Solved: Laptop Very Slow After Formatting
No more lags and unresponsiveness with these tips!
8 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Key notes
- If you've recently formatted your laptop but it's extremely slow, the problem may be related to incompatible software or hardware, so be sure to update your device drivers.
- Your laptop may also be running low on memory so check for any RAM issues.
- For more solutions, keep reading to find out how to move from slow to fast speeds.

Formatting your laptop is like cleaning out your closet. It’s an organized way to get rid of unnecessary files and free up space on your computer. But what happens when you get unexpected results like a slower device?
This can happen to anyone, even if your laptop is brand new. It’s no cause for alarm as we’ll walk you through how to speed it up after a format so that it works like new again.
Does formatting a laptop affect performance?
When you format a laptop or desktop computer, you are deleting everything on it, including registry files. These files are critical for your operating system to run properly.
Since this information needs to be created again from scratch, it will take longer for your programs to open and for websites to load. That’s why you might notice the boot time is longer because the operating system will be reset to its default settings.
How do I fix my laptop if it’s slow after formatting?
Begin with the following basic steps before attempting the somewhat technical solutions:
- Check for the latest Windows updates and install if available. You can also roll back to previous updates, especially if your PC is slow after a Windows update.
- Turn off unnecessary processes and disable unneeded startup programs.
- Uninstall the default apps you won’t be using.
- Run a hardware diagnostics test to ensure no hardware damage occurred during formatting.
- Perform a memory test to ensure your RAM speeds are optimal.
1. Clear Windows cache
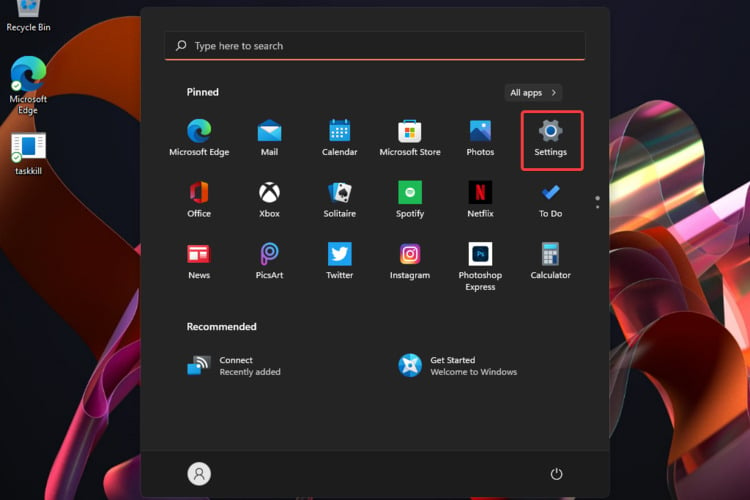
- Hit the Windows key, then click on the Settings menu.
- From the left window pane, select System, then, from the right window side, navigate to Storage.
- Wait for your OS to scan and assess the temporary cache files stored on your system.
- Click on the Temporary files option.
- The various cache files will now be listed.
- Scroll down, then select the files that you want to delete, and click on the Remove files button.
- In the pop-up window, click on Continue to complete the process.
- Now your selected files are deleted.
You might also want to perform a comprehensive PC cleanup if you don’t have a lot of RAM to work with.
