8 Ways to Fix DHCP is Not Enabled for Wi-Fi
Make sure IP and DNS are set to automatic
7 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- When DHCP client is not enabled for Wi-Fi, you won't be able to access the Internet.
- The problem arises due to misconfigured network settings, outdated drivers, or a temporary glitch.
- To fix things, run the dedicated troubleshooter, re-enable the DHCP Client service, or reset the network settings, amongst other solutions.

DHCP plays a vital role for devices on a network. Besides allowing effective communication, it also assigns critical parameters. But many found that DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi in Windows.
The error message appears after you run the built-in Windows Network Diagnostics troubleshooter when the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray reads, No Internet. However, other devices on the network have proper connectivity.
Keep reading to find out how to fix things and enable DHCP for Wi-Fi!
What is DHCP?
As the name suggests, DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) dynamically assigns IP addresses and other critical parameters to the devices when connected to a network. This is essential for the device to interact and have a stable Internet connection.
In addition, DHCP also provides devices with a DNS server address, which is responsible for locating websites on the Internet. This is done by turning the domain name we enter into the IP address used by the website.
All the functions of DCH are automatic in nature and require minimal to no human intervention as long as things are configured correctly. But when you can’t access the Internet and find that DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi, issues are bound to appear.
What is the DHCP problem with Wi-Fi?
Here are a few reasons you find that DHCP is not enabled for Wireless Network Connection:
- Misconfigured network settings: Often, it’s the incorrect network settings to blame when DHCP is not enabled or working for Wi-Fi.
- The dedicated service is not running: Windows devices have a dedicated DHCP client service installed, which, when not running or if the startup type is set to Disabled, can trigger issues.
- Outdated or incompatible driver software: The driver software play a critical role when it comes to network & Internet, and if you have corrupt, incompatible, or outdated drivers, chances are DHCP will fail to work.
- Software conflicts: Several third-party applications are known to conflict with DHCP and affect the IP address allocation.
- Issues with the router: When you find that DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi, there’s also the possibility of a hardware issue, usually one with the router.
How do I fix DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi?
Before we move to the slightly complex solutions, try these quick ones:
- Restart the computer and the router. For the latter, ensure it’s kept in the powered-off state for at least 60 seconds.
- Scan the PC for malware using the built-in Windows Security.
- Disable any third-party antivirus installed on the PC.
If none work, move to the fixes listed next.
1. Run the network troubleshooter
- Press Windows + I to open Settings, and click Troubleshoot on the right in the System tab.
- Click on Other troubleshooters.
- Now, click the Run button next to the Network & Internet troubleshooter.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process and make the recommended changes.
Often the quickest way to fix things when DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi is to run the dedicated troubleshooter. The built-in Windows tool will automatically identify the underlying cause, recommend the changes, and enforce them for you, all within a matter of minutes.
2. Run the DHCP Client service
- Press Windows + S to open the Search bar, type Services in the text field, and click on the relevant search result.
- Right-click on the DHCP Client entry from the list of services, and then select Properties.
- Select Automatic from the Startup type dropdown menu, click the Start button if the service is not running, and then on OK to save the changes.
The DHCP client service is vital for the network protocol to function. So you must set it to run automatically when Windows boots. Also, this will help when Windows is unable to get DHCP address.
3. Update network drivers
- Press Windows + X to open the Power User menu, and select Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters entry, right-click on the Wi-Fi adapter, and select Update driver.
- Now, select Search automatically for drivers and wait for Windows to install the best available stored locally.
When you have a faulty network adapter driver, it’s best that you update the network drivers. When Windows can’t find an update, head to the device manufacturer’s official website, find the latest version, download it, and then manually install the driver.
Updating the network drivers will also help if you get the Unable to contact DHCP server error.
Anyhow, you have a greater alternative to update the network drivers or any other devices with dedicated support given by a driver manager application. All you have to do is press one button to proceed and fix all your drivers.
