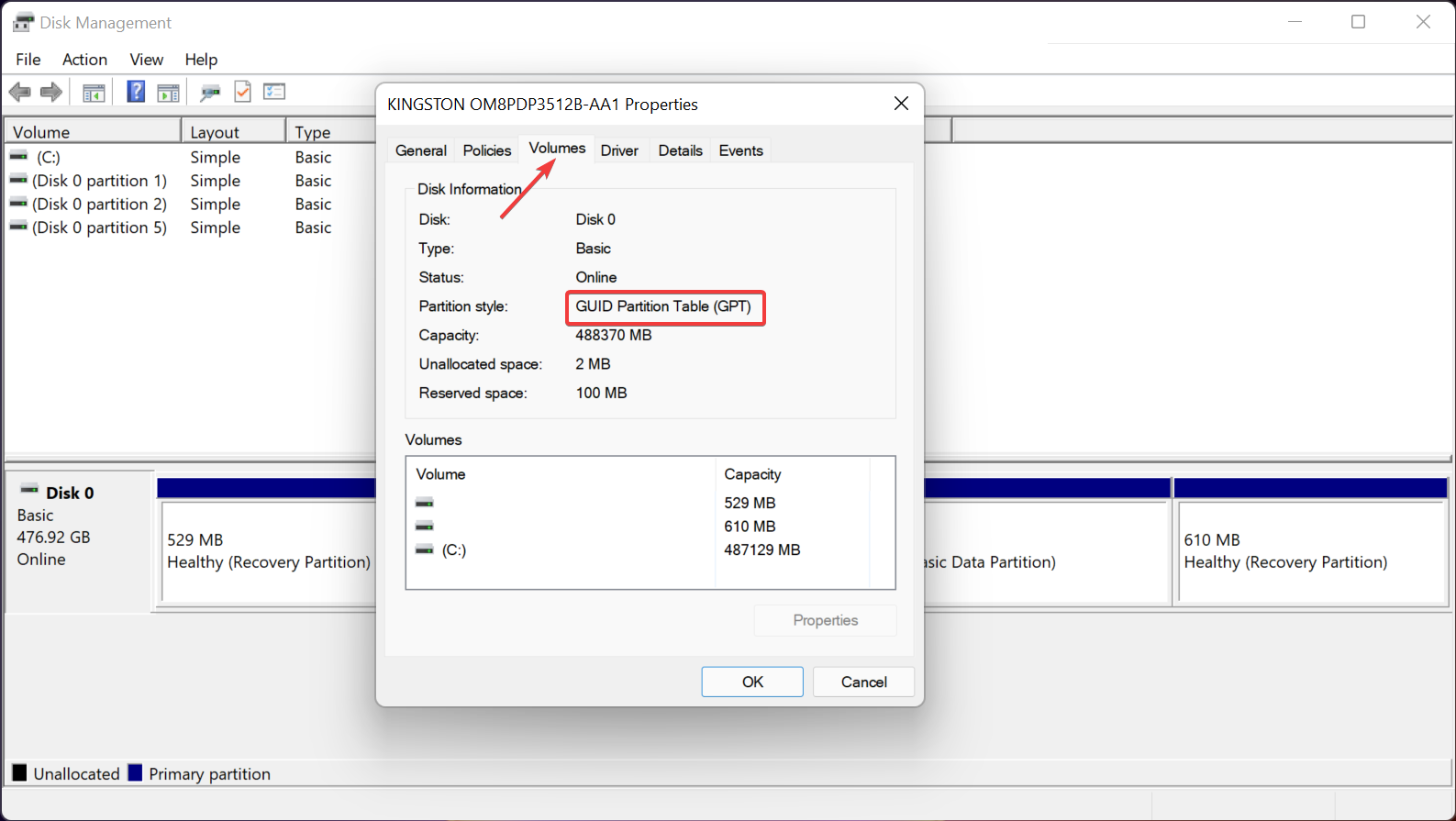
- Click on the Volume tabs and you should see the Partition style on the list. In this case, it’s GPT.
Although usually, you can only install Windows 11 on a GUID Partition Table (GPT), it is possible to do that on MBR.
That’s why we first need to check what we’re dealing with because the solutions for the two cases are slightly different.
