Why is Local Security Authority Trying to Access the Internet?
Find the correct answer right away
5 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- The Local Security Authority process is critical in Windows and is primarily responsible for security.
- This process authenticates and validates credentials and sign-ins.
- When it’s trying to access the Internet, verify the file path and repair the corrupt system files.
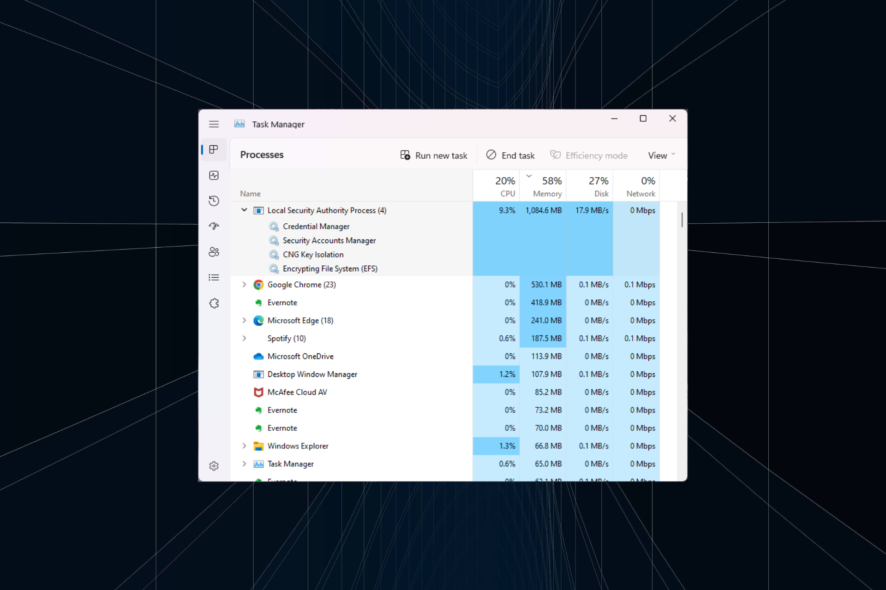
Processes and apps consume background resources to perform a series of vital functions. But some apps tend to consume excess network resources, affecting the workflow. A similar situation arises when the Local Security Authority process is trying to access the Internet.
The problem with most users is that they are unaware of the process’s role and often consider LSA a virus. And you can’t blame them because LSA also consumes high CPU and RAM in many cases. Keep reading to find out all about the process!
What does the Local Security Authority do?
Local Security Authority, as the name suggests, is a local process meant to ensure security on the PC by preventing unauthorized access.
Its role is to authenticate the credentials for any sign-ins, password changes, token creation for applications, and permissions related to administrative access.
Local Security Authority (lsass.exe) is enabled by default on the PC. The file location is:C:\Windows\System32
It’s a critical built-in Windows file, and you should not stop the Local Security Authority process. Doing so will compromise the PC’s security. But you must verify that the lsass.exe process running on the PC is legitimate.
Microsoft has found that Sasser, a malware, used the vulnerabilities in lsass.exe to steal computer data. Since a problem with the process has been reported, we can’t ignore the possibility of it happening again. So, verify the file path and always have a reliable antivirus running!
Why is LSA trying to access the Internet?
As per available reports, the lsass.exe process shouldn’t try to access the Internet. But things change with updates, which could be the case with LSA. So, we have to identify why it consumes network resources and take the necessary approach.
Here are a few reasons the Local Security Authority process is trying to access the Internet:
- Running an update: If you are updating the OS, chances are the process, too, is accessing the Internet.
- PC infected with malware: As stated earlier, since a virus has previously breached the process, it could be the case again.
- A recent update broke things: Windows updates, though meant to boost the PC’s performance and introduce new features, often make changes detrimental to its effective functioning.
- Corrupt system files: In a few cases, users reported that the corrupt system files led to issues with the Windows Local Security Authority process.
What can I do if Local Security Authority is trying to access Internet?
1. Verify the file path
Your primary approach here should be to verify the file path. Make sure the lsass.exe process is stored in the following location:C:\Windows\System32
To do that, locate the process, right-click on it, and choose Open file location. If it’s stored in any other location, delete the file immediately and head to the next solution.