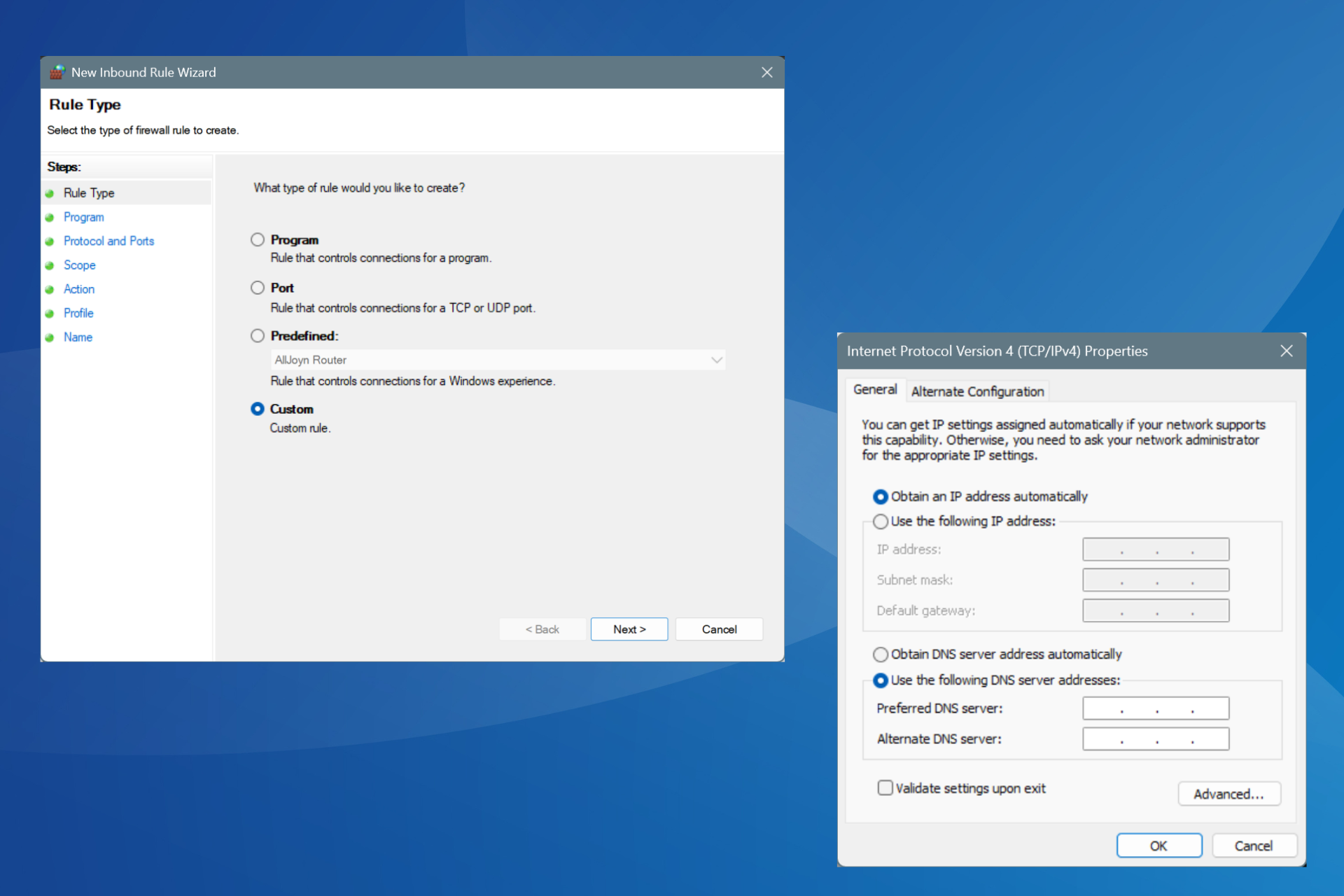
3. Configure the network adapter settings
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type ncpa.cpl in the text field, and hit Enter.
- Right-click on the active network adapter, and select Properties from the context menu.
- Select the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) entry, and click on Properties.
- Now, check the radio buttons for Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain the DNS server address automatically, then click OK to save the changes.
- Make similar changes to Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) if your network connection relies on the protocol.
- Once done, restart the computer and check for improvements.
If DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi, the Wi-Fi network adapter settings could be set such that users must manually enter the DNS server and IP address. And in the absence of these two parameters of the Wireless Network Connection, you wouldn’t be able to access the Internet.
4. Re-enable the network adapter and DHCP service
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type ncpa.cpl, and then click OK.
- Right-click on the active network adapter, and select Disable.
- Now, open the Services window, right-click on DHCP Client, and select Restart.
- Head back to Network Connections, right-click on the same network adapter, and this time, select Enable.
For some users, when the wireless adapter didn’t have access to DHCP, the underlying cause turned out to be a temporary glitch, and simply restarting the service and re-enabling the adapter did the trick!
6. Disable proxy
- Press Windows + I to open Settings, go to Network & Internet from the navigation pane, and click on Proxy.
- Now, disable the toggle for Automatically detect settings, and make sure there are no entries under Manual proxy setup.
7. Disable Windows Firewall
- Press Windows + S, type Control Panel in the search bar, and click on the relevant search result.
- Click on System and Security.
- Click on Windows Defender Firewall.
- Now, select Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off from the left.
- Choose Turn off Windows Defender Firewall (Not recommended) under both Private network settings and Public network settings, then click OK to save the changes.
Once done, verify whether the DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi error disappears. If yes, your firewall was conflicting with the active network connection, and that triggered the error.
8. Reset the network settings
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type cmd, and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
- Now, paste the following commands individually and hit Enter after each:
netsh winsock reset catalognetsh int ip reset resetlog.txtipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew - Once done, restart the computer.
When everything else fails to work, the last option is to reset the network settings, i.e., reset Winsock and release the IP address. A network reset also helps when you find DHCP not working.
You should have fixed the DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi error by now. Remember, the solutions here work on all iterations of the OS, including Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Does Wi-Fi need DHCP?
While this wasn’t the case a decade ago, Wi-Fi now needs the DHCP running. You don’t just need the protocol running on devices, but DHCP must be enabled in the router settings.
DHCP is, more or less, a norm now, and you will end up facing issues when it’s disabled or not working.
Before you leave, find out how to speed up the Internet connection in Windows 11.
For any queries or to share what worked for you, drop a comment below.

















User forum
0 messages