2. Run the CHKDSK command
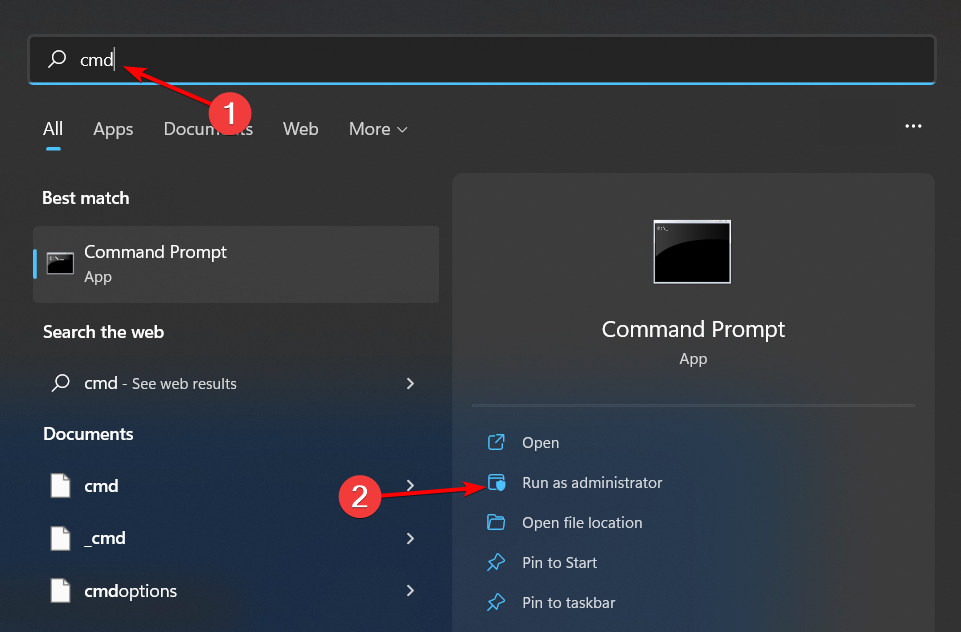
- Hit the Windows key, type cmd in the search bar, and click Run as administrator.
- Type the following command and hit Enter. You can replace the drive letter C with yours:
chkdsk C: /f
3. Restart the SysMain service
- Press Windows + S to launch the Search menu, enter Services in the text field at the top, and click on the relevant search result.
- Locate the SysMain entry here, right-click on it, and select Properties from the context menu. Alternatively, you can double-click on the service.
- Now, click on the Startup type dropdown menu, select Automatic from the list of options and click Start.
- Hit the Apply and OK buttons to save changes.
The SysMain service is a system file that is used by Windows to help run various processes, such as starting programs and loading data into memory. While it is meant to boost the performance of your PC, if your PC is running low on memory, it can lead to a slow laptop and cause other performance issues.
If this is the case, you can disable it and see if there are any notable changes.
4. Perform clean boot
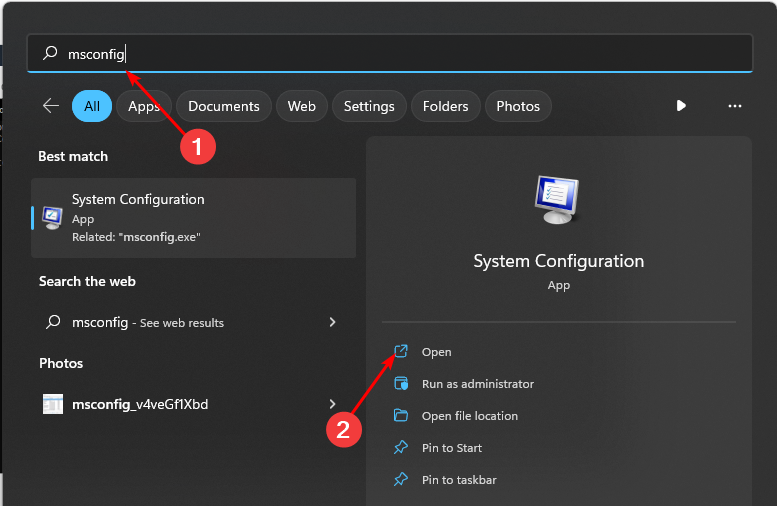
- Hit the Windows key, type msconfig, and open System Configuration.
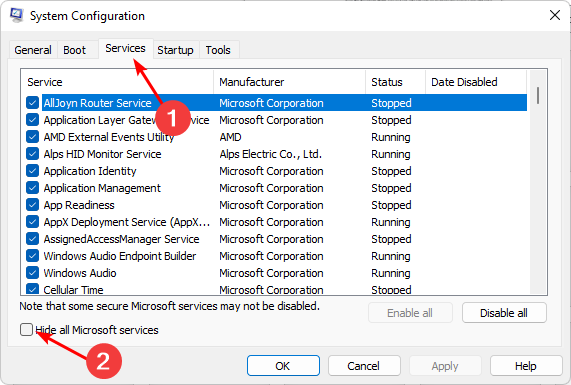
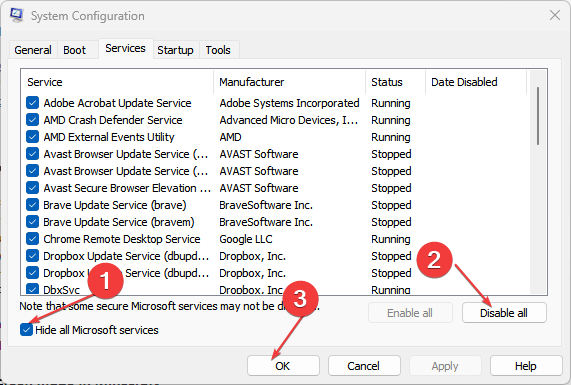
- Switch to the Services tab and select Hide all Microsoft services.
