How to Fix Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler High CPU Usage?
Close the process from Task Manager
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler High CPU usage issues could occur due to corrupted or incomplete installation of the .Net Framework.
- To fix it, close the process in Task Manager, stop the Microsoft Common Runtime service, or reset the NGen cache.
- For more solutions and detailed steps, keep reading!
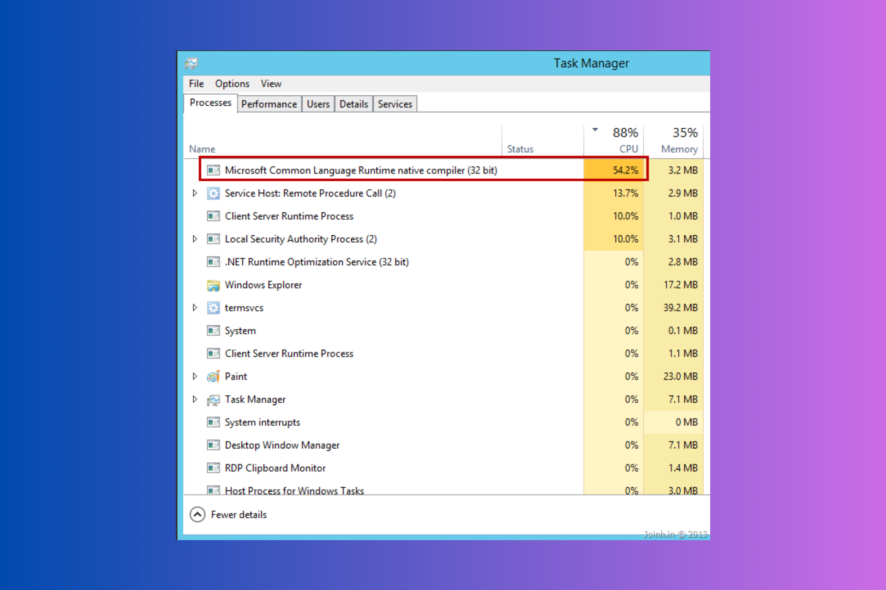
If you notice a process ngen.exe or Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler is causing high CPU usage, this guide can help! We will discuss the expert-tested methods to fix the issue right after explaining the causes.
Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler (ngen.exe) plays an essential component of the .Net Framework, and it creates a Runtime environment that supervises the operation of apps written for the .Net platform, irrespective of their programming language.
It handles various tasks such as converting code into machine language, garbage collection, exception handling, and thread management to enhance the performance of managed apps in Windows.
If you see high CPU usage due to this process, here are some of the reasons for the same:
- The process is scheduled to run as a part of system maintenance.
- Incorrect configuration settings.
- Multiple apps are using the process for compilation.
- The process is running in the background with other system resources.
- Corrupted system files or services
- Malware disguising as the process
How to stop CLR Native Compiler’s high CPU usage?
Before engaging in advanced troubleshooting steps, you should consider performing the following checks:
- Restart your computer.
- Wait for the process to complete the compilation process.
- Run a deep scan using a reliable antivirus to ensure there is no malware infection.
- Check for Windows Updates.
- Back up your important data.
- Uninstall unwanted apps from your PC.