2. Scan for viruses
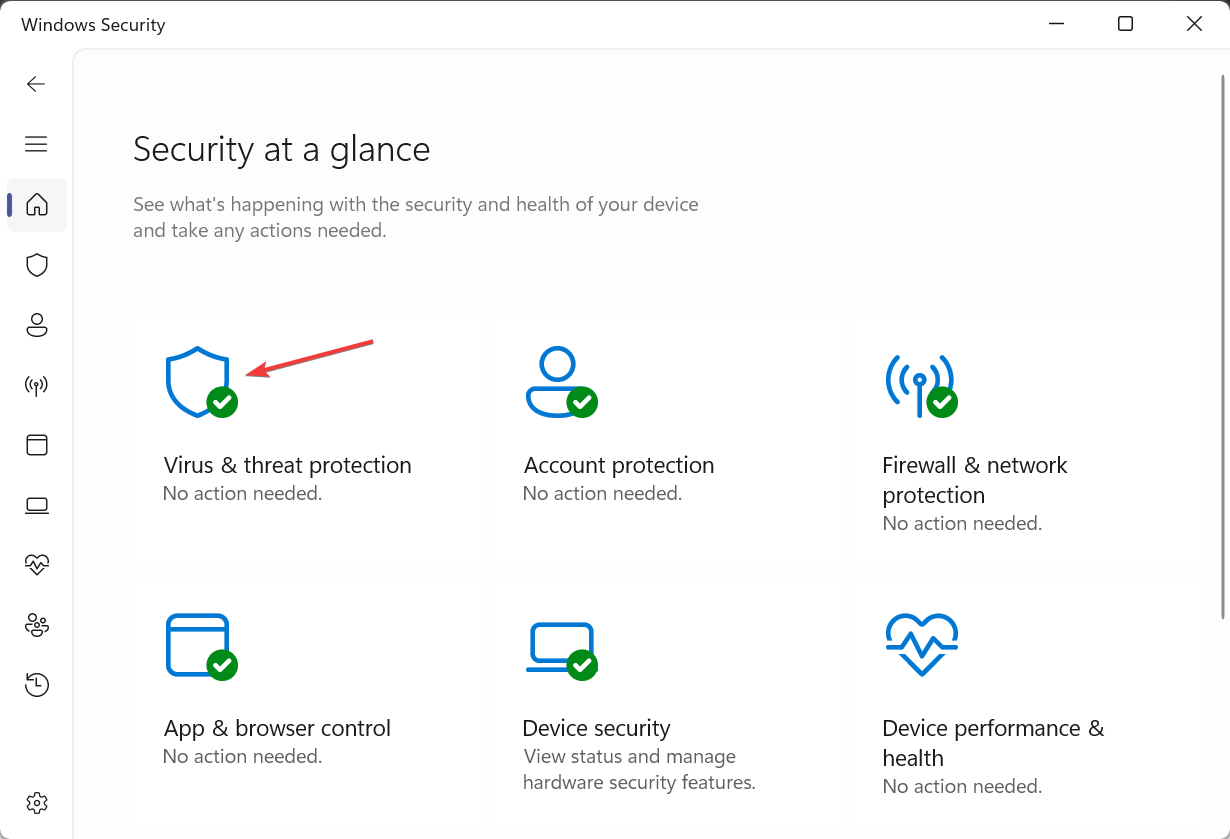
- Press Windows + S to open Search, type Windows Security, and click on the relevant search result.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click on Scan options.
- Now, choose Full scan and click the Scan now button.
- Wait for the scan to complete.
When faced with the Local Security Authority process trying to access the Internet or any other unknown process trying to do that, scan the PC for malware. You could use both the built-in Windows Security or an effective third-party antivirus solution.
3. Run the DISM and SFC scan
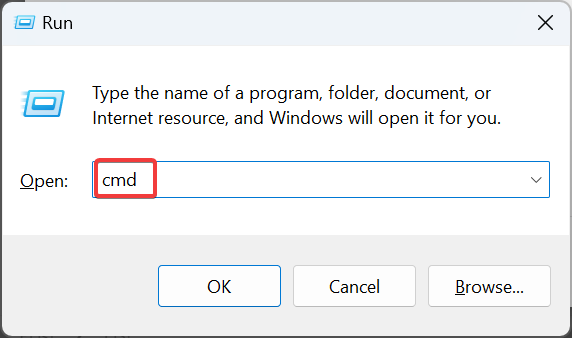
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type cmd, and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
- Paste the following commands one at a time, and hit Enter after each:
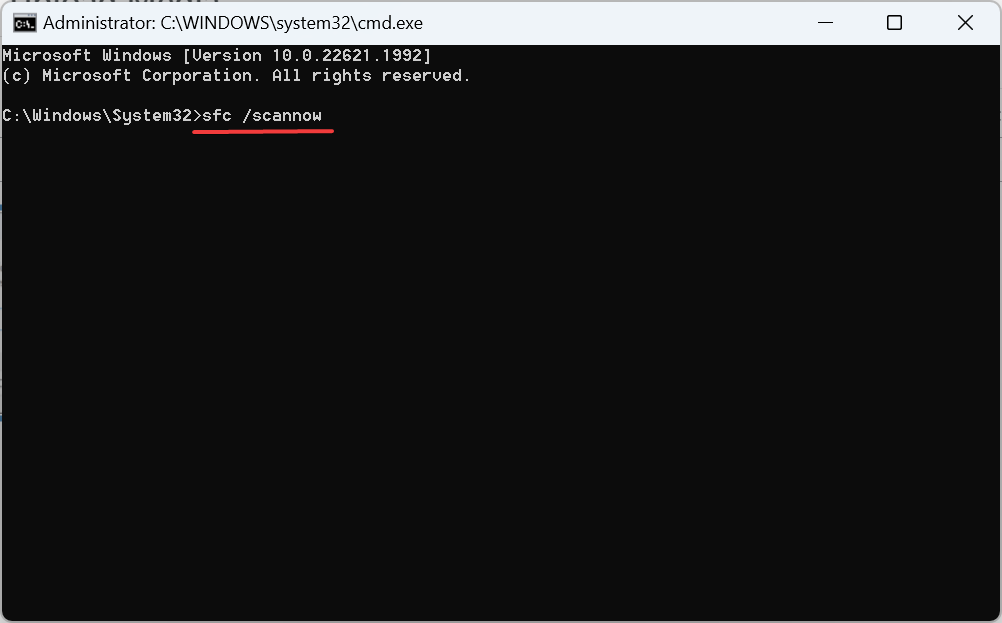
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealthDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Next, execute this command to run the SFC scan:
sfc /scannow - Finally, restart the computer for the changes to come into effect.