2. Delete the font files
2.1 For GUID Partition Table (GPT)
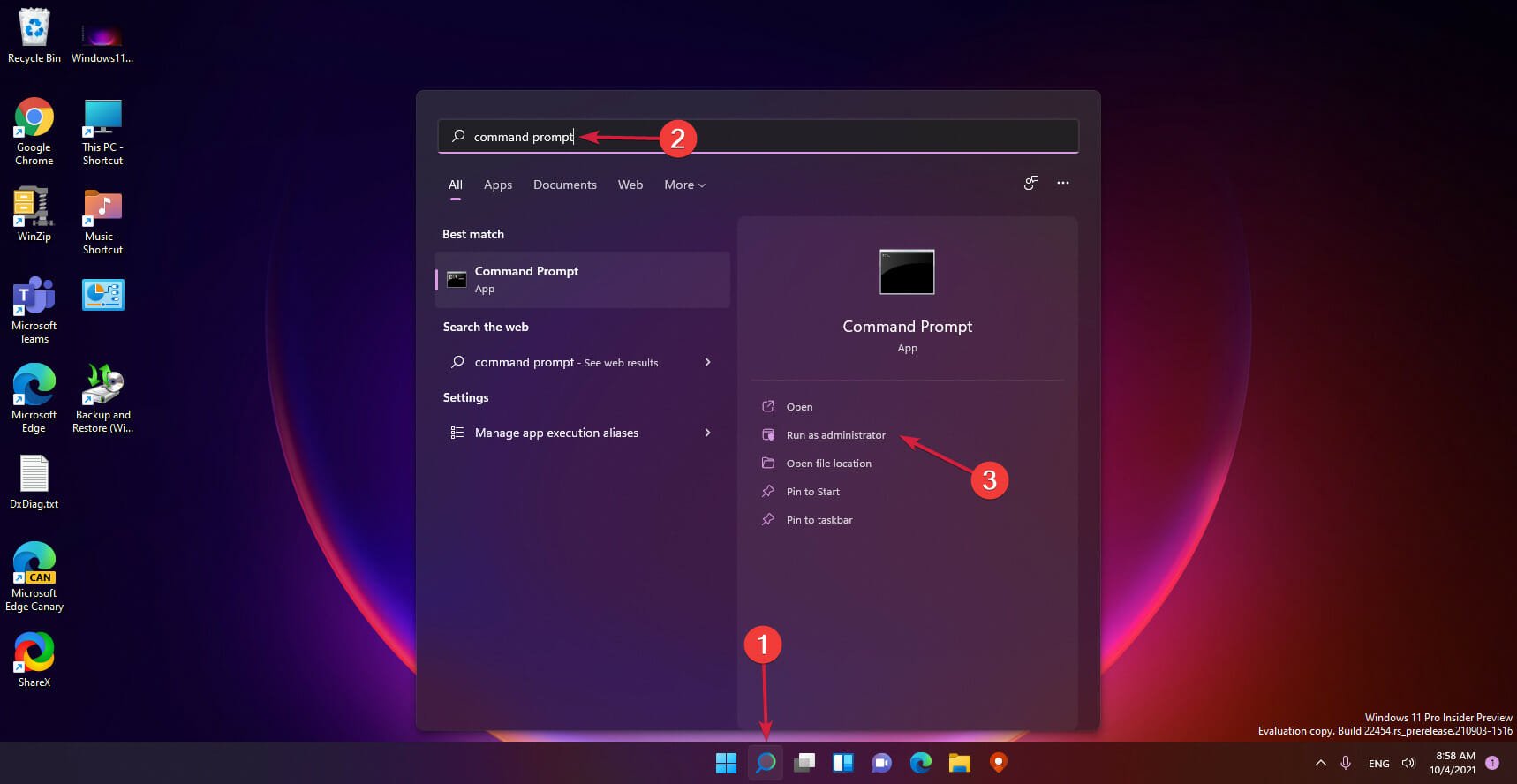
- Click the Start button, type cmd, and select Run as administrator.
