MBR2GPT to Convert MBR to GPT: How to Do It
Quickly convert the partition style without file loss using MBR2GPT
3 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- We often need to convert the MBR partition style to GPT, with the latter being the more prevalent style now.
- Of the many methods available for the conversion, many prefer MBR2GPT, the built-in option found in the System32 directory.
- While you need to run the command from a preinstallation environment ideally, a small change will help bypass the limitation.
Windows introduced a new console tool called MBR2GPT, which lets you convert an MBR disk (Master Boot Record) to a GPT disk (GUID Partition Table) without data loss or modification.
MBR is an old method of partitioning disks that uses a special boot sector at the beginning of the partitioned storage to identify the location of the bootable operating system.
PCs with BIOS used to have MBR before the newer UEFI standard, which gave rise to GPT. It refers to the standard layout for partition tables using globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). But what’s the need for MBR2GPT? Let’s find out!
Why do I need the MBR2GPT command?
Earlier, users had to choose between MBR or GPT at the time of formatting the disk. That means changing the partition table style would erase data on the disk.
But with MBR2GPT released later, users can now convert an existing MBR disk to a GPT disk without deleting it. MBR2GPT.exe runs from a Windows Preinstallation Environment command prompt and a regular Windows 10 copy.
For those wondering where MBR2GPT is stored, its executable file can be found in the System32 folder. If the file is not there, repair the corrupt system files or perform an in-place upgrade.
How do I use Windows MBR2GPT?
Use Command Prompt
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type cmd, and then hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
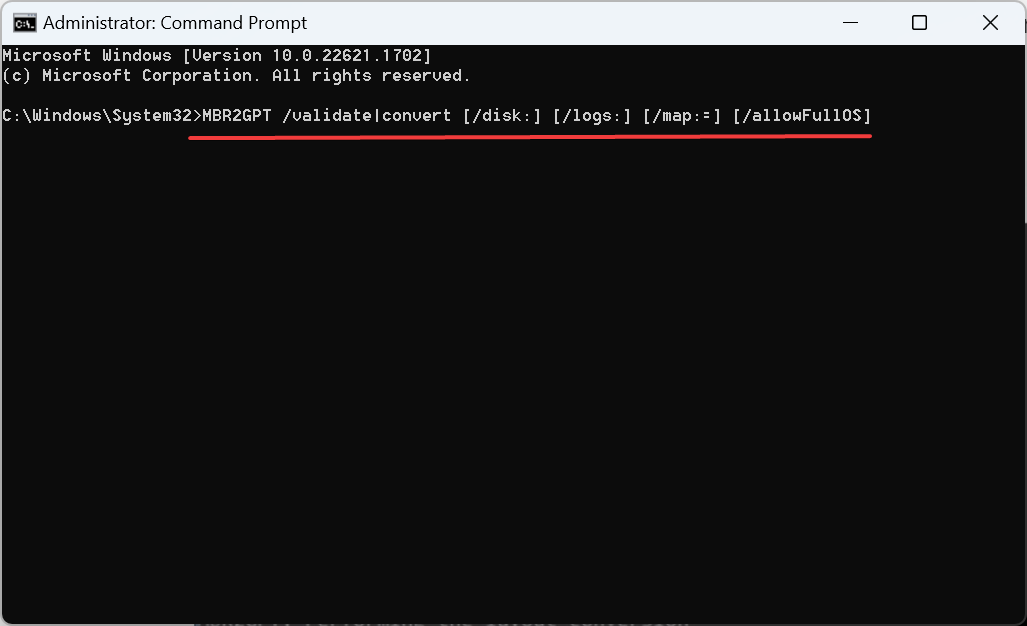
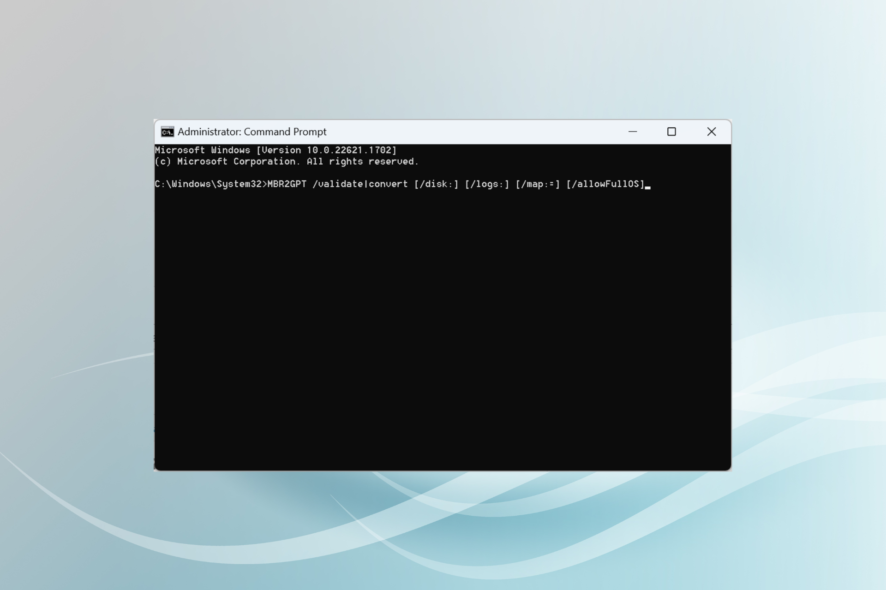
- Now, paste the following command and then hit Enter:
MBR2GPT /validate|convert [/disk:] [/logs:] [/map:=] [/allowFullOS]
The command line parameters are described as follows:
- /validate: Instructs MBR2GPT.exe to perform only the disk validation steps and report whether the disk is eligible for conversion.
- /convert: Instructs MBR2GPT.exe to perform the disk validation and to proceed with the conversion if all validation tests pass.
- /disk: Specifies the disk number of the disk to be converted to GPT. If not specified, then the system disk is used. The mechanism used is the same as that used by the diskpart.exe tool’s SELECT DISK SYSTEM command.
- /logs: Specifies the directory where MBR2GPT.exe logs should be written. If not specified, %windir% is used. If specified, then the directory must already exist. It will not be automatically created or overwritten.
- /map: Specifies additional partition type mappings between MBR and GPT. The MBR partition number is specified in decimal notation, not hexadecimal. The GPT GUID can contain brackets, for example, /map:42={af9b60a0-1431-4f62-bc68-3311714a69ad}. Multiple /map options can be specified if required.
- /allowFullOS: By default, MBR2GPT.exe is blocked unless it is run from Windows PE. This option overrides this block and then enables disk conversion while running in the full Windows environment.
That’s all! You can now easily convert the partition style from MBR to GPT with the MBR2GPT command. This is useful technique, especially if you want to access the GPT protective partition without file loss.
If you find the process a little tricky, there are several other ways to convert MBR to GPT. Use one that seems straightforward and quick.
For any queries or to share whether the method worked for you, drop a comment below.