- Run the Farbar Recovery Scan Tool to find the exact cause
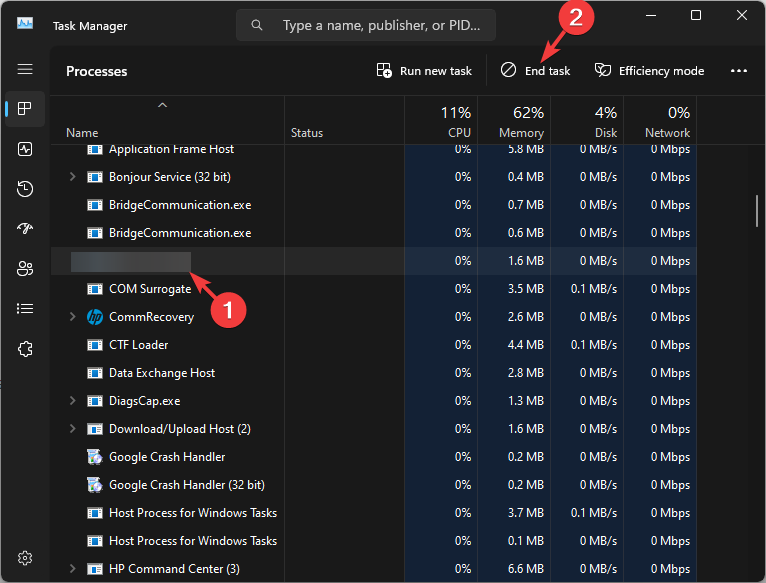
1. Stop the process
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Go to the Processes tab, locate Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler or ngen.exe, select it, and click End task.
Closing the process causing performance issues is a workaround that you can follow before moving to other solutions. You can apply the same approach to other processes, such as Runtime Broker.
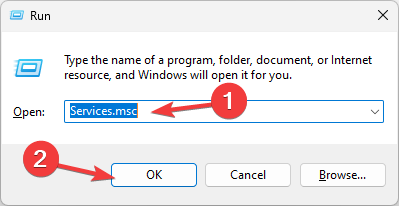
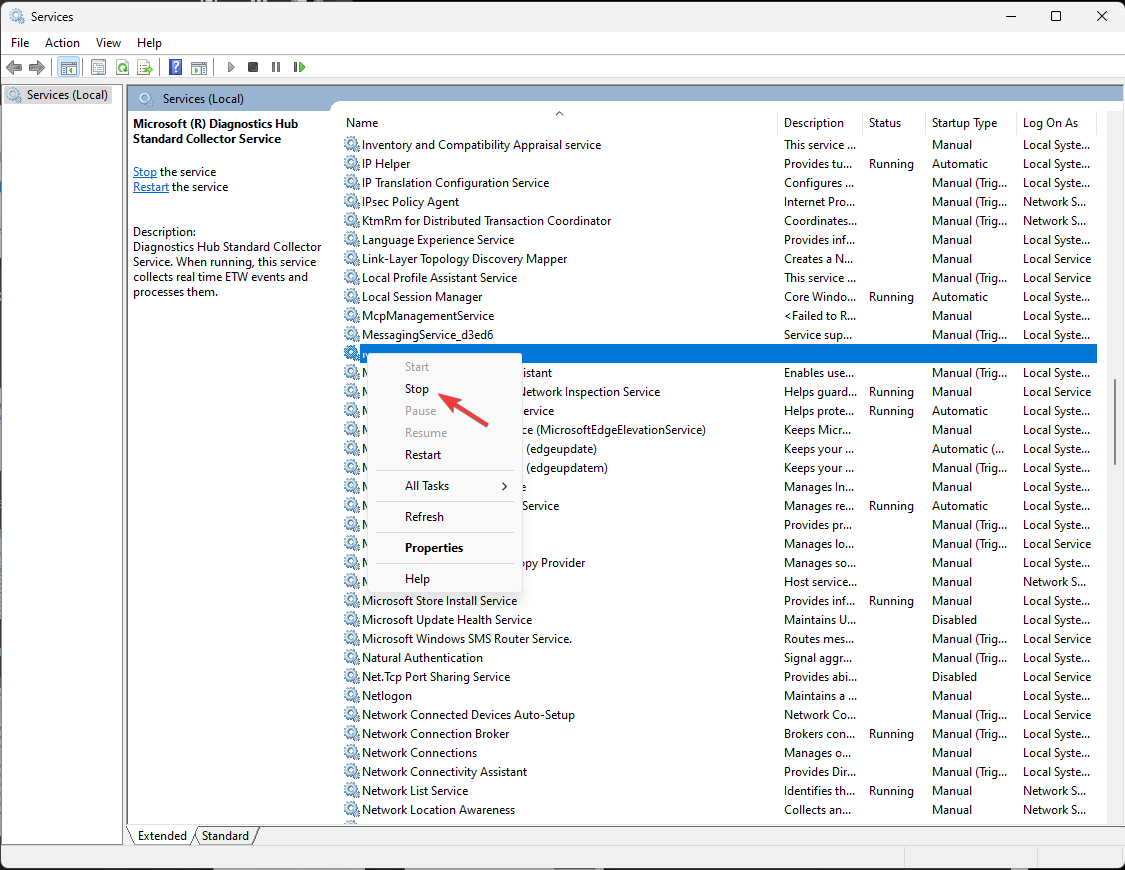
2. Restart the service
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type services.msc and click OK to open the Services app.
