NTFS Vs FAT32 Vs exFAT: Which File System Should You Use

NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT remain the most common file system options for PCs and portable drives. This guide explains how each one works, their pros and cons, and when to use them.
Table of contents
NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT: Here’s What You Should Know
NTFS Explained
What NTFS Offers
- Supports very large files and partitions
- Provides advanced permissions and security
- Includes file compression and encryption
- Maintains strong reliability for internal Windows drives
When To Use NTFS
Use it for system drives, SSDs, and internal storage that require stability and permissions control. If you want to understand how the format works at a deeper level, you can check a full breakdown of the NTFS file system.
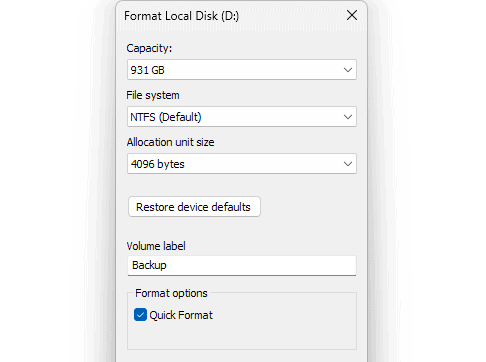
NTFS Cons
- Limited compatibility with macOS without extra tools
- Limited support on smart TVs, consoles, and cameras
- Not ideal for portable drives used across platforms
FAT32 Explained
What FAT32 Offers
- Works on nearly all legacy devices
- Provides strong compatibility with cameras, TVs, and car systems
- Offers simple structure for basic storage
When To Use FAT32
Use it for small USB drives or older devices. If you want to confirm Windows support, see how Windows 10 reads FAT32 in practice.
FAT32 Cons
- Maximum file size is 4 GB
- Maximum partition size is 32 GB on Windows
- Not suited for modern high capacity storage
exFAT Explained
What exFAT Offers
- Supports extremely large files
- Runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, consoles, and smart TVs
- Provides lightweight structure without NTFS overhead
- Works well for fast flash storage
When To Use exFAT
Use it for external drives that move large files between multiple platforms. If you ever need guidance on switching formats, you can check a practical guide on converting exFAT to FAT32.
You can manage partitions and switch file systems more easily with tools designed for safe disk operations, such as the one available at AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard.
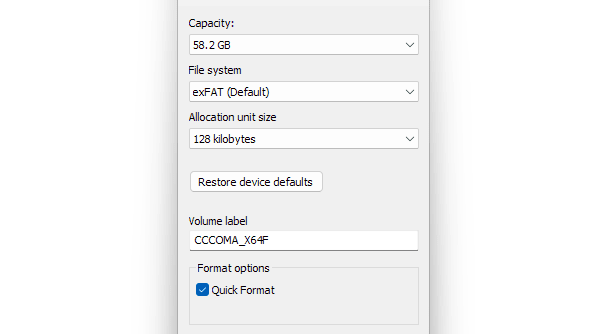
exFAT Cons
- Lacks NTFS style permissions
- Not ideal for system drives
- Some older devices may not support it without updates
NTFS Vs FAT32 Vs exFAT Key Differences
- NTFS supports the largest files and partitions
- FAT32 offers the widest compatibility with older hardware
- exFAT supports very large files across modern platforms
- NTFS includes advanced permissions and security features
- FAT32 restricts file size to 4 GB
- exFAT balances flexibility and capacity for portable drives
FAQs
Choose exFAT when you need to transfer large files between Windows and macOS.
Yes, FAT32 works well for legacy devices that do not support exFAT or NTFS.
It can, because NTFS includes extra features that portable flash storage does not always need.
The file system design limits individual files to 4 GB.
NTFS suits internal Windows drives that need strong security and modern features. FAT32 still works for older devices but shows clear limits when you handle large files. exFAT offers the best experience for portable storage, giving you cross platform support without strict size restrictions. Choose the file system that matches your devices, your file sizes, and how you plan to move data between different systems.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more



User forum
0 messages