What is BIOS: Everything You Need to Know Explained
Check this comprehensive guide for thorough understanding of BIOS
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- BIOS is an acronym for Basic Input/Output System, a critical component, and one must know what it is.
- BIOS is installed on a small chip on your motherboard and was invented in 1975.
- The BIOS is the first to kick in when you turn on the computer and helps load the devices and boot the OS.
- In the present day, BIOS is being replaced by UEFI, a more efficient tool.
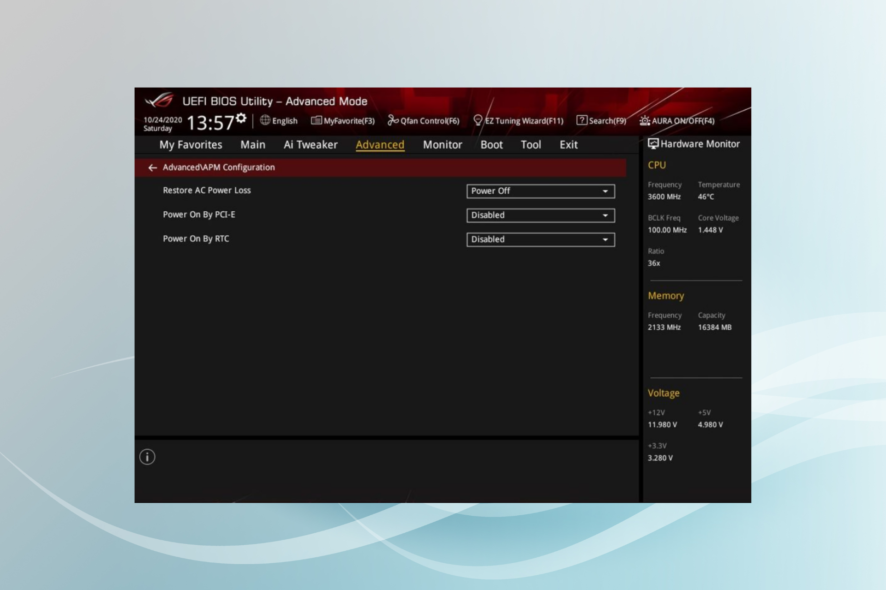
BIOS is one of the critical parts of the computer and is responsible for the most important task, turning on the PC and booting the OS. But most of us often overlook its importance or don’t have the slightest clue about what BIOS is.
You can easily access the BIOS when turning on the computer using the dedicated keyboard shortcut or through the Recovery Mode in Windows. Users who can’t boot Windows choose the former option. Let’s now find out the role played by BIOS.
What does BIOS stand for?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System, and is the first thing that loads when you hit the power button on the computer. Here are the primary functions of BIOS:
- Checks for issues: When you turn on the PC, the BIOS first runs POST (Power On Self Test), checking whether the connected hardware works fine and wouldn’t impede the startup process.
- Loads the hardware: After POST, the next course of action on the part of the BIOS is to load the critical hardware and its drivers.
- Boots the OS: Most importantly, the BIOS is responsible for identifying and booting the installed version of Windows.
Remember, while older computers came with BIOS, the new-generation ones offer UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), basically a newer and advanced version that helps either bypass or eliminate the limitations of the former. And in most cases, having either of the two works just fine.
Why is BIOS needed?
BIOS is much more than it’s perceived to be. While most are unaware of this aspect, BIOS can also be used to enhance security by adding a password. Once the protection is enabled, no BIOS activity will occur unless the password is entered.
Besides, it can also relay commands between the OS and the device where accuracy and timing are vital, especially with the graphics adapter.