- Locate and right-click Microsoft Common Language Runtime and click Stop.
- Wait for the service to stop, then close the Services window.
3. Reset the NGen cache & change the priority settings
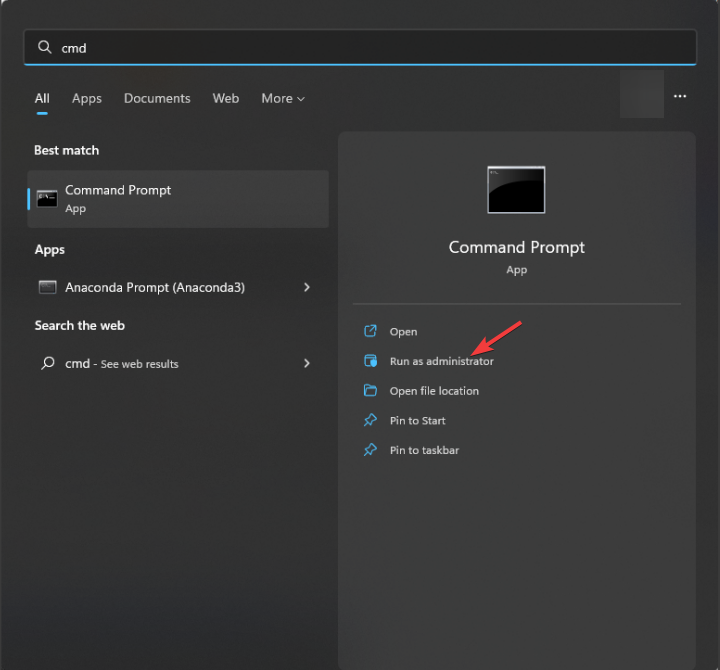
- Press the Windows key, type cmd, and click Run as administrator.
- Type the following command to reset the NGen cache to resolve conflicts and corruption and hit Enter:
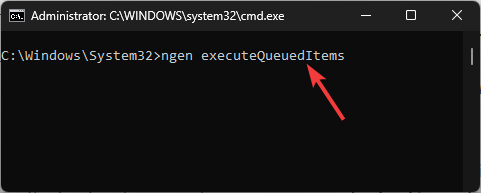
ngen executeQueuedItems - Copy & paste the following command to adjust the priority and scheduling of the process to reduce the load and press Enter:
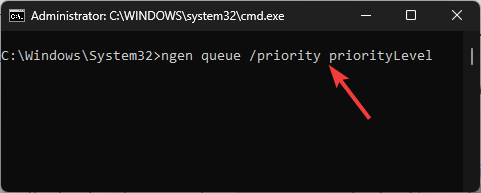
ngen queue /priority priorityLevel
4. Run your computer in a clean boot environment
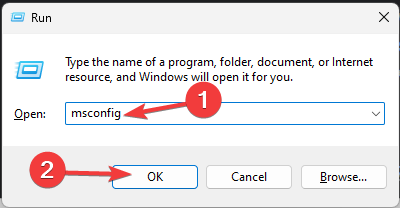
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msconfig and click OK to open the System Configuration window.