- Click on the Disable all button, then hit the Apply button to save the changes.
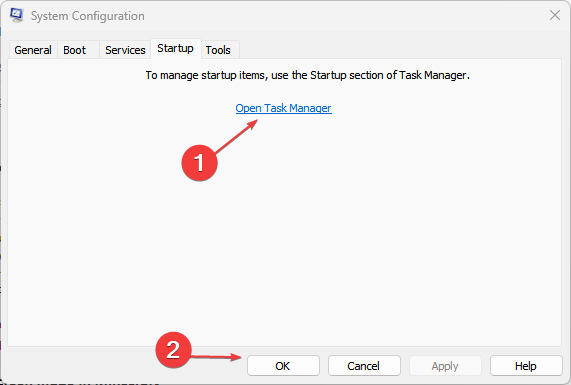
- Go back and click on the Startup tab, select Open Task Manager then click OK.
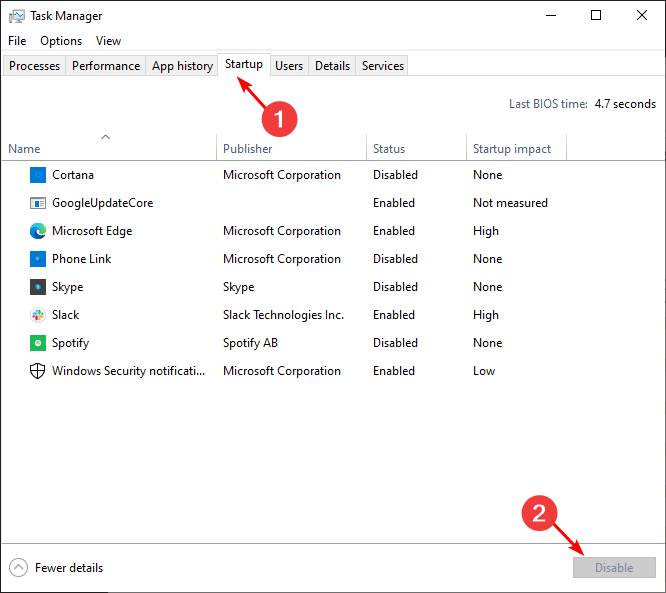
- In the Startup tab of the Task Manager, Disable all the Enabled startup items.
- Close Task Manager and restart your PC.
5. Increase Virtual memory
- Press Windows + S to open Search, type View advanced system settings, and click on the relevant search result.
- In the Advanced tab, click on Settings.
- Now, navigate to the Advanced tab, and then click on Change under Virtual memory.
- Untick the checkbox for Automatically manage paging file size for all drives, select No paging file, and click Set.
- Now, choose Custom size and enter the paging file size based on the available RAM using the following formula:
- For instance, if the physical RAM is 4 GB, the initial and maximum sizes become 6144 MB (1.5 x 4 x 1042) and 12288 MB (3 x 3 x 1024), respectively.
- Once done, click Set and OK to save the changes.
6. Create a new user profile
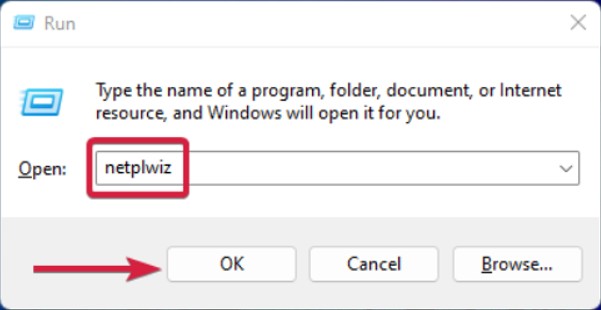
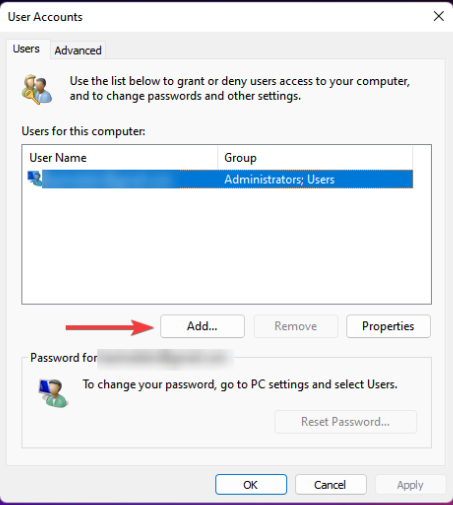
- Press Windows + R to launch the Run console, enter netplwiz in the text field, and click OK.
