What is the NTFS File System & Should I Use it?
Up your data storage game with NTFS
5 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Your choice of storage device comes with a file system format like the New Technology File System (NTFS) that manages and organizes the data stored inside.
A file system is crucial because it is what dictates how the content stored inside an HDD or SDD will be saved, stored, retrieved and updated. These rules minimize the loss of data and encrypt files from unauthorized persons where need be.
What are the key features of the NTFS file system?
- File management – Modern storage needs require advanced file system formats that support large file sizes and volumes and NTFS delivers this effortlessly. It can handle up to 256TB. You can also use it on advanced storage configurations like RAID.
- Data integrity and security – At the cornerstone of data storage is data integrity. If you’re storing large amounts of data, you need to be assured that it is safe and the NTFS makes this possible with its advanced security features. Aside from encryption of files, users can also set permissions on NTFS files to restrict access.
- File compression – Although NTFS supports storage of large volumes of data, it can easily become unmanageable. With its file and folder compression feature, you can reduce the size of these files through compression and get an additional bonus by saving disk space.
- Error handling and recovery – Power failures can happen any time and can lead to data corruption. Thanks to NTFS’ journaling feature, it keeps a separate log files, checks for inconsistencies and failures then attempts to repair them.
- Offloaded Data Transfer – This is another winning feature that makes the transfer of files seamless. It speeds up the file transfer process by offloading the task to your storage device instead of your OS. This saves your system resources and optimizes the file transfer process making it faster and more efficient.
How can I convert a raw disk to NTFS format?
When you have an unformatted drive, it is in its raw format and you need to convert it to a compatible file system format to manage the data stored effectively.
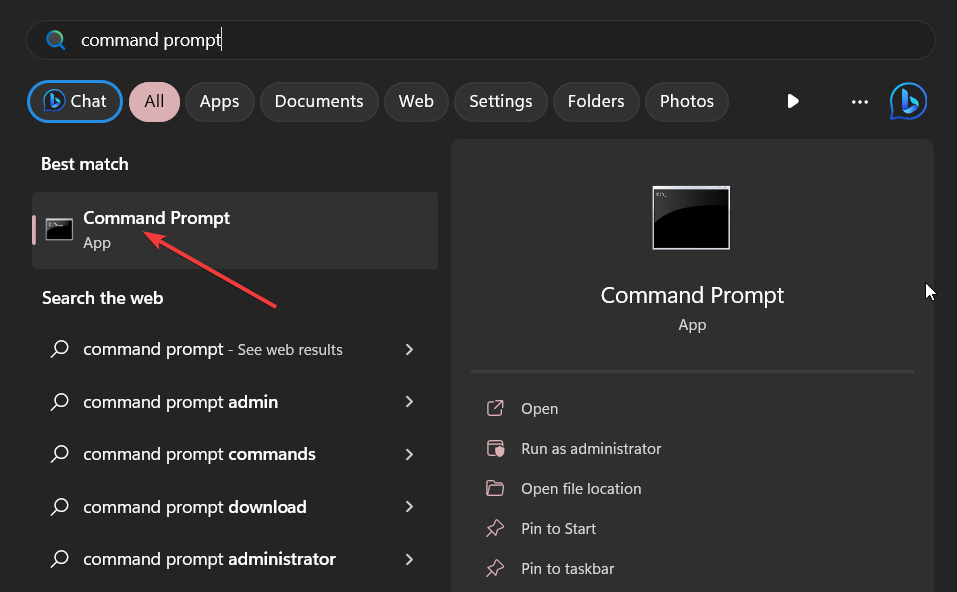
- Press the Windows key to open the Start menu.
- Type command prompt into the search box and run it as an administrator.
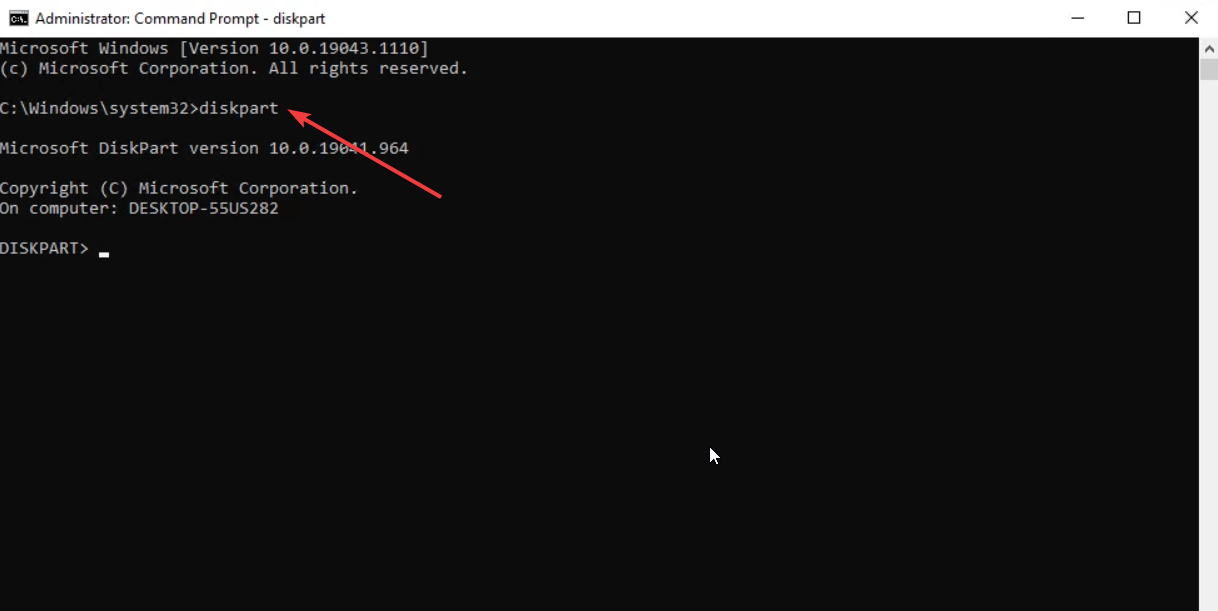
- Type the below command and press Enter.