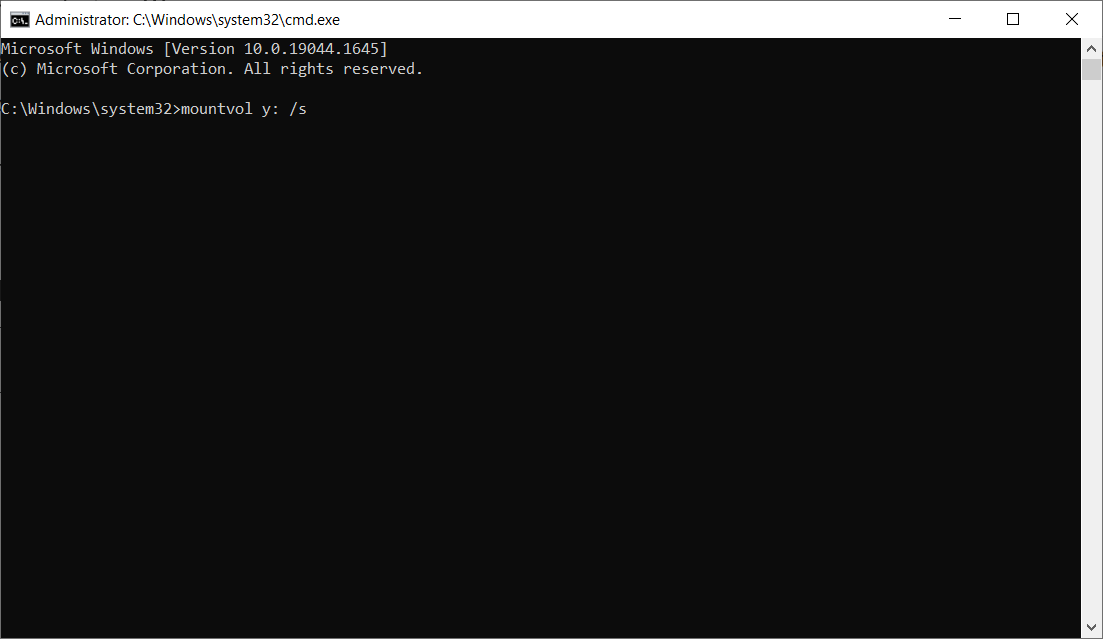
- Type the following command to assign drive letter Y to the System Partition and press Enter:
mountvol y: /s - Type Y: and press Enter to switch to the Y drive.
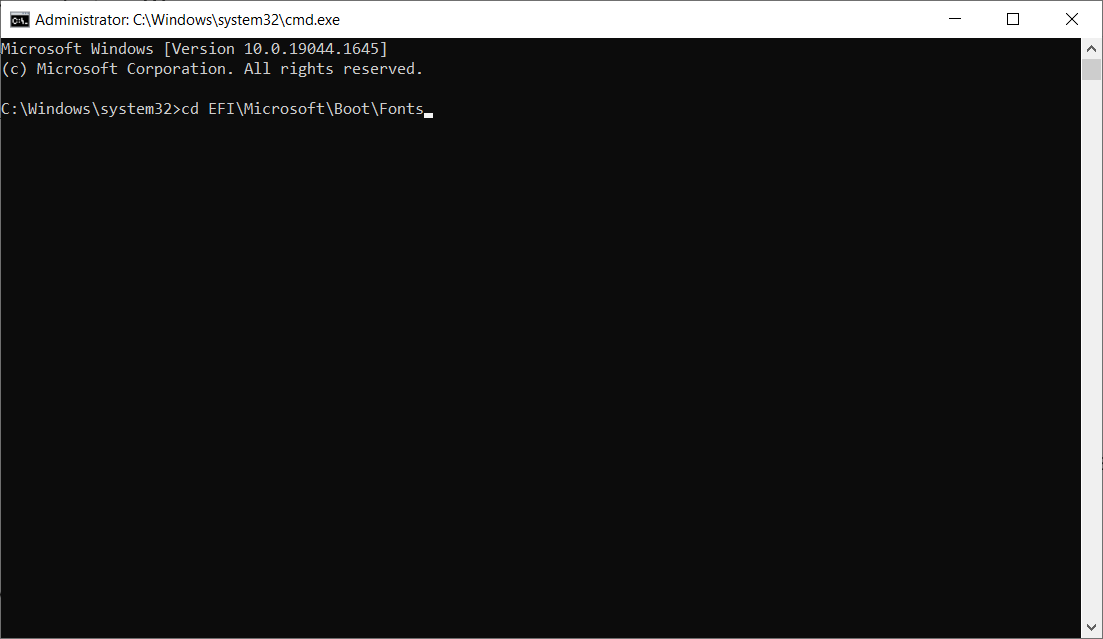
- Navigate to the Fonts folder by typing the following command:
cd EFI\Microsoft\Boot\Fonts - Then, delete the font files therein using the following command, followed by Enter:
del *.* - Type Y if prompted by the system to continue the deletion of the files.
Apparently, by removing the fonts, you should now have enough space in the SRP to continue with your upgrades or installation.
2.2 For MBR (BIOS)
- Right-click the Windows button and choose Disk Management from the list.
- Right-click the System Reserved Partition, select Change Drive Letter and Paths and press Add.
- Choose Y as the drive letter and finally click OK to apply the changes.
- Next, click the Search icon, type cmd, and click on Run as Administrator from the resulting overlay menu.
- Type Y: and press Enter to switch to that drive.