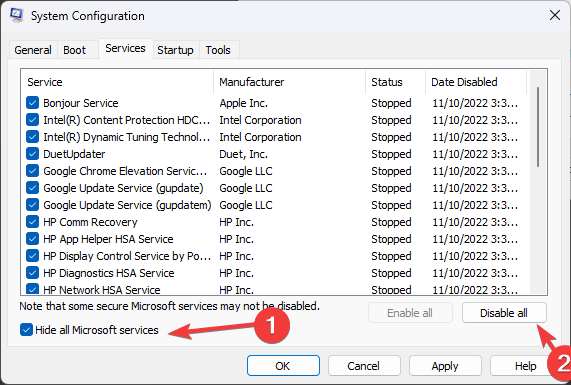
- Go to the Services tab, click Hide all Microsoft Services, then select Disable all.
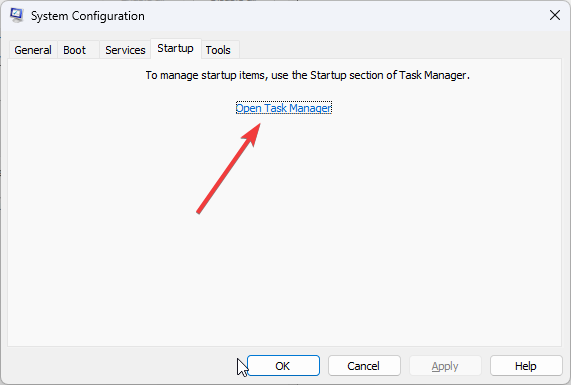
- Switch to the Startup tab and click the Open Task Manager link.
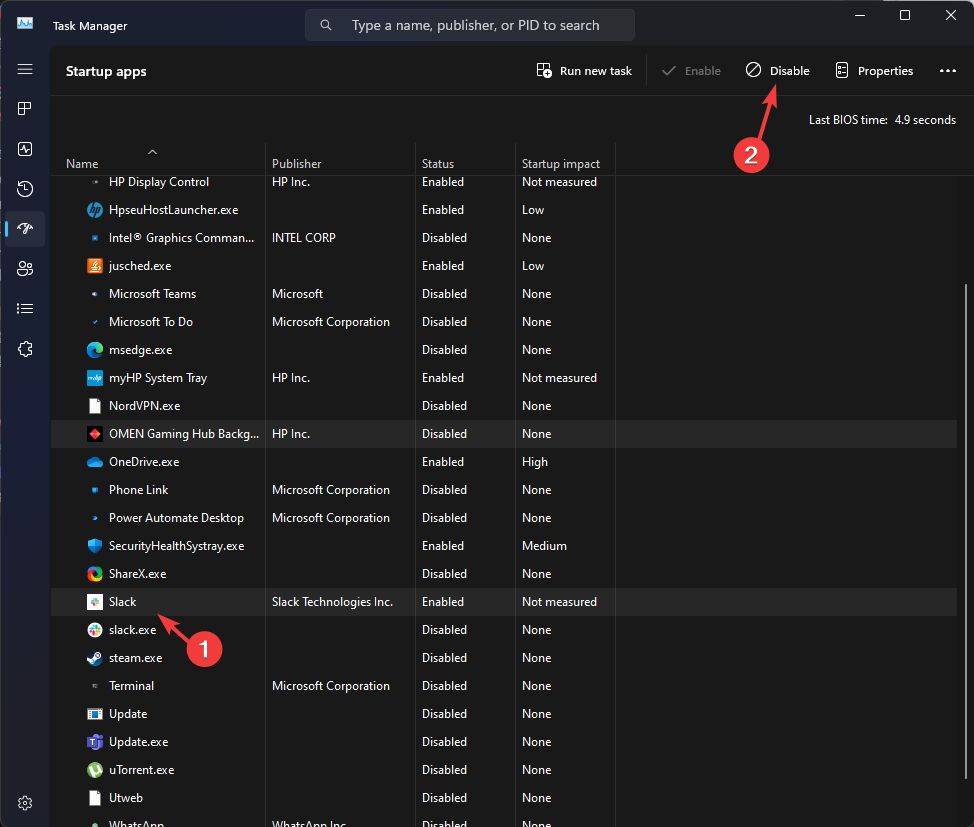
- On the Task Manager window, locate each Enabled task and click Disable.