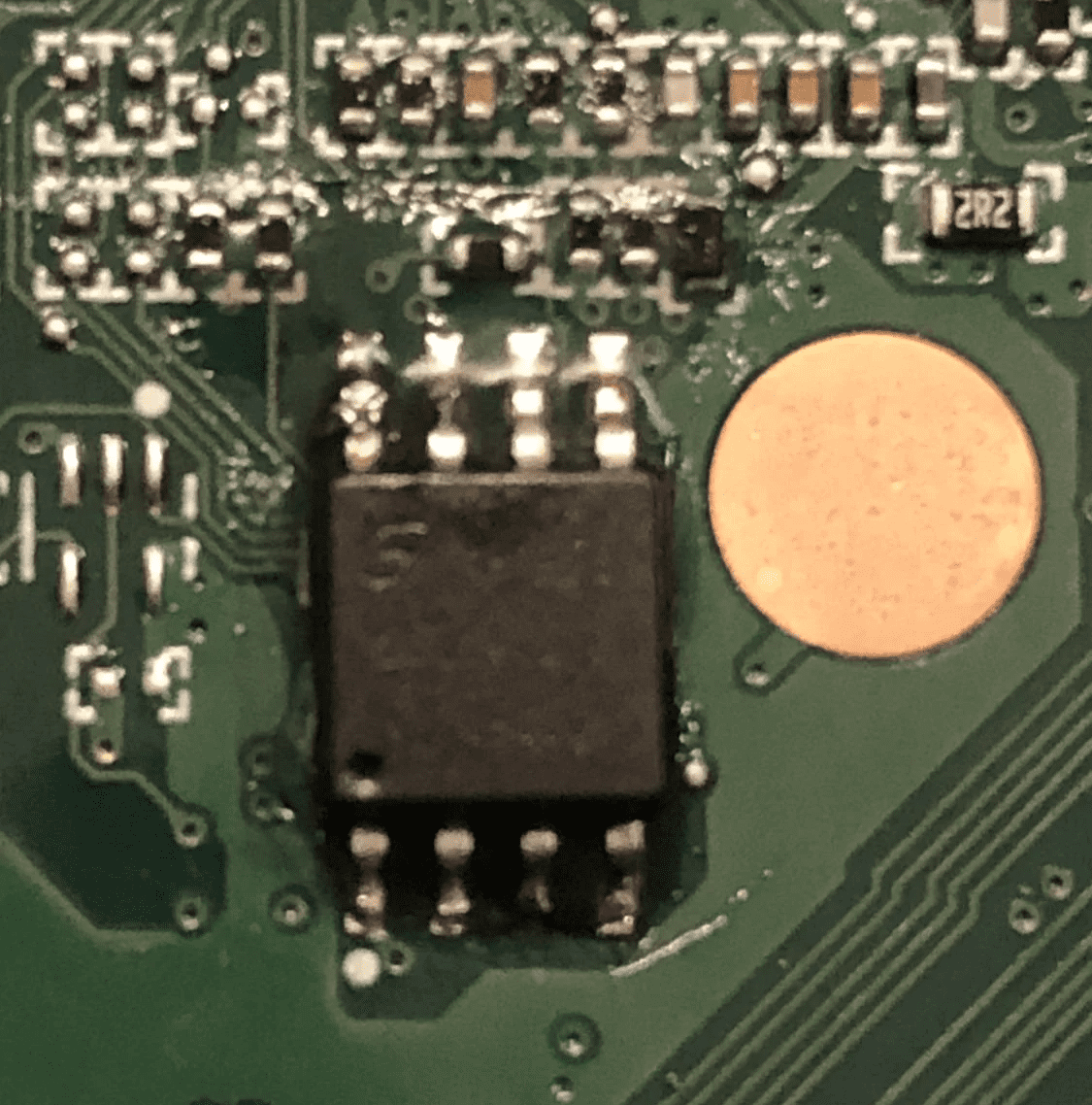
Where is BIOS stored?
BIOS is stored on flash memory or EEPROM (Electronically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory) to allow quick changes to it to upgrade the BIOS and introduce new features or settings.
Remember, this wasn’t the case earlier, and the BIOS was originally stored on a read-only chip in the computer’s motherboard because back then, there were no frequent updates or upgrades.
Is BIOS hardware or software?
BIOS is a software component that kicks in when the computer is powered on. Also, you can get into the BIOS to configure several critical settings on the PC or even change the boot order.
Though a software, the BIOS is responsible for effectively functioning the connected hardware and critical components.
What is a BIOS update?
Like any other software on the PC, the BIOS, too, receives periodic updates. The updates are meant to enhance its functionality, add new features, and introduce patches for any previously known bugs, though that’s extremely rare.