If the Local Security Authority process is trying to access the Internet due to corrupt system files, a quick solution is to run the DISM tool and the SFC scan. The two will help identify any problematic system files and replace them with the cached copy.
Or if you want to try a more straightforward solution, you can opt for a specialized third-party repair program.
4. Modify the Registry
- Press Windows + R to open Run, type regedit in the text field, and hit Enter.
- Click Yes in the prompt that appears.
- Paste the following path in the address bar at the top and hit Enter:
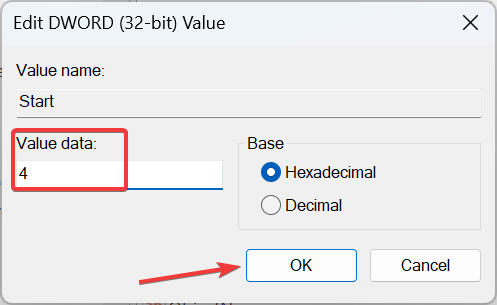
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Schedule - Double-click the Start DWORD on the right.
- Enter 4 under Value data, and click OK to save the changes.
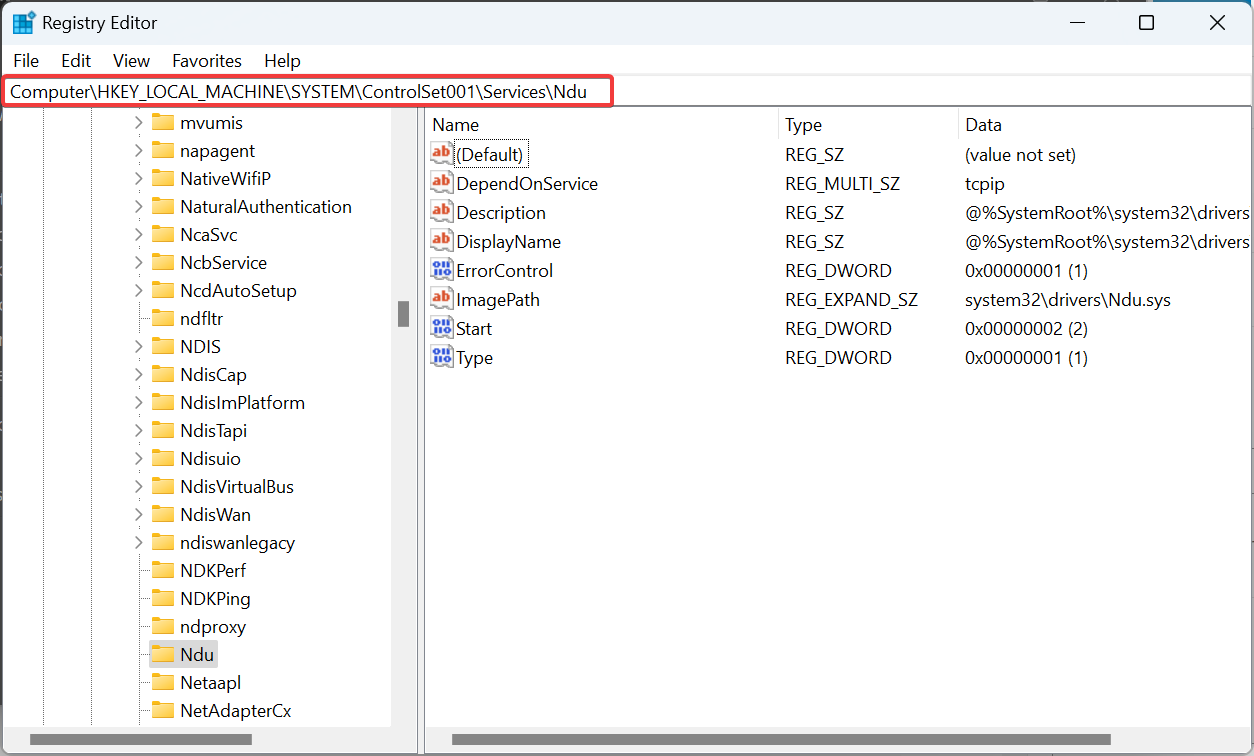
- Now, navigate the following path:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services\Ndu - Again, change the Value data for the Start DWORD to 4, as you did earlier.