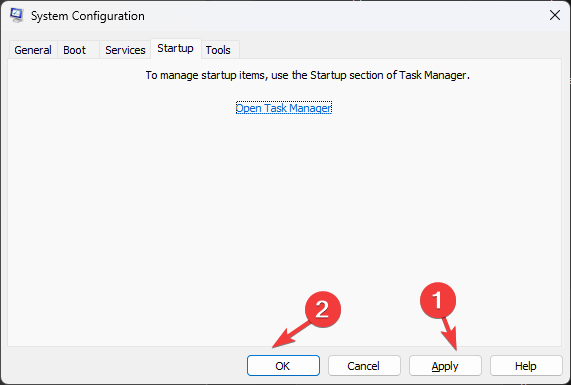
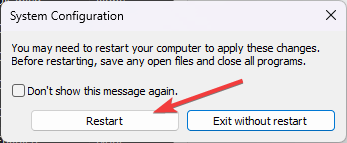
- Close Task Manager, click Apply, then OK on the System Configuration window.
- Click Restart.
Your computer will restart with limited functionalities so that you can identify the third-party software or service causing the conflict. Once done, follow the steps above to undo the changes and restart your computer normally.
5. Run SFC & DISM scans
- Press the Windows key, type cmd, and click Run as administrator.
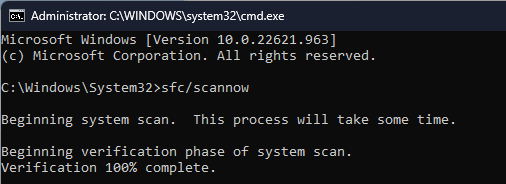
- Copy & paste the following command to repair system files and press Enter:
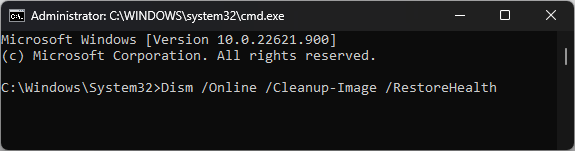
sfc/scannow - Wait for the scan to complete, then type the following command to restore the Windows OS image and hit Enter:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Once the command is executed, restart your computer.
6. Delete a registry key
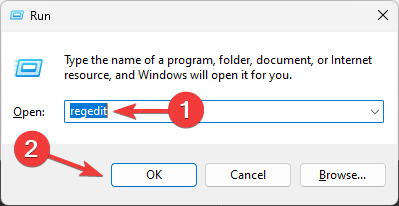
- Press Windows +R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type regedit and click OK to open Registry Editor.
- First, take a backup, go to File, then select Export. Save the file in .reg format on your computer in an accessible location.