Diskpart - Execute the below command to list all the disks on your computer.
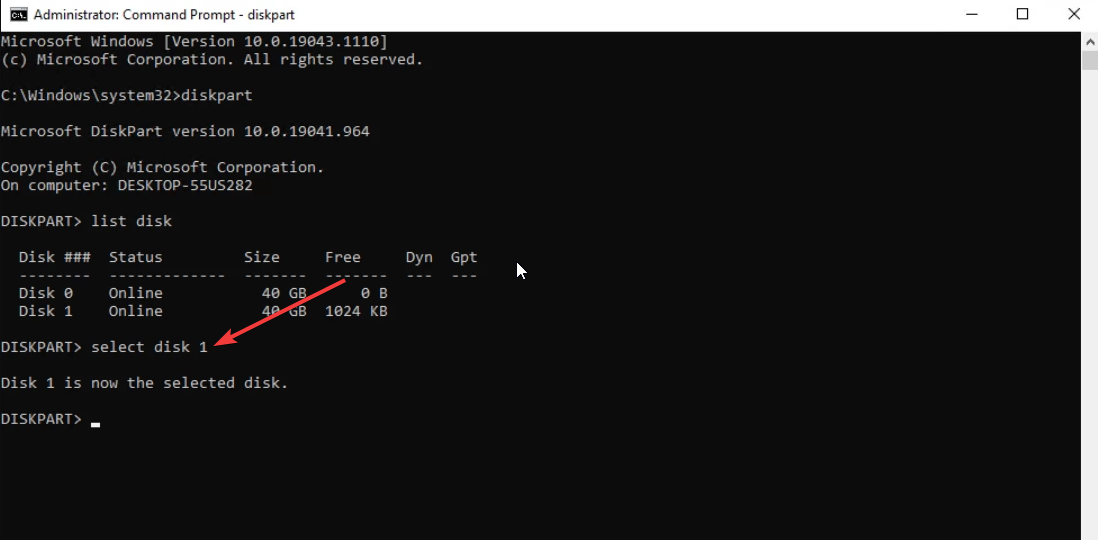
list disk - Type the below command to select the partition and press Enter.
select disk 1(Replace the number with the number for the RAW drive) - Execute the below command to wipe the disk and prepare it to accept a new partition.
clean - Type the below command and press Enter.
create partition primary - Run the below command to format the drive with the NTFS file system.
format fs=ntfs - Type the below command and press Enter to assign a drive letter to the partition.
assign
For more ways to convert your raw drive to NTFS, check out our comprehensive guide.
Pros and cons of the NTFS file system
Pros
- Advanced security features – The disk quotas, page file support, and encrypting file system are just some of the security features you enjoy when you convert to the NTFS file format.
- Reliability – Since NTFS has a feature that tracks changes, your data is safe because there’s a log file and even in the case of damage, there are built-in tools to repair and recover them.
- Support for large files – You can store huge amounts of data and even create more space when you use its compression feature for storage efficiency.
- Storage management – You have full control on your drive. You can set permissions to restrict access and also disk quotas to assign disk space to different users.
Cons
- Limited Cross-Platform support – While it supports large storage of large volumes, NTFS is not universally compatible as it is primarily designed for Windows. There may be workarounds for other OSes but even if you manage to get support, it will be limited and not work as well as with Windows.
- Requires extensive system resources – As you enjoy the advanced features of NTFS, they come at a cost of performance overheads. Your device and OS must be able to handle the large volumes so if you have lower-end hardware, you may experience performance bottlenecks especially with high CPU usage and memory.
- Fragmentation – Any file format can experience fragmentation over time. And while you can defragment your hard drive, it exposes it to early wear and tear and can significantly slow it down.
- Reliant on hardware – The NTFS system relies heavily on the hardware so your HDD failing can greatly affect its performance and risk at data corruption or loss.
Is NTFS good or bad?
In comparison to other file systems like FAT32 and exFAT, NTFS might be a superior choice but this also depends on your storage needs and your hardware specs.
NTFS is known for its ability to accommodate your large storage needs, has impeccable performance on Windows devices and has a robust security profile that ensures your data is safe. If all these check your boxes then it is the file system for you.
However, if you’re looking for a file system compatible with multiple operating systems, you’re better off with other formats. For a more detailed comparison of NTFS vs FAT32 or NTFS vs ReFS, check out our articles.
So far, the NTFS file system seems like a viable option with the good outweighing the bad. If you’re a Windows diehard, we think this will be a great file system format for you. And even though you may run into the NTFS file error or other file system errors, it’s nothing beyond your control.
Have you used the NTFS format before? How was your experience and would you recommend it to other users? Share your thoughts with us in the comment section below.










User forum
0 messages