- Once done, restart the computer for the changes to come into effect.
This will disable the Windows Schedule and prevent issues like this and those with other services configured to run automatically.
5. Perform an in-place upgrade
- Go to Microsoft’s official website, choose the product language and edition of the OS, and then download the Windows 11 ISO.
- Launch the ISO and then run the setup.exe file.
- Click Yes in the prompt.
- In the Windows 11 Setup, click Next to proceed.
- Click on Accept to agree to Microsoft’s license terms.
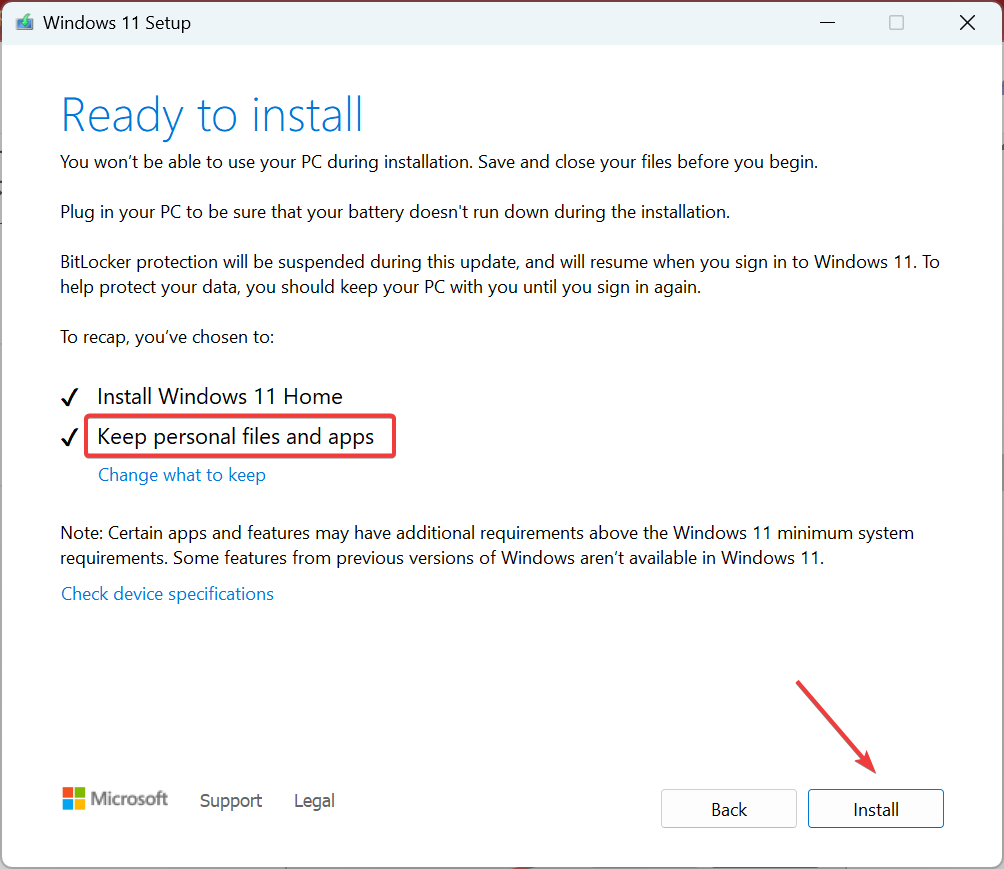
- Finally, verify that the setup reads Keep personal files and apps, and click on Install.
That’s it! If the previous solutions couldn’t fix the problem and the Local Security Authority process is still trying to access the Internet, performing an in-place upgrade will do the trick! It will replace all Windows files without affecting the stored data or apps.
Before you leave, check some quick tips to increase the Internet speed in Windows. We also have a guide on what to do if Local Security Authority Protection is off, so don’t miss it.
For any queries or to share more solutions with us, drop a comment below.







User forum
0 messages