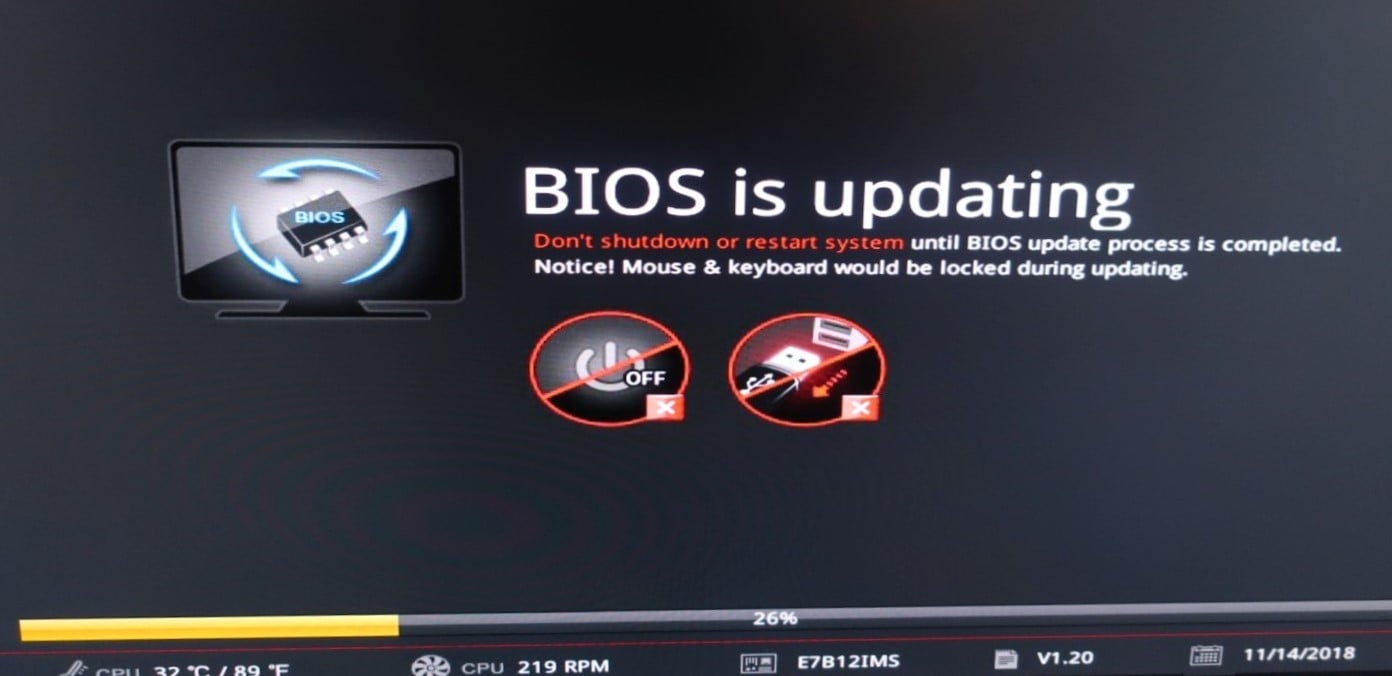
Updating the BIOS can often be tricky because the process is completely manual, and even the slightest of mistakes can render the PC unusable, at least for the time being, until a fresh BIOS is loaded. So, we recommend you check the manufacturer’s website for the exact steps and follow them as it is.
What is BIOS flashback?
BIOS flashback, as the name suggests, is a quick way to update the BIOS without the need to enter it or access the operating system, generally Windows.
The process involves connecting a USB drive holding the updated BIOS to the relevant port on the motherboard and then pressing the dedicated flashback button for 5 seconds. You should then see a light blink as an indication of when the process starts and finally completes.
Even for the BIOS flashback, we recommend checking the manufacturer’s website or contacting a professional because the process is way more intricate than it initially appears.
Can a PC run without BIOS?
A computer can very well run without the BIOS. But here’s the catch, it can’t boot the OS without one.
While the BIOS is stored on the motherboard, the operating stored is stored on the drive. And for the OS to load, the drive has to be active or enabled, which is the core function of the BIOS, as discussed earlier.
But you can always remove the BIOS chip after the computer has been turned on and Windows (or another operating system) has taken over.
Can BIOS be repaired?
Since the BIOS plays such a vital role on the PC, there’s always a chance that it might corrupt or run into other errors, which leads to a situation where users need to repair the BIOS.
There are plenty of ways to go about it, starting from resetting the BIOS, going for a flashback, removing the motherboard battery, or using a dedicated tool.
That’s all there’s to the subject, and by now, you should have a fair understanding of what BIOS is.
Before you leave, find out what to do when the PC won’t boot after a BIOS update, a common problem reported by many. Besides, discover some quick tips to make Windows faster than ever.
For any queries or to share any additional information on the subject, use the comments section below.







User forum
2 messages