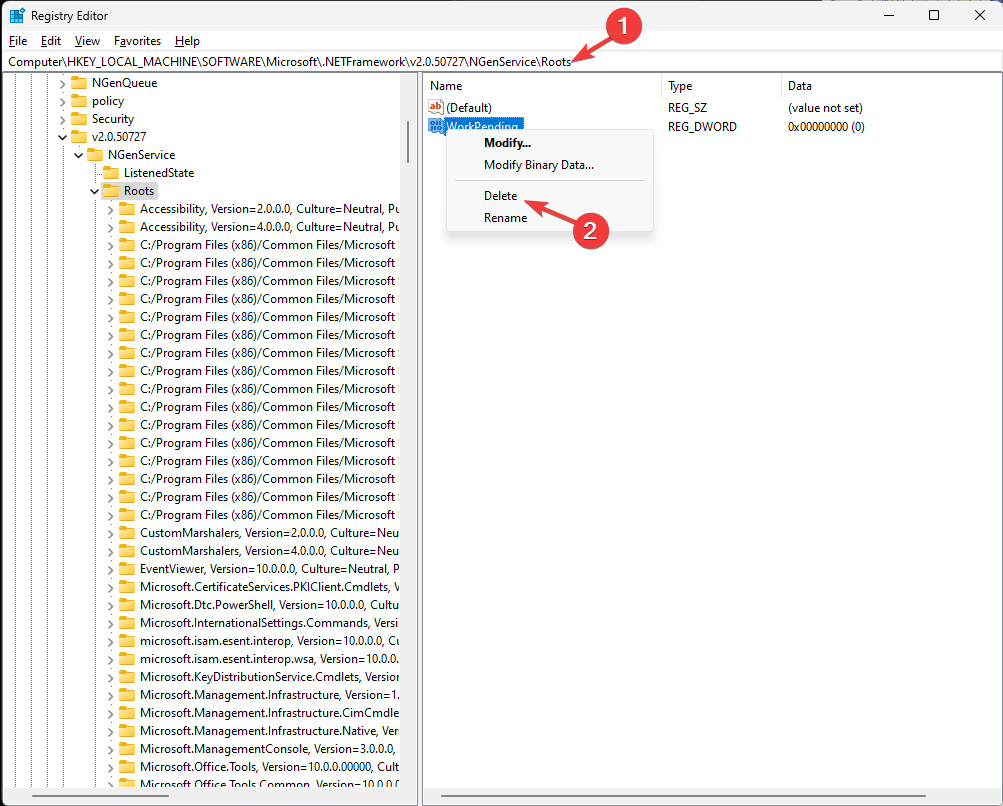
- Navigate to this path:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft.NETFramework\v2.0.50727\NGenService\Roots - Right-click and select Delete to remove all the entries for the Roots folder and close the Registry Editor.
- Reboot your computer.
7. Repair/reinstall .the Net Framework
- Download the Microsoft .NET Framework Repair Tool.
- Double-click the executable file and follow the on-screen instructions to install it.
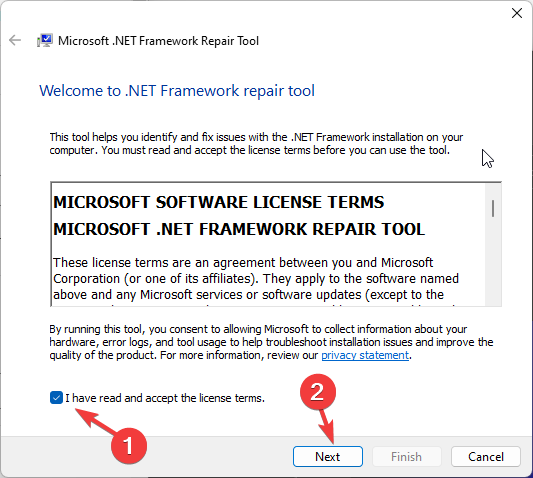
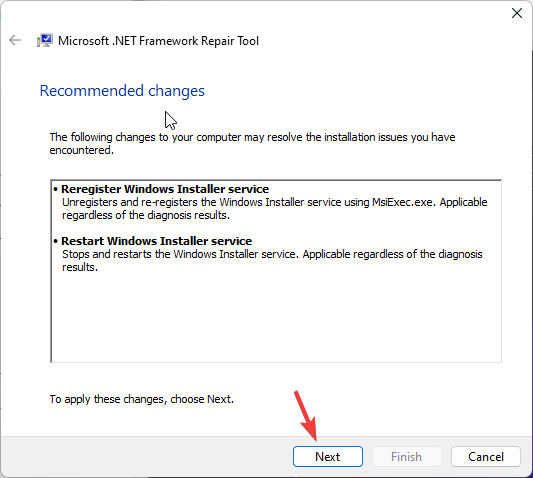
- On the Microsoft .NET Framework Repair Tool window, accept the terms, and click Next.
- The tool will scan for corrupted files in the current .NET Framework and advise solutions to repair them.
- Click Next to apply the fixes.