- Click Add in the User Accounts window.
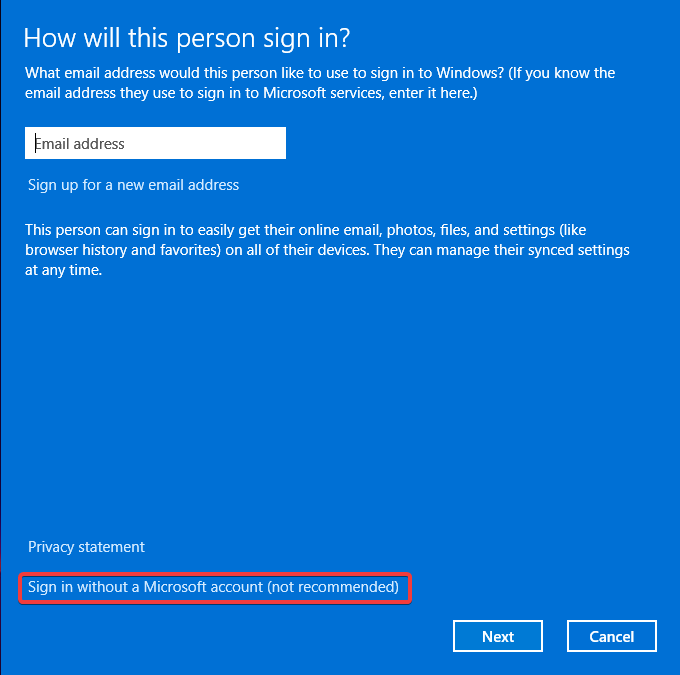
- Select Sign in without a Microsoft account (not recommended).
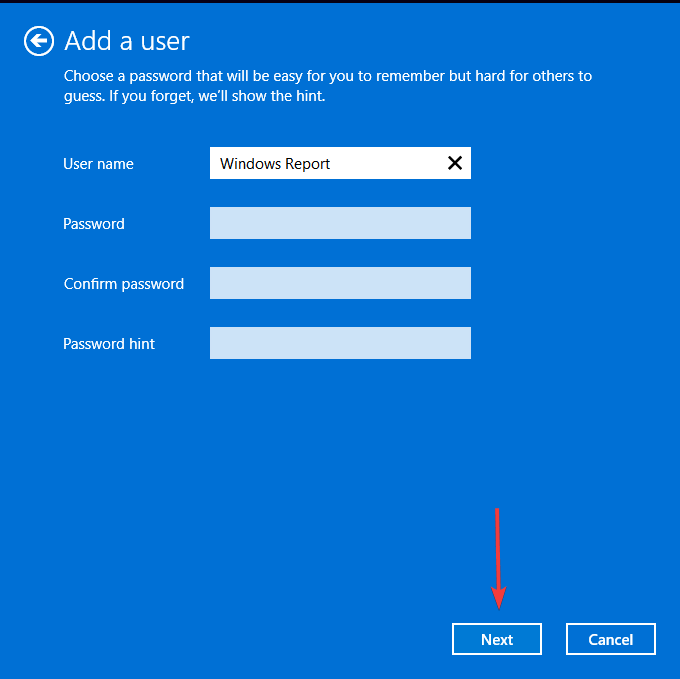
- Click on Local account button.
- Enter a username and password (optional) for the new user account, and a hint, in case you set a password. Once done, click on Next.