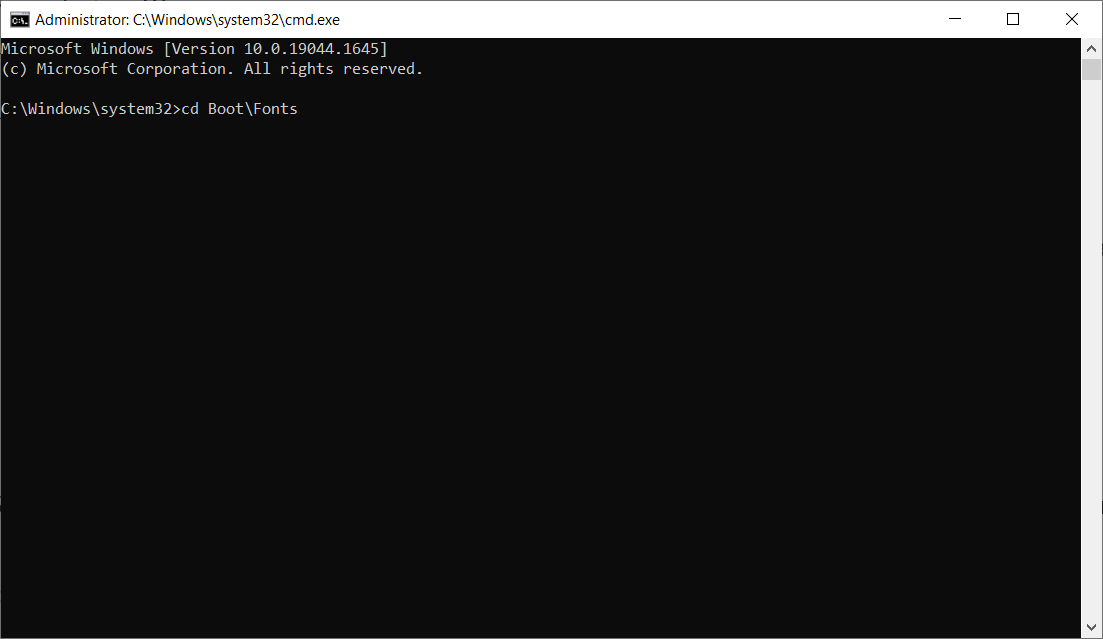
- Type the following command to change the folder to the Fonts:
cd Boot\Fonts - Paste the following command to recover access privileges to files in the folder:
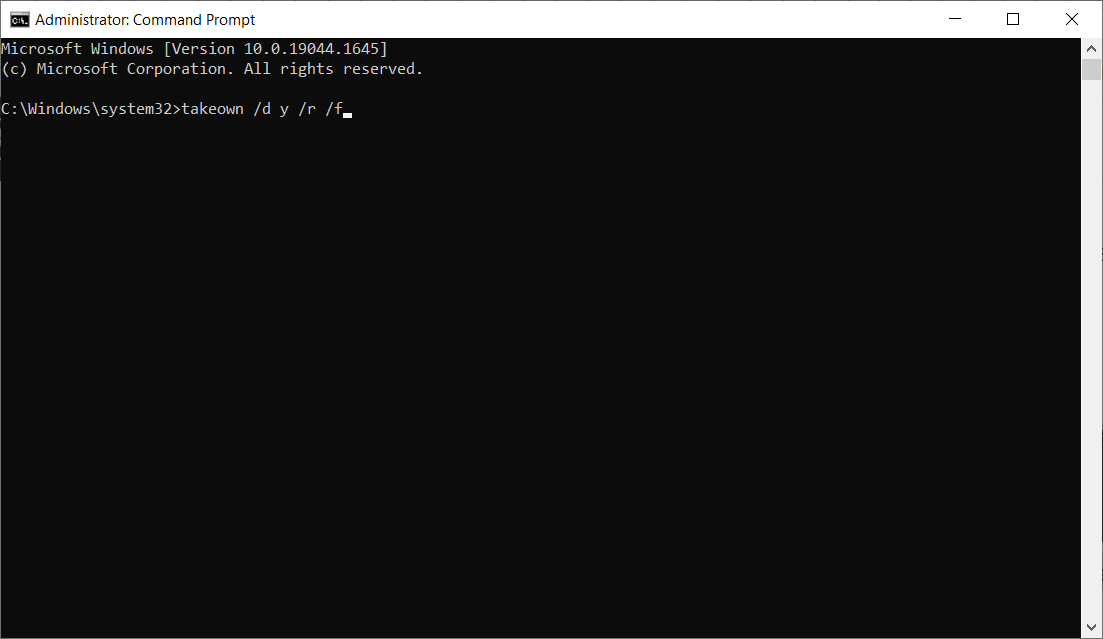
takeown /d y /r /f - Then, save the permission to the drive by pasting the following command and pressing Enter:
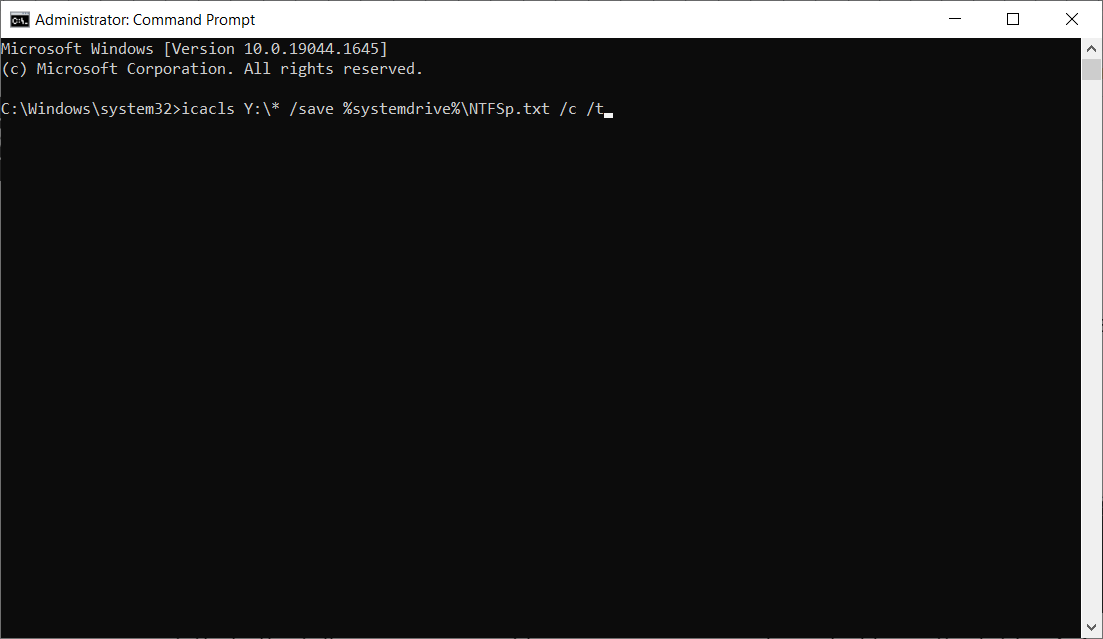
icacls Y:\* /save %systemdrive%\NTFSp.txt /c /t - To display the name of the current user account type whoami then press Enter.
- To grant access to the user type the following command and press Enter:
icacls . /grant <the username you got from whoami>:F /t - Delete all files in the folder by typing the following command and pressing Enter:
del *.* - To restore permissions, type in the following command and press Enter:
icacls Y:\ /restore %systemdrive%\NTFSp.txt /c /t - Then, revert the access control list (ACL) to the system by typing the next command and pressing Enter:
icacls . /grant system:f /t - Lastly, hand ownership of the drive back to the System by pasting the following command and pressing Enter to run it:
icacls Y: /setowner “SYSTEM” /t /c
The System Reserved Partition should now have more free space. You can confirm this by checking the Disk Management console, where you should then proceed to remove the drive letter.
To remove the Y drive letter, right-click the System Reserved Partition in the Disk Management tool and select Change Drive Letter and Path just like you did within the solution.
But this time, choose the Y: drive, and select Remove, then click OK to save the changes.
Restart the computer (if needed) and proceed with your upgrade or update. The error We couldn’t update system reserved partition should be gone.
3. Extend the System Reserved Partition with third-party Software
If you find the above method daunting, then third-party tools like the MiniTool Partition Wizard and AOMEI’s Diskpart can help solve the problem.
Such tools avail graphical interfaces and near-one-click operations to carry out the various fixes.
In particular, the MiniTool Partition Wizard clearly shows the partition style and other relevant properties for each partition.
Whether it’s a GPT or MBR disk, the software includes intuitive tools to help you extend or shrink the partitions. Just be sure to follow their documentation to the letter.
 NOTE
NOTE
In a nutshell, these tools help you shrink the main C: drive and extend the System Reserved Partition with the resulting Unallocated Space.
As a last resort, you might want to consider performing a clean install of the affected Windows version.
Essentially, a clean install resets the hard drive and creates a fresh System Reserved Partition out of the main system drive. Remember to back up all your data before proceeding with a fresh install.





User forum
4 messages