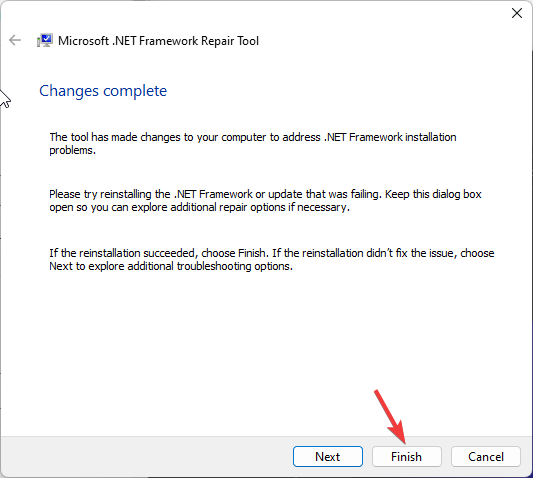
- Then, click Finish to close the Repair tool window.
If this doesn’t help, follow these steps to reinstall .Net Framework:
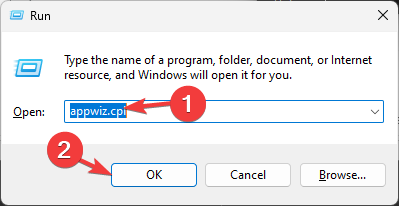
- Press Windows +R to open the Run window.
- Type appwiz.cpl and click OK to open the Programs and Features window.
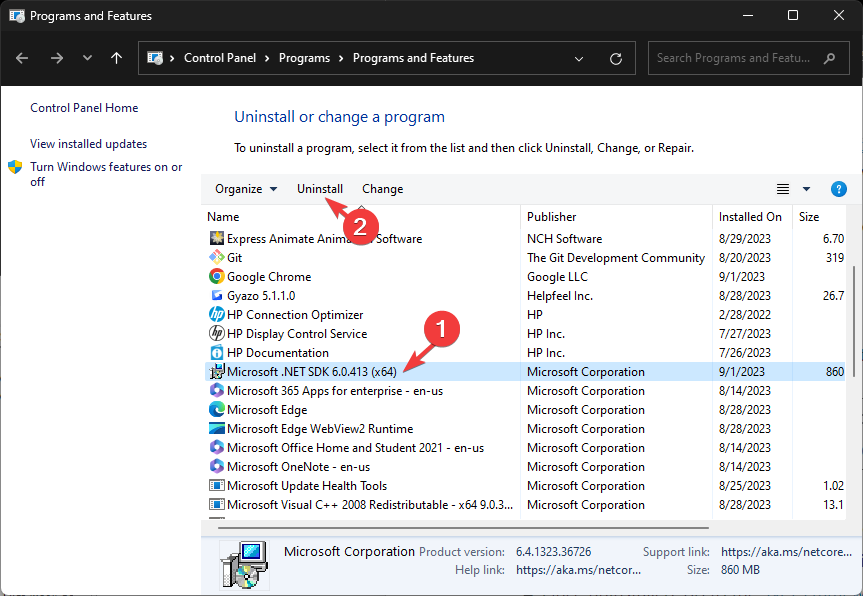
- Select Microsoft .Net Framework and click Uninstall.
- Once uninstalled, go to the .NET Framework’s official website.
- Click the latest version and download it.
- Once the setup is downloaded, go to the file location, and double-click it to initiate the installation.
- Click Install, and wait for the process to complete.
To avoid high CPU performance issues, including the Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler has stopped working issue, make sure to allow the ngen.exe process to run when your system is in an idle state and keep your system & software up to date.
In case the solutions mentioned don’t work for you, try to roll back to an earlier version of Windows using a restore point.
If you often face high CPU usage on your Windows 11 computer, we recommend you check out this guide.
Bumped into any issues, or do you need more info about Microsoft Common Language Runtime Native Compiler? Don’t hesitate to leave a comment in the section below.









User forum
0 messages