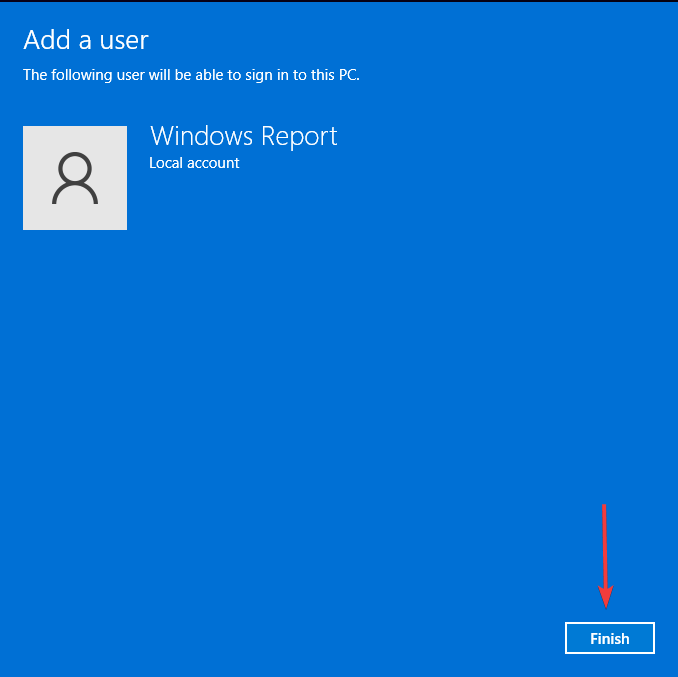
- Click on Finish to create the Local account.
If you notice a performance boost in the new profile, it could mean the previous one was corrupted. In this case, you can repair the corrupted profile or migrate the old one to the new user account.
7. Run an antimalware scan
If your main reason for formatting your laptop was to get rid of malware, there’s a good chance you’ve resolved the issue. However, some viruses are stubborn, and even a format is not enough to remove them.
You can run a virus scan, but to completely remove them, you will need a tool stronger than the built-in Windows Defender. We recommend installing antivirus software with the capability of outing hidden malware.
8. Update your laptop’s BIOS
The BIOS controls the core functions of a computer’s hardware components. It’s important to keep your BIOS up-to-date because it can allow new hardware and software to operate more efficiently on your PC.
If you’re experiencing a problem with your laptop running too slowly after formatting, it may be time for an update.
9. Cleanup your Registry
Cleaning up the registry is one of the most effective ways to speed up your laptop. This can be done using a registry cleaner or by manually removing obsolete files from the Windows Registry. Use a registry cleaner if you don’t know how to do this yourself.
In addition to helping you find and remove obsolete files from the registry, these software programs also offer many other features, including defragmentation, startup management, and privacy protection.
10. Replace your hard drive
Formatting tends to leave unused space on the hard drive. This unused space can lead to fragmentation, which makes the computer run more slowly and experience more crashes and system errors.
However, before you jump to acquire a new one, try defragmenting your hard drive first and see if there’s any improvement. If not, go ahead and upgrade your hard drive. Perhaps it had shown signs of failure all along; you just missed them.
What should I do after formatting my laptop?
- Update your OS – It is always good to update your operating system. This will ensure to fix any compatibility issues with hardware and software.
- Update all drivers – You should also update all drivers for each component of your laptop. This will ensure they match your operating system. Otherwise, they won’t work properly or may cause some problems while booting up or running applications on your PC.
- Install an antivirus program – You will need to secure your laptop from any potential risks, so ensure you install a reliable antivirus solution.
- Restore backups – If you’ve been making backups of your files and settings, restore them now. This will not only get your data back but also any settings and customizations that you had made to the system.
- Set up a System Restore point – If something goes wrong after formatting your laptop, then you can create a System Restore point to revert back to a previous state of the system.
It is evident that formatting of laptop periodically will keep it running smoothly. However, during the inopportune times that it doesn’t, the above fixes should help you bring it up to speed.
It’s also important to get to the root of the problem. Sometimes, your laptop may run slow after a system restore because you created it incorrectly, and other times, it’s just your hardware component setting.
Remember, your PC’s speed is directly proportional to the resources available, such as RAM, CPU cores, and processor type, among others.
Did you manage to boost your laptop’s speed with any of our recommended fixes? We’d love to hear about it, so drop us a comment down below.


















User forum
0 messages